
a)
Interpretation:
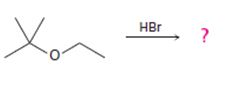
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when tert-butyl ethyl ether is treated with HBr is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2 mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when tert-butyl ethyl ether is treated with HBr is to be given.
Answer to Problem 24MP
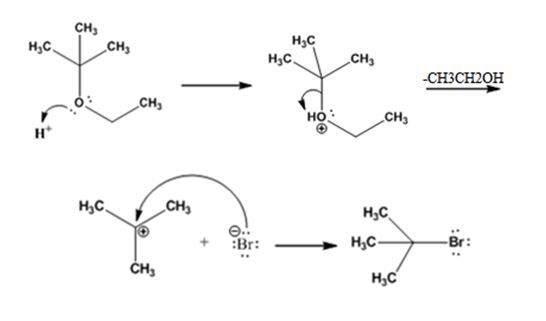
The products formed when tert-butyl ethyl ether is treated with HBr are ethanol and tert-butylbromide.
The mechanism by which they are formed is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction occurs following SN1 mechanism. The acid protonates the ether initially and the protonated ether eliminates ethanol to produce a stable tert-butyl carbocation. In the next step the bromide ion attacks the carbocation to yield tert-butyl bromide as the product.
The products formed when tert-butyl ethyl ether is treated with HBr are ethanol and tert-butylbromide.
The mechanism by which they are formed is given below.
b)
Interpretation:
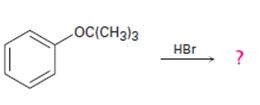
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when tert-butyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2 mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single alkyl halide. Ethers with a tertiary, benzylic or an allylic group cleave either by SN1 or E1 mechanism because these can produce a stable carbocations yielding alkenes and alcohols.
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when tert-butyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr.
Answer to Problem 24MP
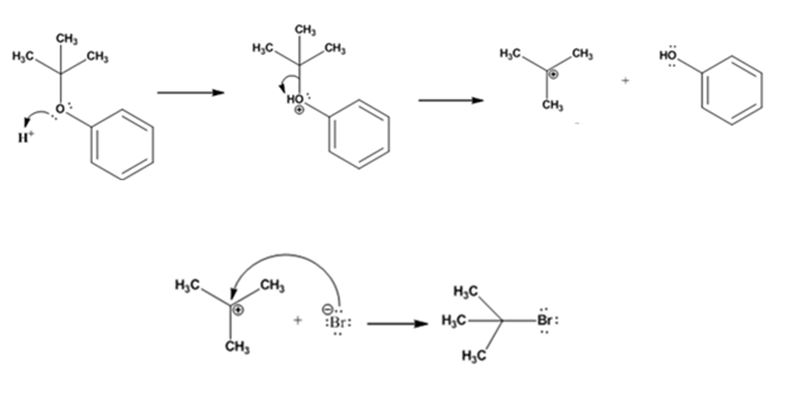
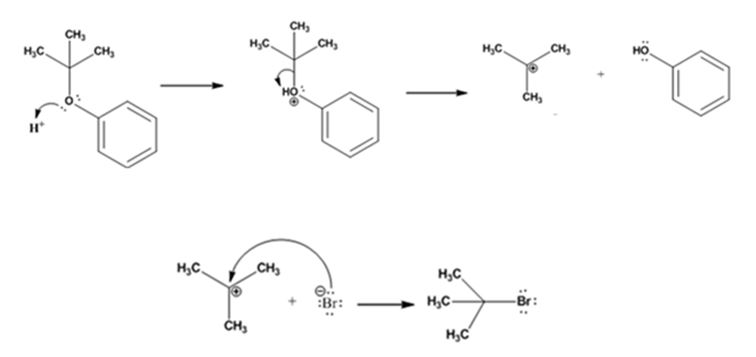
The products formed when tert-butyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr are phenol and tert-butyl bromide.
The mechanism by which they are formed is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction occurs following SN1 mechanism. The acid protonates the ether initially and the protonated ether eliminates phenol to produce a stable tert-butyl carbocation. In the next step the bromide ion attacks the carbocation to yield tert-butyl bromide.
The products formed when tert-butyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr are phenol and tert-butyl bromide.
The mechanism by which they are formed is given below.
c)
Interpretation:
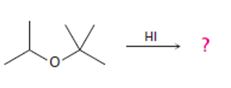
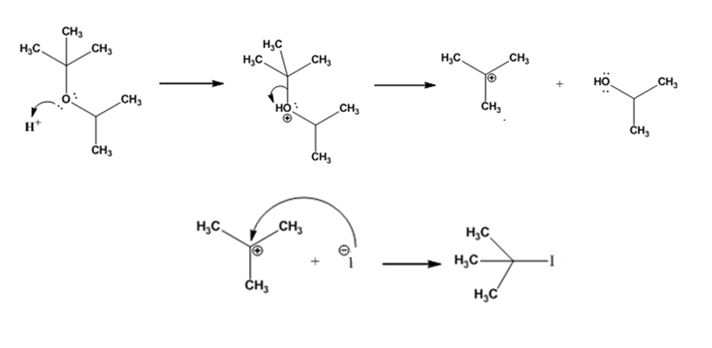
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when tert-butyl isopropyl ether is treated with HI is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2 mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single alkyl halide. Ethers with a tertiary, benzylic or an allylic group cleave either by SN1 or E1 mechanism because these can produce a stable carbocations yielding alkenes and alcohols.
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when tert-butyl isopropyl ether is treated with HI.
