
Concept explainers
For 2019 through 2022, Gire reported pretax financial income and taxable income of the following amounts (the differences are due solely to the depreciation temporary differences):
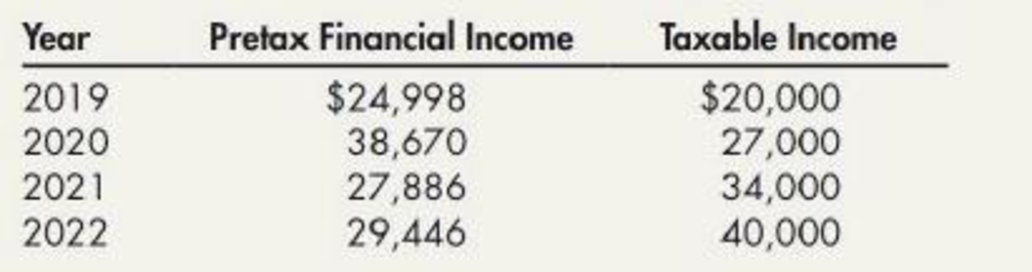
Over the entire 4-year period, Gire was subject to an income tax of 30%, and no change in the tax rate had been enacted for future years.
Required:
- 1. Prepare a schedule that shows for each year, 2019 through 2022, the (a) MACRS depreciation, (b) straight-line depreciation, (c) annual depreciation temporary difference, and (d) accumulated temporary difference at the end of each year.
- 2. Prepare Gire’s income tax
journal entry at the end of (a) 2019, (b) 2020, (c) 2021, and (d) 2022. (Round to the nearest dollar.) - 3. Prepare the lower portion of Gire’s income statement for (a) 2019, (b) 2020, (c) 2021, and (d) 2022.
1 (a)
Prepare a schedule that shows MACRS depreciation from 2019 through 2022.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a schedule that shows MACRS depreciation from 2019 through 2022:
| Year | MACRS Depreciation rate | MACRS Depreciation (Tax purpose) |
| (1) | ||
| 2019 | 33.33% | $19,998 |
| 2020 | 44.45% | $26,670 |
| 2021 | 14.81% | $8,886 |
| 2022 | 7.41% | $4,446 |
Table (1)
1 (b)
Prepare a schedule that shows straight line depreciation from 2019 through 2022.
Explanation of Solution
Straight-line Depreciation: Under the straight-line method of depreciation, the same amount of depreciation is allocated every year over the estimated useful life of an asset. The formula to calculate the depreciation cost of the asset using the residual value is shown as below:
Prepare a schedule that shows straight line depreciation from 2019 through 2022.
Given, the cost of the asset is $60,000 and the estimated useful life is 4 years. So, the straight line depreciation is $15,000
| Year | Straight line Depreciation (Financial reporting purpose) |
| 2019 | $15,000 |
| 2020 | $15,000 |
| 2021 | $15,000 |
| 2022 | $15,000 |
Table (2)
1 (c)
Prepare a schedule that shows the annual depreciation temporary difference from 2019 through 2022.
Explanation of Solution
Temporary Difference: Temporary difference refers to the difference of one income recognized by the tax rules and accounting rules of a company in different periods. Consequently the difference between the amount of assets and liabilities reported in the financial reports and the amount of assets and liabilities as per the company’s tax records is known as temporary difference.
Prepare a schedule that shows the annual depreciation temporary difference from 2019 through 2022:
| Year | MACRS Depreciation (Tax purpose) | Straight line Depreciation (Financial reporting purpose) | Temporary difference between annual depreciation |
| 2019 | $19,998 | $15,000 | $4,998 |
| 2020 | $26,670 | $15,000 | $11,670 |
| 2021 | $8,886 | $15,000 | ($6,114) |
| 2022 | $4,446 | $15,000 | ($10,554) |
Table (3)
Note: The temporary difference of annual depreciation is calculated by subtracting MACRS depreciation (Requirement 1 (a)) and straight line depreciation (Requirement 1 (b)).
