
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name of given below compound has to be given.
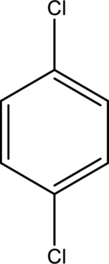
Concept Introduction:
IUAC gives rules for the naming of chemical compounds. These rules are,
For polybstituted benzene compounds, take benzene as a parent compound.
Number the benzene ring by assigning the lowest priorities to the substituents.
Write the position number and substituent name by following alphabet letters then write the parent name of the compound.
If more than one same substitutions are present in a compound means add a prefix like di, tri, tetra, ect…
(b)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name of given below compound has to be given.
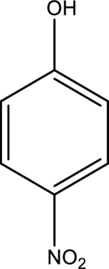
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
IUAC gives rules for the naming of chemical compounds. These rules are,
For polybstituted benzene compounds, take benzene as a parent compound.
Number the benzene ring by assigning the lowest priorities to the substituents.
Write the position number and substituent name by following alphabet letters then write the parent name of the compound.
If more than one same substitutions are present in a compound means add a prefix like di, tri, tetra, ect…
(c)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name of given below compound has to be given.
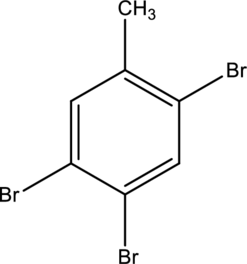
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
IUAC gives rules for the naming of chemical compounds. These rules are,
For polybstituted benzene compounds, take benzene as a parent compound.
Number the benzene ring by assigning the lowest priorities to the substituents.
Write the position number and substituent name by following alphabet letters then write the parent name of the compound.
If more than one same substitutions are present in a compound means add a prefix like di, tri, tetra, ect…
(d)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name of given below compound has to be given.
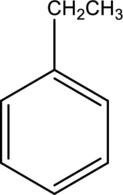
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
IUAC gives rules for the naming of chemical compounds. These rules are,
For polybstituted benzene compounds, take benzene as a parent compound.
Number the benzene ring by assigning the lowest priorities to the substituents.
Write the position number and substituent name by following alphabet letters then write the parent name of the compound.
If more than one same substitutions are present in a compound means add a prefix like di, tri, tetra, ect…
(e)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name of given below compound has to be given.
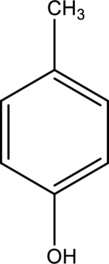
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
IUAC gives rules for the naming of chemical compounds. These rules are,
For polybstituted benzene compounds, take benzene as a parent compound.
Number the benzene ring by assigning the lowest priorities to the substituents.
Write the position number and substituent name by following alphabet letters then write the parent name of the compound.
If more than one same substitutions are present in a compound means add a prefix like di, tri, tetra, ect…
(f)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name of given below compound has to be given.
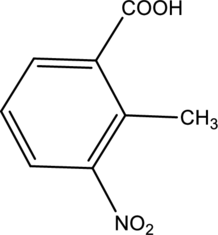
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
IUAC gives rules for the naming of chemical compounds. These rules are,
For polybstituted benzene compounds, take benzene as a parent compound.
Number the benzene ring by assigning the lowest priorities to the substituents.
Write the position number and substituent name by following alphabet letters then write the parent name of the compound.
If more than one same substitutions are present in a compound means add a prefix like di, tri, tetra, ect…
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
FOUNDATIONS OF COLLEGE CHEM +KNEWTONALTA
- b) Circle the substrate that would not efficiently generate a Grignard reagent upon reaction with Mg in ether. CI Br ד c) Circle the Grignard reagents that contain incompatible functional groups. MgBr HO MgBr MgBr MgBr MgBr HO MgBrarrow_forwardQ2: Predict all organic product(s), including stereoisomers when applicable. PCC OH a) CH2Cl2 Page 2 of 5 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 HW Problem Sets b) .OH Na2Cr2O7, H+ OH PCC CH2Cl2 c) OHarrow_forwardd) Circle the substrates that will give an achiral product after a Grignard reaction with CH3MgBr. Harrow_forward
- Explain why the S-F bond strength is 367 kJ/mol in SF2 and 329 kJ/mol in SF6.arrow_forwardWould Si(CH3)3F react with AgCl? If so, write out the balanced chemical equation. If not,explain why no reaction would take place.arrow_forwardNH3 reacts with boron halides (BX3 where X = F, Cl, Br, or I) to form H3N-BX3 complexes.Which of these complexes will have the strongest N-B bond? Justify your answerarrow_forward
 Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





