
Classify each of the following statements as true or false.
a) Some equilibria depend on a steady supply of a reactant in order to maintain the equilibrium.
b) Both forward and reverse reactions continue after equilibrium is reached.
c) Every time reactant molecules collide, there is a reaction.
d) Potential energy during a collision is greater than potential energy before or after the collision.
e) The properties of a transition state are between those of the reactants and products.
f) Activation energy is positive for both the forward and reverse reactions.
g) Kinetic energy is changed to potential energy during a collision.
h) An increase in temperature
i) A catalyst changes the steps by which a reaction is completed.
j) An increase in concentration of a substance on the right-hand side of an equation speeds the reverse reaction rate.
k) An increase in the concentration of a substance in an equilibrium increases the reaction rate in which the substance is a product.
l) Reducing the volume of a gaseous equilibrium shifts the equilibrium in the direction of fewer gaseous molecules.
m) Raising temperature results in a shift in the forward direction of an endothermic equilibrium.
n) The value of an equilibrium constant depends on temperature.
o) A large
(a)
Interpretation:
The statement that in order to maintain equilibrium, a steady supply of a reactant is required is to be classified as true or false.
Concept introduction:
A reaction is said to be in equilibrium if the rate at which the forward reaction takes place becomes equal to the rate at which the backward reaction takes place. If any of the factors that affect the equilibrium changes, then the reaction shifts in either forward or backward direction so that the equilibrium condition is reestablished.
Answer to Problem 80E
The statement that in order to maintain equilibrium, a steady supply of a reactant is required is false.
Explanation of Solution
A change in equilibrium can only occur due to the following changes in the reaction conditions.
• Change in concentration.
• Change in temperature.
• Change in pressure.
At equilibrium, the rate at which the reactants convert into products and vice versa remains the same. A steady supply of reactants is not required to maintain the equilibrium of the reaction.
The statement that in order to maintain equilibrium, a steady supply of a reactant is required is false.
(b)
Interpretation:
The statement that both forward and reverse reactions continue after equilibrium is reached is to be classified as true or false.
Concept introduction:
A reaction is said to be in equilibrium if the rate at which the forward reaction takes place becomes equal to the rate at which the backward reaction takes place. If any of the factors that affect the equilibrium changes, then the reaction shifts in either forward or backward direction so that the equilibrium condition is reestablished.
Answer to Problem 80E
The statement that both forward and reverse reactions continue after equilibrium is reached is true.
Explanation of Solution
At equilibrium, the rate at which the reactants convert into products and vice versa remains the same. This means that the both the forward and the reverse reactions continue to take place even after equilibrium has been attained.
The statement that both forward and reverse reactions continue after equilibrium is reached is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
The statement that a reaction takes place every time when reactant molecules collide is to be classified as true or false.
Concept introduction:
According to collision theory, reactant molecules collide with proper orientation and sufficient energy to form products. Activation energy can be defined as the amount of energy that is required to convert reactant molecules into products.
Answer to Problem 80E
The statement that a reaction takes place, every time when reactant molecules collide is false.
Explanation of Solution
All the collisions of reactant molecules do not lead to the formation of products. Product formation takes place only when the reactant molecules are properly oriented and possess enough kinetic energy to convert into products after collision. Therefore, every time when reactant molecules collide, product formation does not take place.
The statement that a reaction takes place, every time when reactant molecules collide is false.
(d)
Interpretation:
The statement that potential energy during a collision is greater than potential energy before or after the collision is to be classified as true or false.
Concept introduction:
According to collision theory, reactant molecules collide with proper orientation and sufficient energy to form products. Activation energy can be defined as the amount of energy that is required to convert reactant molecules into products.
Answer to Problem 80E
The statement that potential energy during a collision is greater than potential energy before or after the collision is true.
Explanation of Solution
The reactant molecules collide with a high kinetic energy. During collision, the potential energy of the species is the maximum. This is so because the energy of the reactant molecules must be equal to the threshold energy so that they get converted into products. The potential energy before the collision and after the collision is less than that during the collision.
The statement that potential energy during a collision is greater than potential energy before or after the collision is true.
(e)
Interpretation:
The statement that the properties of a transition state are between those of the reactants and products is to be classified as true or false.
Concept introduction:
According to collision theory, reactant molecules collide with proper orientation and sufficient energy to form products. Activation energy can be defined as the amount of energy that is required to convert reactant molecules into products.
Answer to Problem 80E
The statement that the properties of a transition state are between those of the reactants and products is false.
Explanation of Solution
The transition state is the intermediate state at which the energy of the species is the maximum and it converts immediately into products. Since the transition state is highly unstable, its properties cannot be described as those between the reactants and the products.
The statement that the properties of a transition state are between those of the reactants and products is false.
(f)
Interpretation:
The statement that activation energy is positive for both the forward and reverse reactions is to be classified as true or false.
Concept introduction:
According to collision theory, reactant molecules collide with proper orientation and sufficient energy to form products. Activation energy can be defined as the amount of energy that is required to convert reactant molecules into products.
