
Concept explainers
Three point charges are arranged as shown in Figure P19.19. (a) Find the vector electric Field that the 6.00-nC and –3.00-nC charges together create at the origin. (b) Find the vector force on the 5.00-nC charge.
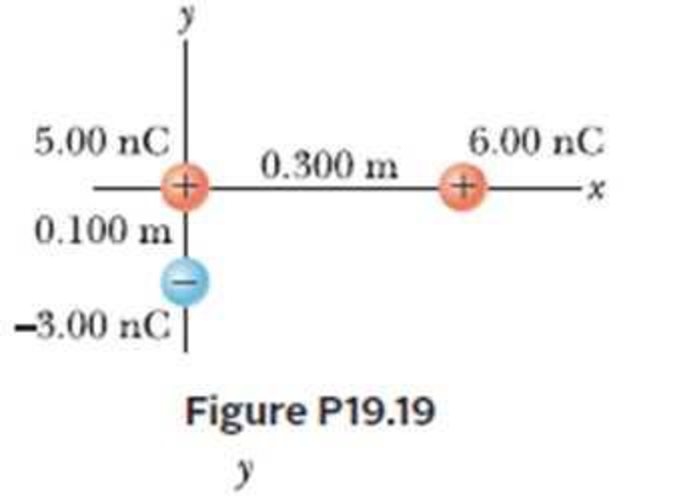
(a)
The electric field at the origin due to charges
Answer to Problem 19P
The electric field at the origin due to charges
Explanation of Solution
Figure 1 represents the electric field at the origin due to charges
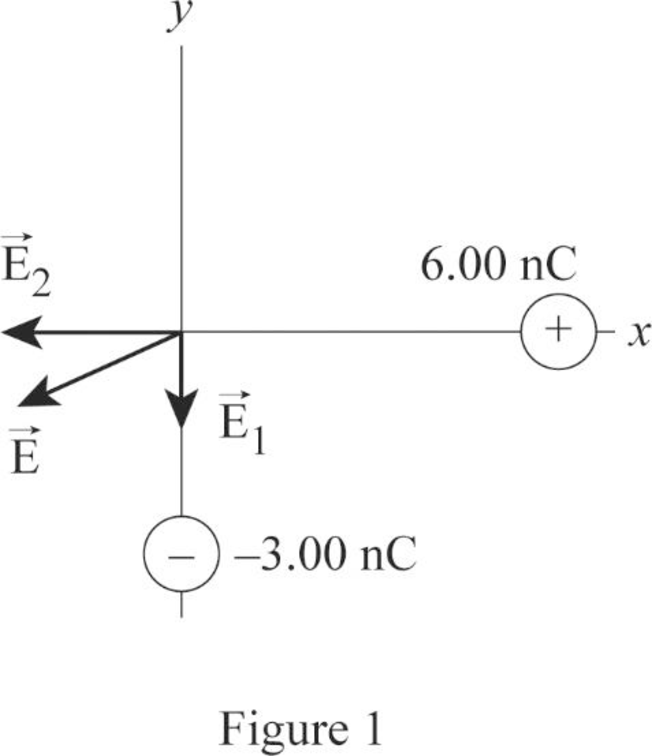
Write the expression for the electric field at the origin due to
Here,
Write the expression for the electric field at the origin due to
Here,
Write the expression for net electric field at the origin.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Use equation (IV) and (V) in equation (III).