1 (d)
Prepare a schedule that shows the accumulated temporary difference from 2019 through 2022.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a schedule that shows the accumulated temporary difference from 2019 through 2022:
| Year | Temporary difference between annual depreciation | Accumulated Temporary difference |
| 2019 | $4,998 | $4,998 |
| 2020 | $11,670 | $16,668 |
| 2021 | ($6,114) | $10,554 |
| 2022 | ($10,554) | $0 |
Table (4)
Note: The accumulated temporary difference is determined by adding the temporary difference of annual depreciation of each of the year from 2019 through 2022.
2 (a)
Record the income tax journal entry at the end of 2019 for Company C.
Explanation of Solution
Record the income tax journal entry at the end of 2019 for Company C.
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post ref. | Amount | |
| Debit | Credit | |||
| 2019 | ||||
| December 31 | Income tax expense (1) | $7,499 | ||
| Income tax payable (2) | $6,000 | |||
| Deferred tax liability (3) | $1,449 | |||
| (To record the income tax payable ) | ||||
Table (5)
- Income tax expense is an expense that decreases the stockholder’s equity and it is increased. Thus, it is debited.
- Income tax Payable is a liability and it is increased. Thus, it is credited.
- Deferred tax liability is a liability and it is increased. Thus, it is credited.
Working note 1: Determine the income tax expense:
Working note 2: Determine the income tax payable:
Given, the taxable income is $20,000 and the tax rate is 30%.
Working note 3: Determine the deferred tax liability:
Given, the accumulated temporary difference is $4,998 for year 2019 as computed in Table (4) and the tax rate is 30%.
2 (b)
Record the income tax journal entry at the end of 2020 for Company C.
Explanation of Solution
Record the income tax journal entry at the end of 2020 for Company C.
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post ref. | Amount | |
| Debit | Credit | |||
| 2020 | ||||
| December 31 | Income tax expense (4) | $11,601 | ||
| Income tax payable (5) | $8,100 | |||
| Deferred tax liability (6) | $3,501 | |||
| (To record the income tax payable ) | ||||
Table (6)
- Income tax expense is an expense that decreases the stockholder’s equity and it is increased. Thus, it is debited.
- Income tax Payable is a liability and it is increased. Thus, it is credited.
- Deferred tax liability is a liability and it is increased. Thus, it is credited.
Working note 4: Determine the income tax expense:
Working note 5: Determine the income tax payable:
Given, the taxable income is $27,000 and the tax rate is 30%.
Working note 6: Determine the deferred tax liability:
Given, the accumulated temporary difference is $16,668 for year 2020 as computed in Table (4) and the tax rate is 30%.
2 (c)
Record the income tax journal entry at the end of 2021 for Company C.
Explanation of Solution
Record the income tax journal entry at the end of 2021 for Company C.
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post ref. | Amount | |
| Debit | Credit | |||
| 2021 | ||||
| December 31 | Income tax expense (balancing figure) | $8,366 | ||
| Deferred tax liability (7) | $1,834 | |||
| Income tax payable (8) | $10,200 | |||
| (To record the income tax payable ) | ||||
Table (7)
- Income tax expense is an expense that decreases the stockholder’s equity and it is increased. Thus, it is debited.
- Deferred tax liability is a liability and it is decreased. Thus, it is debited.
- Income tax Payable is a liability and it is increased. Thus, it is credited.
Working note 7: Determine the deferred tax liability:
Given, the accumulated temporary difference is $10,554 for year 2021 as computed in Table (4) and the tax rate is 30%.
Working note 8: Determine the income tax payable:
Given, the taxable income is $34,000 and the tax rate is 30%.
2 (d)
Record the income tax journal entry at the end of 2022 for Company C.
Explanation of Solution
Record the income tax journal entry at the end of 2022 for Company C.
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post ref. | Amount | |
| Debit | Credit | |||
| 2022 | ||||
| December 31 | Income tax expense (balancing figure) | $8,834 | ||
| Deferred tax liability (9) | $3,166 | |||
| Income tax payable (10) | $12,000 | |||
| (To record the income tax payable ) | ||||
Table (8)
- Income tax expense is an expense that decreases the stockholder’s equity and it is increased. Thus, it is debited.