Answer to Problem 24MP
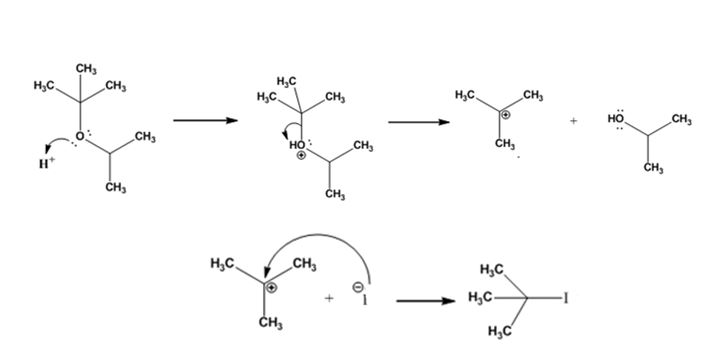
The products formed when tert-butyl isopropyl ether is treated with HI are tert-butyl bromide and 2-propanol.
The mechanism by which they are formed is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction occurs following SN1 mechanism. The acid protonates the ether initially and the protonated ether eliminates 2-propanol to produce a stable tert-butyl carbocation. In the next step the iodide ion attacks the carbocation to yield tert-butyl iodide.
The products formed when tert-butyl isopropyl ether is treated with HI are tert-butyl bromide and 2-propanol.
The mechanism by which they are formed is given below.
d)
Interpretation:
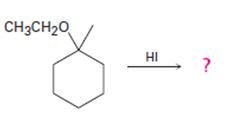
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when ethyl 1-methylcyclohexyl ether is treated with HI is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2 mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single alkyl halide. Ethers with a tertiary, benzylic or an allylic group cleave either by SN1 or E1 mechanism because these can produce a stable carbocations yielding alkenes and alcohols.
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when ethyl 1-methylcyclohexyl ether is treated with HI.
Answer to Problem 24MP
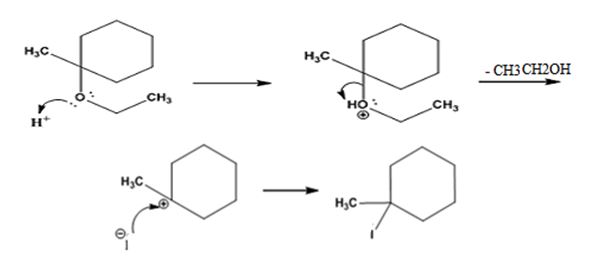
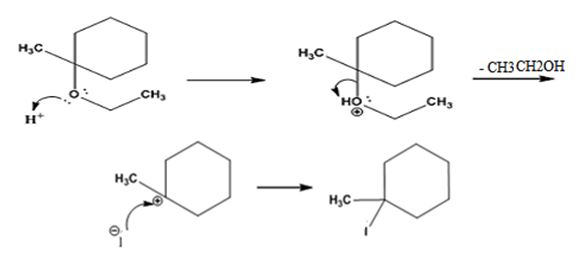
The products formed when ethyl 1-methylcyclohexyl ether is treated with HI are 1-iodo-1-methylcyclohexane and ethanol.
The mechanism by which they are formed is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction occurs following SN1 mechanism. The acid protonates the ether initially and the protonated ether eliminates ethanol to produce a stable tert-butyl carbocation. In the next step the iodide ion attacks the carbocation to yield tert-butyl iodide.
The products formed when ethyl 1-methylcyclohexyl ether is treated with HI are 1-iodo-1-methylcyclohexane and ethanol.
The mechanism by which they are formed is given below.
All the reactions (a), (b), (c) and (d) occur through SN1 mechanism.
All the reactions, (a), (b), (c) and (d) take place following SN1 mechanism. The protonated
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Student Value Bundle: Organic Chemistry, + OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card (NEW!!)
- i need help on how to complete the followingarrow_forwardno AI walkthrough current image is wrong answerarrow_forwarda. Determine whether each of the Followery Molecules is in the R- On the y- Configuration 1-01"/ 1-6-4 Br 4 I el Br b. Draw The Fisher projection For all the Meso compounds that can exist FOR The Following molenlearrow_forward
- 1- Refer to the monosaccharides below to answer each of the following question(s): CH₂OH CHO CH₂OH CH₂OH 0 H- OH 0 0 HO- H H- -OH HO H HO H H OH HO- H CH₂OH H. OH HO H HO- H CH₂OH CH₂OH CH3 a. Sorbose b. Rhamnose c. Erythrulose d. Xylulose Classify each sugar by type; for example, glucose is an aldohexose. a. Xylulose is .. b. Erythrulose is . c. Sorbose is .. d. Rhamnose is .. 2- Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). CHO H OH CH₂OH CH₂OH HO- H HO HO + H. -OH HO OH HO. H OH OH H -OH H OH CH₂OH Q Z a. Refer to Exhibit 25-11. Place a triangle around the anomeric carbon in compound Q. Compound Z is: b. 1. the D-anomer. 2. the a-anomer. 3. the ẞ-anomer. 4. the L-anomer. c. Which anomer is the LEAST stable? d. Q and Z are cyclic examples of: a. acetals b. hemiacetals c. alditols d. hemialditolsarrow_forwardi need help identifying the four carbon oxygen bonds in the following:arrow_forwardImagine each of the molecules shown below was found in an aqueous solution. Can you tell whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral? molecule HO H3N + The solution is... X O acidic OH O basic H3N-CH-C-O O neutral ○ (unknown) O acidic ○ basic CH2 CH 3-S-CH2 O neutral ○ (unknown) H3N O OH O acidic O basic Oneutral O (unknown) 0 H3N-CH-C-O CH3 CH CH3 O acidic O basic O neutral ○ (unknown) ? olo Ar BHarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


