
Energy from me Ocean
Whenever two objects are at different temperatures, thermal energy can be extracted with a
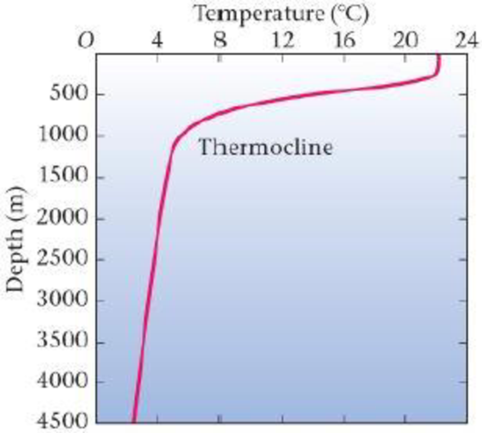
Figure 18-37 Temperature versus depth for ocean waters in the tropics (Problems 93, 94. 95. and 96)
The idea of tapping this potential source of energy has been around for a long time. In 1870, for example, Captain Nemo in Jules Verne’s Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea, said, “I owe all to the ocean; it produces electricity, and electricity gives heat, light, motion, and, in a word, life to the Nautilus.” Just 11 years later, the French physicist Jacques Arsene d’Arsonval proposed a practical system referred to as Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC), and in 1930 Georges Claude, one of d’Arsonval’s students, built and operated the first experimental OTEC system off the coast of Cuba.
OTEC systems which are potentially low-cost and carbon neutral, can provide not only electricity, but also desalinated water as part of the process. In fact, an OTEC plant generating 2 MW of electricity is expected to produce over 14,000 cubic feet of desalinated water a day. The governments of Hawaii, Japan, and Australia are actively pursuing plans for OTEC systems.
96. •• A commercial OTEC system may take in 1500 kg of water per second at 22 °C and cool it to 4.0 °C. How much energy is released in one second by this system? (For comparison, the energy released in burning a gallon of gasoline is 1.3 × 108 J .)
- A. 2.5 × 107 J
- B. 1.1 × 108 J
- C. 1.4 × 108 J
- D. l.6 × 108 J
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
Physics, Books a la Carte Plus Mastering Physics with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (5th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
- The kitchen had a temperature 46 degrees Fahrenheit and was converted it to Kelvin. What is the correct number for this temperature (46 F) on the Kelvin scale?arrow_forwardWater is traveling at a speed of 0.65 m/s through a pipe with a cross-section radius of 0.23 meters. The water enters a section of pipe that has a smaller radius, only 0.11 meters. What is the speed of the water traveling in this narrower section of pipe?arrow_forwardA particular water pipe has a radius of 0.28 meters. If the pipe is completely filled with water, moving with average velocity 0.45 m/s, what is the flow rate of water through the pipe with units of cubic meters of water per second?arrow_forward
- Water is flowing through a horizontal pipe with two segments. In one segment, the water flows at a speed v1 = 4.52 m/s. In the second segment the speed of the water is v2 = 2.38 m/s. Based on Bernoulli's Principle, what is the difference in pressure (P2 - P1) between the two segments? Assume that the density of the water is 997 kg/m3 and give your answer as the number of Pascals (i.e. N/m2).arrow_forwardWater from the faucet is supplied to the hose at a rate of 0.00057 m3/s. At what speed (number of meters per second) does the water exit the nozzle if the cross sectional area of the narrow nozzle is 2.1 x 10-6 m2?arrow_forwardJason Fruits/Indiana University Research Communications Silver/ silver oxide Zinc zinc/oxidearrow_forward
- Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals. At instant 3, cars P and Q are adjacent to one another (i.e., they have the same position). In the reference frame o f the road, at instant 3 i s the speed o f car Q greater than, less than, or equal to the speed of car P? Explain.arrow_forwardCar P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals.arrow_forwardCar P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals. Sketch and label a vector diagram illustrating the Galilean transformation of velocities that relates velocity of car P relative to the road, velocity of car Q relative to road, and velocity of car Q relative to car P at instant 3. In the frame of car P, at instant 3 is car Q moving to the west, moving to the east, or at rest? Explain.arrow_forward
- Just 5 and 6 don't mind 7arrow_forwardIn an electron gun, electrons are accelerated through a region with an electric field of magnitude 1.5 × 104 N/C for a distance of 2.5 cm. If the electrons start from rest, how fast are they moving after traversing the gun?arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





