
(a)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of the given target molecule from phenylmethanol (benzyl alcohol) is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Acid is converted to ester group by esterification reaction with the help of a strong base like
Answer to Problem 19.75P
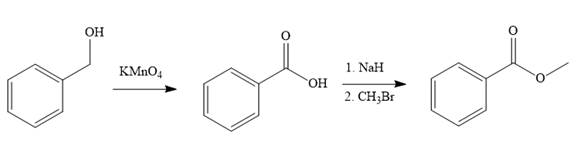
Synthesis of the target molecule from phenylmethanol (benzyl alcohol) is
Explanation of Solution
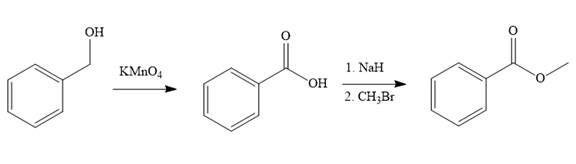
Structure of the target molecule is
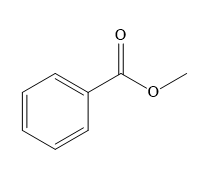
In the first step of the reaction, phenylmethanol (benzyl alcohol) is treated with oxidizing agent
In the second step of the reaction, benzoic acid undergoes esterification reaction. In this step, benzoic acid is first treated with a strong base like
The complete synthesis of the target molecule is as shown below.
By using the
(b)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of the given target molecule from phenylmethanol (benzyl alcohol) is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
For the conversion of alcohol group to Grignard reagent, alcohol (bad leaving group) is treated with
When Grignard reagent is reacted with
For the removal of water, tertiary alcohol is treated with conc.
The bromination reaction on alkene takes place in presence of
Answer to Problem 19.75P
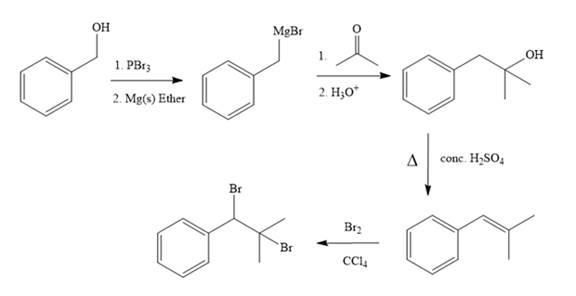
Synthesis of the target molecule from phenylmethanol (benzyl alcohol) is
Explanation of Solution
Structure of the target molecule is
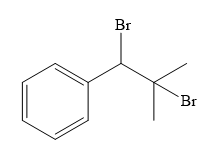
In the first step, the formation of Grignard reagent takes place. In this step, benzyl alcohol is treated with
The complete synthesis of the target molecule is as shown below.
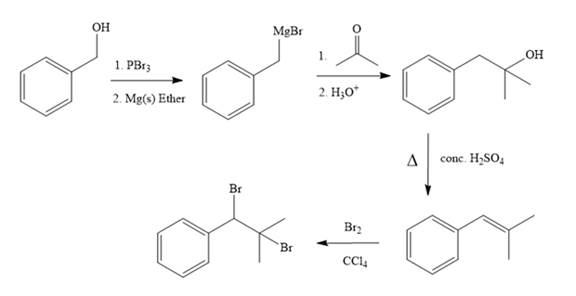
By using the functional group conversion reactions, the synthesis of the target molecule is determined.
(c)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of the given target molecule from phenylmethanol (benzyl alcohol) is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Grignard reagent, in presence of acidic condition, is used for the conversion of aldehyde or ketone to alcohol.
For the removal of water, tertiary alcohol is treated with conc.
Reaction of alkene with diazomethane in presence of heat results in the formation of cyclopropane ring.
