![MindTap Engineering for Garber/Hoel's Traffic and Highway Engineering, 5th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months)](https://www.bartleby.com/isbn_cover_images/9781305577398/9781305577398_largeCoverImage.gif)
MindTap Engineering for Garber/Hoel's Traffic and Highway Engineering, 5th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781305577398
Author: Nicholas J. Garber; Lester A. Hoel
Publisher: Cengage Learning US
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 18, Problem 8P
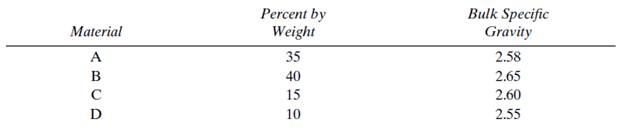
Given four different types of aggregates to be used to produce a blended aggregate for use in the manufacture of asphaltic concrete, determine the bulk specific gravity of the aggregate mix.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Vehicles begin to arrive at an amusement park
entrance at 8:00 A.M. at a rate of 1000veh/h. Some of
these vehicles have electronic identifiers that allow
them to enter the park immediately, beginning at 8:00
A.M., without stopping (they are billed remotely). All
vehicles without such identifiers stop at a single
processing booth, but they wait in line until it opens at
8:10 A.M. Once open, the operator processes vehicles
at μ(t) = 8 + 0.5t [where μ(t) is in vehicles per minute
and t is in minutes after 8:10 A.M.]. An observer notes
that at 8:25 there are exactly 20 vehicles in the queue.
What percent of arriving vehicles have electronic
identifiers and what is the total delay (from the 8:00
A.M. until the queue clears) for those vehicles without
the electronic identifiers (assume D/D/1 queuing)?
1. For truss given in a figure below, determine reactions, and forces in all truss members. De-
termine forces using two methods independently: (a) method of joints, and (b) method of
sections. Compare your results and verify that your solutions are accurate. Assume that force
F
=
10kN.
2m 2m
2m
▼F ▼F
4m
▼F
4m
1) Determine if the existing sedimentation basins are sufficient to accommodate the
projected future capacity. If not, design upgrades to the sedimentation basins.
A) Current Capacity: 22.5 MGD
B) Future Capacity: 34.5 MGD for 110,000 residents
C) If not, design upgrades to the sedimentation basins.
2) Specify the design flow rate, the type of basin (circular vs. rectangular)
3) Specify the basin dimensions (length, width, water depth or diameter and water
depth).
4) Specify the dimensions of the launders (if applicable) and the length of the weir.
Chapter 18 Solutions
MindTap Engineering for Garber/Hoel's Traffic and Highway Engineering, 5th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months)
Ch. 18 - Prob. 1PCh. 18 - Prob. 2PCh. 18 - Prob. 3PCh. 18 - Prob. 4PCh. 18 - Given the specifications for an asphaltic concrete...Ch. 18 - Given the particle size distributions of two...Ch. 18 - Given the particle size distributions of two...Ch. 18 - Given four different types of aggregates to be...Ch. 18 - Prob. 9PCh. 18 - Prob. 10P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The capacity of a freeway lane with free-flow speed of 70mph and jam density average vehicle spacing 40ft assuming greenshields’s model applies. Please explain step by step and show formulaarrow_forward3. For problems given below, determine all the reaction forces and plot force diagrams for normal forces (N), shear force (T), and moments (M). 150 lb/ft 10 ft C B 2 ft 2 ft -4 ft D 250 lb/ft 50 lb/ft B 150 lb-ft 150 lb-ft -20 ft 10 ft -20 ft 200 lb-ftarrow_forwardPlease explain step by step and show all the formula usedarrow_forward
- By using the yield line theory, determine the moment (m) for an isotropic reinforced concrete two- way slab shown in figure under a uniformly distributed load. Using moment method 5 2 7.0m 1 A I c.g. * B c.g 5 2 B c. g. ㄨˋ A A 2.5 2.0 2.5 5.0marrow_forwardPlease explain step by step and include any formula usedarrow_forwardPlease explain step by step and include any formular usedarrow_forward
- 2 1d/T₁₂ = 1/2 n First impulse E ("œw / ])÷(1) '7 J-1 -1- -2+ 0 0.5 1 1.5 2arrow_forwardBars AD and CE (E=105 GPa, a = 20.9×10-6 °C) support a rigid bar ABC carrying a linearly increasing distributed load as shown. The temperature of Bar CE was then raised by 40°C while the temperature of Bar AD remained unchanged. If Bar AD has a cross-sectional area of 200 mm² while CE has 150 mm², determine the following: the normal force in bar AD, the normal force in bar CE, and the vertical displacement at Point A. D 0.4 m -0.8 m A -0.4 m- B -0.8 m- E 0.8 m C 18 kN/marrow_forwardDraw the updated network. Calculate the new project completion date. Check if there are changes to the completion date and/or to the critical path. Mention the causes for such changes, if any. New network based on the new information received after 15 days (Correct calculations, professionally done). Mention if critical path changes or extended. Write causes for change in critical path or extension in the critical path.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage,
Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage,

Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305086272
Author:William P. Spence, Eva Kultermann
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Solid Waste Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635203
Author:Worrell, William A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Materials Science And Engineering Properties
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781111988609
Author:Charles Gilmore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals Of Construction Estimating
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337399395
Author:Pratt, David J.
Publisher:Cengage,
Aggregates: Properties; Author: nptelhrd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=49yGZYeokKM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY