
Concept explainers
Interpretation: Position on benzene ring that most likely to undergo given electrophilic substitution has to be determined and the major product of the reaction has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
- Electrophilic substitution reaction is a type of reaction in which a particular group or atom in a compound is replaced by electrophile. An electrophile is a species that is deficient of electrons
- Benzene is an electron rich
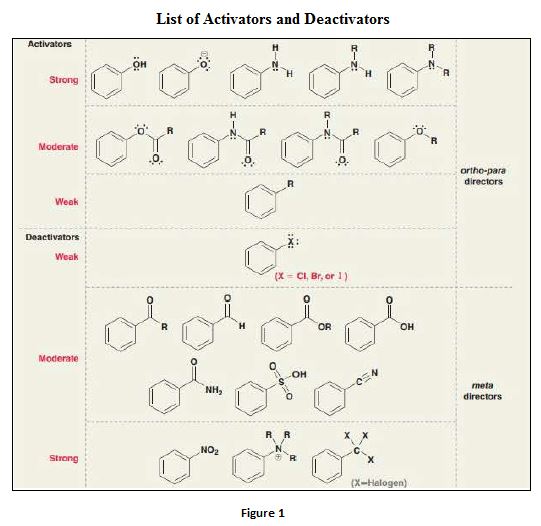
aromatic compound and undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions. - The position that the electrophile occupies in the ring system depends on various factors like – presence of substituents, activation and deactivation of the ring etc.
- The pi electrons of the aromatic system must be available freely for the reaction to occur. Further, the aromatic ring must not have many bulk substituents on it to ease the any type of electrophilic substitution reaction. Presence of many bulk substituents hinders the ability of the delocalizing pi electrons to bond with the electrophile.
Deactivators are electron withdrawing groups attached to the benzenes that have either positive charge or an atom with high electronegativity. They are meta directors.
Activators are electron donating groups attached to the benzenes that have either electron density that is able to push into benzene ring or a lone pair of electrons. They are ortho–para directing.
Reduction: If electrons are gained to a species or hydrogen atoms are added to a species or oxygen atom gets removed from a species during a
Nitration: in nitration reaction, one nitro group
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: W/ACCESS
- Show the mechanism steps to obtain the lowerenergy intermediate: *see imagearrow_forwardSoap is made by the previous reaction *see image. The main difference between one soap and another soap isthe length (number of carbons) of the carboxylic acid. However, if a soap irritates your skin, they mostlikely used too much lye.Detergents have the same chemical structure as soaps except for the functional group. Detergentshave sulfate (R-SO4H) and phosphate (R-PO4H2) functional groups. Draw the above carboxylic acidcarbon chain but as the two variants of detergents. *see imagearrow_forwardWhat are the reactions or reagents used? *see imagearrow_forward
- The two pKa values of oxalic acid are 1.25 and 3.81. Why are they not the same value? Show the protontransfer as part of your explanation. *see imagearrow_forwardасть Identify all the bonds that gauche interact with C-OMe in the most stable conformation of the above compound.arrow_forwardPredict the reactants used in the formation of the following compounds using Acid-Catalyzed dehydration reactionarrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this?arrow_forward.. Give the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show ll relevant stereochemistry [3 ONLY]. A H Br 1. NaCN 2 NaOH, H₂O, heat 3. H3O+ B. CH₂COOH 19000 1. LiAlH4 THF, heat 2 H₂O* C. CH Br 1. NaCN, acetone 2 H3O+, heat D. Br 1. Mg. ether 3. H₂O+ 2 CO₂ E. CN 1. (CH) CHMgBr, ether 2 H₂O+arrow_forwardAssign this COSY spectrumarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