Therefore, the electric field at the origin due to charges
(b)
The vector force on the charge
Answer to Problem 19P
The vector force on the charge
Explanation of Solution
From subpart (a) the electric field at the origin due to charges
Write the expression for vector force on the charge.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the vector force on the charge
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Bundle: Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Serway/Jewett's Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th Edition, Multi-Term
- Required information In a standard tensile test, a steel rod of 1 3 -in. diameter is subjected to a tension force of P = 21 kips. It is given that v= 0.30 and E= 29 × 106 psi. 1-in. diameter P P -8 in. Determine the change in diameter of the rod. (Round the final answer to six decimal places.) The change in diameter of the rod is - in.arrow_forward5.84 ... If the coefficient of static friction between a table and a uni- form, massive rope is μs, what fraction of the rope can hang over the edge of the table without the rope sliding? 5.97 Block A, with weight Figure P5.97 3w, slides down an inclined plane S of slope angle 36.9° at a constant speed while plank B, with weight w, rests on top of A. The plank is attached by a cord to the wall (Fig. P5.97). (a) Draw a diagram of all the forces acting on block A. (b) If the coefficient of kinetic friction is the same between A and B and between S and A, determine its value. B 36.9°arrow_forward5.60 An adventurous archaeologist crosses between two rock cliffs by slowly going hand over hand along a rope stretched between the cliffs. He stops to rest at the middle of the rope (Fig. P5.60). The rope will break if the tension in it exceeds 2.50 X 104 N, and our hero's mass is 90.0 kg. (a) If the angle is 10.0°, what is the tension in the rope? (b) What is the smallest value can have if the rope is not to break? Figure P5.60arrow_forward
- please answer the question thanks!arrow_forward5.48 ⚫ A flat (unbanked) curve on a highway has a radius of 170.0 m. A car rounds the curve at a speed of 25.0 m/s. (a) What is the minimum coefficient of static friction that will prevent sliding? (b) Suppose that the highway is icy and the coefficient of static friction between the tires and pavement is only one-third of what you found in part (a). What should be the maximum speed of the car so that it can round the curve safely?arrow_forward5.77 A block with mass m₁ is placed on an inclined plane with slope angle a and is connected to a hanging block with mass m₂ by a cord passing over a small, frictionless pulley (Fig. P5.74). The coef- ficient of static friction is μs, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is Mk. (a) Find the value of m₂ for which the block of mass m₁ moves up the plane at constant speed once it is set in motion. (b) Find the value of m2 for which the block of mass m₁ moves down the plane at constant speed once it is set in motion. (c) For what range of values of m₂ will the blocks remain at rest if they are released from rest?arrow_forward
- 5.78 .. DATA BIO The Flying Leap of a Flea. High-speed motion pictures (3500 frames/second) of a jumping 210 μg flea yielded the data to plot the flea's acceleration as a function of time, as shown in Fig. P5.78. (See "The Flying Leap of the Flea," by M. Rothschild et al., Scientific American, November 1973.) This flea was about 2 mm long and jumped at a nearly vertical takeoff angle. Using the graph, (a) find the initial net external force on the flea. How does it compare to the flea's weight? (b) Find the maximum net external force on this jump- ing flea. When does this maximum force occur? (c) Use the graph to find the flea's maximum speed. Figure P5.78 150 a/g 100 50 1.0 1.5 0.5 Time (ms)arrow_forward5.4 ⚫ BIO Injuries to the Spinal Column. In the treatment of spine injuries, it is often necessary to provide tension along the spi- nal column to stretch the backbone. One device for doing this is the Stryker frame (Fig. E5.4a, next page). A weight W is attached to the patient (sometimes around a neck collar, Fig. E5.4b), and fric- tion between the person's body and the bed prevents sliding. (a) If the coefficient of static friction between a 78.5 kg patient's body and the bed is 0.75, what is the maximum traction force along the spi- nal column that W can provide without causing the patient to slide? (b) Under the conditions of maximum traction, what is the tension in each cable attached to the neck collar? Figure E5.4 (a) (b) W 65° 65°arrow_forwardThe correct answers are a) 367 hours, b) 7.42*10^9 Bq, c) 1.10*10^10 Bq, and d) 7.42*10^9 Bq. Yes I am positve they are correct. Please dont make any math errors to force it to fit. Please dont act like other solutiosn where you vaugley state soemthing and then go thus, *correct answer*. I really want to learn how to properly solve this please.arrow_forward
- I. How many significant figures are in the following: 1. 493 = 3 2. .0005 = | 3. 1,000,101 4. 5.00 5. 2.1 × 106 6. 1,000 7. 52.098 8. 0.00008550 9. 21 10.1nx=8.817arrow_forwardplease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!! (Hint in second photo)arrow_forwardplease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