Answer to Problem 19.75P
Synthesis of the target molecule from phenylmethanol (benzyl alcohol) is
Explanation of Solution
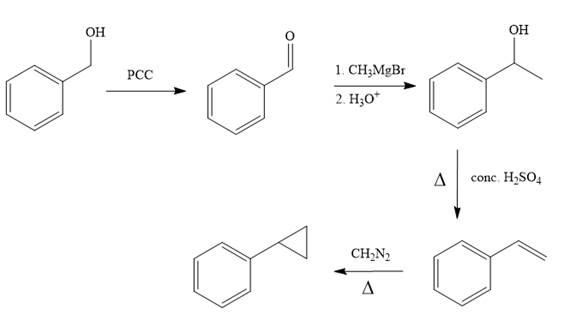
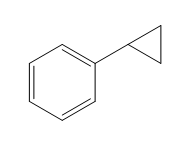
Structure of the target molecule is
In the first step, benzyl alcohol is treated with the oxidizing agent
In the second step, benzaldehyde is treated with Grignard reagent
In the third step, the presence of conc.
In the last step, alkene is treated with diazomethane in presence of heat that results in the formation of the cyclopropane ring.
The complete synthesis of the target molecule is as shown below.
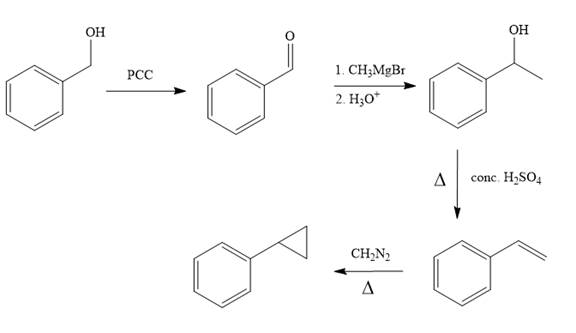
By using the functional group conversion reactions, the synthesis of the target molecule is determined.
(d)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of the given target molecule from phenylmethanol (benzyl alcohol) is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Grignard reagent, in presence of acidic condition, is used for the conversion of aldehyde or ketone to alcohol.
Answer to Problem 19.75P
Synthesis of the target molecule from phenylmethanol (benzyl alcohol) is
Explanation of Solution
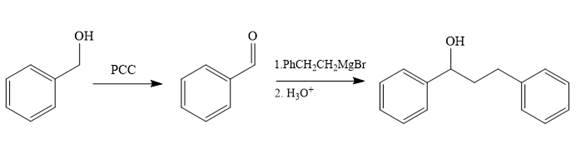
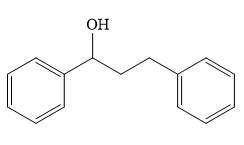
Structure of the target molecule is
In the first step, benzyl alcohol is treated with the oxidizing agent
In the second step, benzaldehyde is treated with Grignard reagent
The complete synthesis of the target molecule is as shown below.

By using the functional group, conversion reactions synthesis of the target molecule is determined.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY PRINCIPLES & MECHANISM
- Basic strength of organic bases.arrow_forwardNucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: What is the product of the reaction? What is the name of the intermediate complex? *See imagearrow_forwardPredict the final product. If 2 products are made, list which should be “major” and “minor” *see attachedarrow_forward
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: What is the product of the reaction? *see imagearrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardThe answer here says that F and K have a singlet and a doublet. The singlet and doublet are referring to the H's 1 carbon away from the carbon attached to the OH. Why don't the H's two carbons away, the ones on the cyclohexane ring, cause more peaks on the signal?arrow_forward
- Draw the Birch Reduction for this aromatic compound and include electron withdrawing groups and electron donating groups. *See attachedarrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardBlocking Group are use to put 2 large sterically repulsive group ortho. Show the correct sequence toconnect the reagent to product with the highest yield possible. * see imagearrow_forward
- Elimination-Addition: What molecule was determined to be an intermediate based on a “trapping experiment”? *please solve and see imagearrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardPredict the final product. If 2 products are made, list which should be “major” and “minor”. **see attachedarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