- Deferred tax liability is a liability and it is decreased. Thus, it is debited.
- Income tax Payable is a liability and it is increased. Thus, it is credited.
Working note 9: Determine the deferred tax liability:
Given, the accumulated temporary difference is $0 for year 2022 as computed in Table (4) and the tax rate is 30%.
Working note 10: Determine the income tax payable:
Given, the taxable income is $40,000 and the tax rate is 30%.
3 (a)
Prepare the lower portion of Company G’s income statement.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare the lower portion of Company G’s income statement:
| Company G | |
| Income Statement | |
| For the year ended 2019 | |
| Pretax Operating Income | $24,998 |
| Less: Income tax expense | ($7,499) |
| Net Income | $17,499 |
Table (9)
Thus, the net income of Company G is $17,499.
3 (b)
Prepare the lower portion of Company G’s income statement.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the lower portion of Company G’s income statement:
| Company G | |
| Income Statement | |
| For the year ended 2020 | |
| Pretax Operating Income | $38,670 |
| Less: Income tax expense | ($11,601) |
| Net Income | $27,069 |
Table (10)
Thus, the net income of Company G is $27,069.
3 (c)
Prepare the lower portion of Company G’s income statement.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the lower portion of Company G’s income statement:
| Company G | |
| Income Statement | |
| For the year ended 2021 | |
| Pretax Operating Income | $27,886 |
| Less: Income tax expense | ($8,366) |
| Net Income | $19,520 |
Table (11)
Thus, the net income of Company G is $19,520.
3 (d)
Prepare the lower portion of Company G’s income statement.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the lower portion of Company G’s income statement:
| Company G | |
| Income Statement | |
| For the year ended 2017 | |
| Pretax Operating Income | $29,446 |
| Less: Income tax expense | ($8,834) |
| Net Income | $20,612 |
Table (12)
Thus, the net income of Company G is $20,612.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Interm.acct.:reporting.(ll)-w/access
- Coronado Fire, Inc. manufactures steel cylinders and nozzles for two models of fire extinguishers: (1) a home fire extinguisher and (2) a commercial fire extinguisher. The home model is a high-volume (54,000 units), half-gallon cylinder that holds 2 1/2 pounds of multi- purpose dry chemical at 480 PSI. The commercial model is a low-volume (10,200 units), two-gallon cylinder that holds 10 pounds of multi-purpose dry chemical at 390 PSI. Both products require 1.5 hours of direct labor for completion. Therefore, total annual direct labor hours are 96,300 or [1.5 hours x (54,000+ 10,200)]. Estimated annual manufacturing overhead is $1,566,090. Thus, the predetermined overhead rate is $16.26 or ($1,566,090 ÷ 96,300) per direct labor hour. The direct materials cost per unit is $18.50 for the home model and $26.50 for the commercial model. The direct labor cost is $19 per unit for both the home and the commercial models. The company's managers identified six activity cost pools and related…arrow_forwardThe completed Payroll Register for the February and March biweekly pay periods is provided, assuming benefits went into effect as anticipated. Required: Using the payroll registers, complete the General Journal entries as follows: February 10 Journalize the employee pay. February 10 Journalize the employer payroll tax for the February 10 pay period. Use 5.4 percent SUTA and 0.6 percent FUTA. No employees will exceed the FUTA or SUTA wage base. February 14 Issue the employee pay. February 24 Journalize the employee pay. February 24 Journalize the employer payroll tax for the February 24 pay period. Use 5.4 percent SUTA and 0.6 percent FUTA. No employee will exceed the FUTA or SUTA wage base. February 28 Issue the employee pay. February 28 Issue payment for the payroll liabilities. March 10 Journalize the employee pay. March 10 Journalize the employer payroll tax for the March 10 pay period. Use 5.4 percent SUTA and 0.6 percent FUTA. No employees will exceed the FUTA or SUTA wage base.…arrow_forwardPlease given step by step explanation general accounting questionarrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT




