
(a)
Interpretation:
The validation corresponding to the fact that aspartame is chiral is to be stated. If aspartame is chiral, then the possible number of stereoisomers for aspartame is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
A compound that contains a chiral carbon is known as chiral compound. Carbon atom that contains all the four different atoms or group of atoms attached to it is referred as the chiral atom. This carbon is also known as stereocenter.
The possible number of stereoisomers is calculated by the expression
Answer to Problem 19.13P
Aspartame is a chiral compound. The possible number of stereoisomers for aspartame is
Explanation of Solution
The aspartame is a chiral compound. The structure of aspartame which contains chiral carbon atoms is shown as,
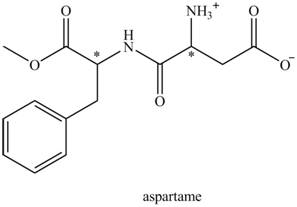
There are two chiral carbon atoms present in aspartame which are marked with asterisk sign. In the structure of aspartame, one carbon atom is directly bonded to
Thus, the possible number of stereoisomers in aspartame is,
Where,
- is the number of stereocenter.
Thus, the possible stereoisomers of aspartame is
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of each functional group present in aspartame is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as
Answer to Problem 19.13P
The name of each functional group present in aspartame is ester group
Explanation of Solution
According to the structure of aspartame shown in Figure 1, there are four functional groups present in the structure of aspartame.
The name of all the functional group of aspartame is ester group
(c)
Interpretation:
The net charge on aspartame molecule in an aqueous solution at
Concept Introduction:
The negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration of the solution is known as
Answer to Problem 19.13P
The net charge on aspartame molecule in an aqueous solution at
Explanation of Solution
In an aqueous solution of
Hence, there is no change of charge takes place in aspartame and it possesses zero net charge.
(d)
Interpretation:
The validation corresponding to the fact that aspartame is whether soluble in water or not is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
According to the concept of solubility, it is mentioned that like dissolves like. Generally, polar compound can only be dissolved in polar solvents and non-polar or weakly polar compounds can only be dissolved in non-polar solvents or weakly polar solvents.
Answer to Problem 19.13P
Aspartame is soluble in water.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure of asparatame is present in zwitterion form which suggests that it is a polar molecule. According to the concept of like dissolves like, aspartame is soluble in water because water is also a polar molecule.
(e)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
Concept Introduction:
An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as functional groups. The functional group is the most reactive part present in the molecule. The main functional groups are
The addition of water molecule to the compound is known as hydrolysis that compound.
Answer to Problem 19.13P
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
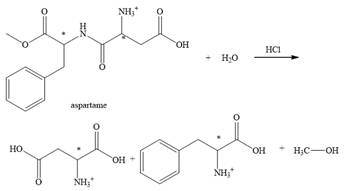
Explanation of Solution
The hydrolysis of aspartame in the presence of aqueous
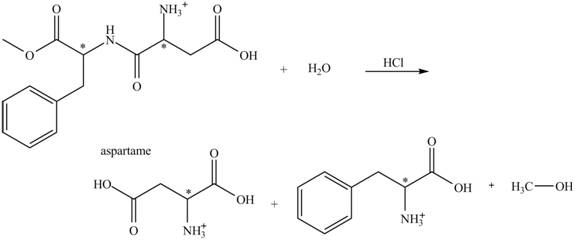
Figure 2.
The reaction of aspartame with aqueous
(f)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
Concept Introduction:
An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as functional groups. The functional group is the most reactive part present in the molecule. The main functional groups are
The addition of water molecule to the compound is known as hydrolysis that compound.
Answer to Problem 19.13P
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
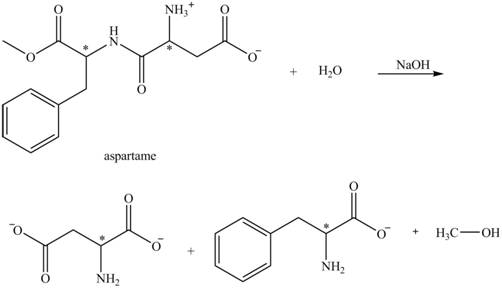
Explanation of Solution
The hydrolysis of aspartame in the presence of aqueous
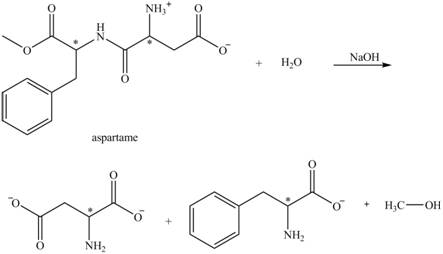
Figure 3.
The reaction of aspartame with aqueous
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual for Bettelheim/Brown/Campbell/Farrell/Torres' Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry, 11th
- Please helparrow_forward(a) 21.8 Name the following compounds. & (b) Br (e) O₂N. (h) H (c) Br (d) NH2 ☑N Br H ہیں Ph (g) OMe бл .0-0.e 21.9 Draw a structural formula for each compound. (a) 2,3-Dinitrotoluene (c) Diphenylmethanol (e) p-Nitroaniline (b) 3-Propylanisole (d) m-Propylphenol (f) Pentabromobenzenearrow_forwardIs this the major product of this reaction?arrow_forward
- Help me solve this problem.arrow_forwardDraw a mechanism for the following synthetic transformation including reagents and any isolable intermediates throughout the process. Please clearly indicate bond cleavage/formation using curly arrows. MeO2Carrow_forwardCHEM 310 Quiz 8 Organic Chemistry II Due: Tuesday, April 25th, at 11:59 pm. This quiz is open textbook / open notes - but you must work alone. You cannot use the internet or the solutions manual for the book. Scan in your work and record an explanation of your mechanism. You may record this any way that you like. One way would be to start an individual Zoom meeting, start recording, "share your screen" and then talk through the problem. This will be converted to an .mp4 file that you can upload into Canvas using the "record/upload media" feature. Pyridine, benzoic acid and benzene are dissolved in ethyl acetate. Design and provide a plan / flow chart for separating and isolating each of these components. Pyridine and benzene are liquids at room temperature. Benzoic acid is a solid. You have ethyl acetate, 2M NaOH, 2M HCI and anhydrous MgSO4 available, as well as all the glassware and equipment that you used in the organic lab this year. Provide accurate acid/base reactions for any…arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co


