
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The mechanism of the given reaction has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
- Nucleophilic substitution reaction is a type of reaction in which a particular group or atom in a compound is replaced by nucleophile. A nucleophile is a species that is rich of electrons
- Substitution reaction is a type of organic reaction where one group that is present in the substrate is replaced by another group.
- Nucleophile: donates pair of electrons to positively charged substrate resulting in the formation of
chemical bond .
Ipso substitution reaction: It is the one of the
The mechanism of desulfonation curved arrow pattern is given below.
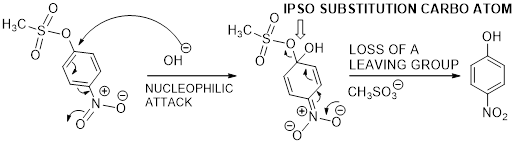
(b)
Interpretation: The rate determining step of the given reaction has to be given based on the observed regiochemical outcome.
Concept Introduction:
- Nucleophilic substitution reaction is a type of reaction in which a particular group or atom in a compound is replaced by nucleophile. A nucleophile is a species that is rich of electrons
- Substitution reaction is a type of organic reaction where one group that is present in the substrate is replaced by another group.
- Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves substrate with a pair of electrons via heterolytic bond cleavage.
- Nucleophile: donates pair of electrons to positively charged substrate resulting in the formation of chemical bond.
Ipso substitution reaction: It is the one of the aromatic substitution reaction in which both the substituent (nucleophile and the parent substituent) present in the same ring position in an intermediate compound. Finally the parent substituent leave from the intermediate leads to the formation of product.
The mechanism of desulfonation curved arrow pattern is given below.

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Which of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? O O OH OH 1. BH 2. H₂O₂, NaOH OH OHarrow_forwardDraw the products formed when each ester is hydrolyzed with water and sulfuric acid.arrow_forward
- Draw the products of the hydrolysis reaction between the ester molecule and water. Determine the products of the following reaction.arrow_forwardWhat is the unsaturation number for compounds with the formula C₂H₁₂Cl₂? O õ õ o o 4 3arrow_forwardIndicate the product obtained (formula). F3C. CF3 Br NH2 NH OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