Answer to Problem 80E
The statement that activation energy is positive for both the forward and reverse reactions is true.
Explanation of Solution
The energy versus reaction progress graph is shown below.
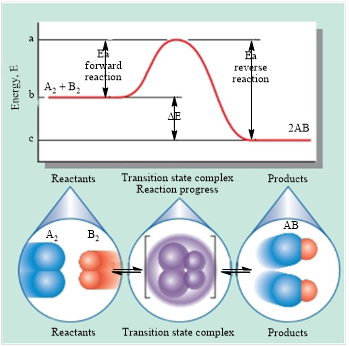
Figure 1
Consider the forward reaction,
In the graph represented in Figure 1, the point b represents the energy of the reactants, that is
The point a in the graph represents the state at which the energy is maximum. This state is known as the transition state. The reactant molecules need to cross the transition state in order to form products. Activation energy can be defined as the amount of energy that is required to convert reactant molecules into products. Therefore, the difference between the energy of the reactants and the energy of the transition state gives the activation energy of the reaction. The algebraic expression for the activation energy of the forward reaction is shown below.
Consider the reverse reaction,
In the graph represented in Figure 1, the point c represents the energy of the reactants, that is
The point a in the graph represents the state at which the energy is maximum. This state is known as the transition state. The reactant molecules need to cross the transition state in order to form products. Activation energy can be defined as the amount of energy that is required to convert reactant molecules into products. Therefore, the difference between the energy of the reactants and the energy of the transition state gives the activation energy of the reaction. The algebraic expression for the activation energy of the reverse reaction is shown below.
In the graph given in Figure 1, the point a is higher than both the points b and c. Therefore, the value of energy corresponding to the point a is higher than the values of energies corresponding to the points b and c. This indicates that the signs of activation energies for both the forward and reverse reactions are the same, that is, positive.
The statement that activation energy is positive for both the forward and reverse reactions is true.
(g)
Interpretation:
The statement that kinetic energy is changed to potential energy during a collision is to be classified as true or false.
Concept introduction:
According to collision theory, reactant molecules collide with proper orientation and sufficient energy to form products. Activation energy can be defined as the amount of energy that is required to convert reactant molecules into products.
Answer to Problem 80E
The statement that kinetic energy is changed to potential energy during a collision is true.
Explanation of Solution
The reactant molecules collide with a high kinetic energy. During collision, the kinetic energy of the reactant molecules is converted into potential energy. The potential energy of the species at the transition state is the maximum. This is so because the energy of the reactant molecules must be equal to the threshold energy so that they get converted into products. Therefore, kinetic energy is changed to potential energy during a collision.
The statement that kinetic energy is changed to potential energy during a collision is true.
(h)
Interpretation:
The statement that an increase in temperature speeds the forward reaction but slows the reverse reaction is to be classified as true or false.
Concept introduction:
A reaction is said to be in equilibrium if the rate at which the forward reaction takes place becomes equal to the rate at which the backward reaction takes place. If any of the factors that affect the equilibrium changes, then the reaction shifts in either forward or backward direction so that the equilibrium condition is reestablished.
Answer to Problem 80E
The statement that an increase in temperature speeds the forward reaction but slows the reverse reaction is false.
Explanation of Solution
When the temperature of a reaction is increased, more number of molecules collides with high kinetic energies and form products due to higher number of collisions. The rate of both the forward and the reverse reactions increases as the temperature is increased.
The statement that an increase in temperature speeds the forward reaction but slows the reverse reaction is false.
(i)
Interpretation:
The statement that a catalyst changes the steps by which a reaction is completed is to be classified as true or false.
Concept introduction:
According to collision theory, reactant molecules collide with proper orientation and sufficient energy to form products. Activation energy can be defined as the amount of energy that is required to convert reactant molecules into products.
Answer to Problem 80E
The statement that a catalyst changes the steps by which a reaction is completed is true.
Explanation of Solution
In a chemical reaction, the reactant molecules need to cross the transition state in order to form products. The activation energy is the energy required by the reactant molecules, other than the energy possessed by them, to form the transition state that decomposes to form products. A catalyst is a substance that does not get consumed in the reaction but it participates by lowering the activation energy of the reaction. A catalyst creates a new reaction pathway, having lower activation energy. Due to this, more amounts of reactants collide to form products, thereby attaining the equilibrium of the reaction at a faster rate.
The statement that a catalyst changes the steps by which a reaction is completed is true.
(j)
Interpretation:
The statement that an increase in concentration of a substance on the right-hand side of an equation speeds the reverse reaction rate is to be classified as true or false.
Concept introduction:
A reaction is said to be in equilibrium if the rate at which the forward reaction takes place becomes equal to the rate at which the backward reaction takes place. If any of the factors that affect the equilibrium changes, then the reaction shifts in either forward or backward direction so that the equilibrium condition is reestablished.
Answer to Problem 80E
The statement that an increase in concentration of a substance on the right-hand side of an equation speeds the reverse reaction rate is true.
Explanation of Solution
According to the Le Chatelier’s principle, if the concentration of a species is increased on one of the sides, then the reaction would shift in the direction that consumes the amount of substance added. If the concentration of a substance on the right-hand side of an equation is increased, then the reaction would shift in the reverse reaction, that is, the speed of the reverse reaction is increased.
The statement that an increase in concentration of a substance on the right-hand side of an equation speeds the reverse reaction rate is true.
(k)
Interpretation:
The statement that an increase in the concentration of a substance in an equilibrium increases the reaction rate in which the substance is a product is to be classified as true or false.
Concept introduction:
A reaction is said to be in equilibrium if the rate at which the forward reaction takes place becomes equal to the rate at which the backward reaction takes place. If any of the factors that affect the equilibrium changes, then the reaction shifts in either forward or backward direction so that the equilibrium condition is reestablished.
Answer to Problem 80E
The statement that an increase in the concentration of a substance in an equilibrium increases the reaction rate in which the substance is a product is false.
Explanation of Solution
According to the Le Chatelier’s principle, if the concentration of a species is increased on one of the sides, then the reaction would shift in the direction that consumes the amount of substance added. Therefore, an increase in the concentration of a substance in an equilibrium increases the reaction rate in which the substance is a reactant.
The statement that an increase in the concentration of a substance in an equilibrium increases the reaction rate in which the substance is a product is false.
(l)
Interpretation:
The statement that reducing the volume of a gaseous equilibrium shifts the equilibrium in the direction of fewer gaseous molecules is to be classified as true or false.
Concept introduction:
A reaction is said to be in equilibrium if the rate at which the forward reaction takes place becomes equal to the rate at which the backward reaction takes place. If any of the factors that affect the equilibrium changes, then the reaction shifts in either forward or backward direction so that the equilibrium condition is reestablished.
Answer to Problem 80E
The statement that reducing the volume of a gaseous equilibrium shifts the equilibrium in the direction of fewer gaseous molecules is true.
Explanation of Solution
According to Le Chatelier’s principle, on increasing pressure or decrease in the volume of a reaction, the direction of equilibrium shifts to the side of the reaction that contains less number of molecules. Therefore, reducing the volume of a gaseous equilibrium shifts the equilibrium in the direction of fewer gaseous molecules.
The statement that reducing the volume of a gaseous equilibrium shifts the equilibrium in the direction of fewer gaseous molecules is true.
(m)
Interpretation:
The statement that raising the temperature of an endothermic equilibrium results in a shift in the forward direction is to be classified as true or false.
Concept introduction:
A reaction is said to be in equilibrium if the rate at which the forward reaction takes place becomes equal to the rate at which the backward reaction takes place. If any of the factors that affect the equilibrium changes, then the reaction shifts in either forward or backward direction so that the equilibrium condition is reestablished.
Answer to Problem 80E
The statement that raising the temperature of an endothermic equilibrium results in a shift in the forward direction is true.
Explanation of Solution
According to Le Chatelier’s principle, when the temperature of an endothermic reaction is increased, the reaction shifts in the forward reaction, that is, in the direction that removes the heat from the system. Therefore, raising the temperature of an endothermic equilibrium, results in a shift in the forward direction.
The statement that raising the temperature of an endothermic equilibrium results in a shift in the forward direction is true.
(n)
Interpretation:
The statement that the value of an equilibrium constant depends on temperature is to be classified as true or false.
Concept introduction:
A reaction is said to be in equilibrium if the rate at which the forward reaction takes place becomes equal to the rate at which the backward reaction takes place. If any of the factors that affect the equilibrium changes, then the reaction shifts in either forward or backward direction so that the equilibrium condition is reestablished.
Answer to Problem 80E
The statement that the value of an equilibrium constant depends on temperature is true.
Explanation of Solution
A change in equilibrium can only occur due to the following changes in the reaction conditions.
• Change in concentration.
• Change in temperature.
• Change in pressure.
This indicates that the value of equilibrium constant depends on temperature.
The statement that the value of an equilibrium constant depends on temperature is true.
(o)
Interpretation:
The statement that a large
Concept introduction:
A reaction is said to be in equilibrium if the rate at which the forward reaction takes place becomes equal to the rate at which the backward reaction takes place. If any of the factors that affect the equilibrium changes, then the reaction shifts in either forward or backward direction so that the equilibrium condition is reestablished.
Answer to Problem 80E
The statement that a large
Explanation of Solution
The equilibrium constant
The statement that a large
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Bundle: Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach, 6th + LMS Integrated for OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Explain that equilibrium is dynamic, and that at equilibrium the forward and backward reaction rates are equal.arrow_forwardConsider the following equilibrium system. N2(g)+O2(g)2NO(g) a. Write the chemical equation for the forward reaction. b. Write the chemical equation for the reverse reaction.arrow_forwardUse Le Chteliers principle to predict the direction of the equilibrium shift in the following equilibria when the indicated stress is applied: a. Ag+(aq)+Cl(aq)AgCl(s); some Ag+ is removed. b. 2HI(g)+heatH2(g)+I2(g); the system is heated. c. 6Cu(s)+N2(g)+heat2Cu3N(s); the system is cooled and some N2 is removed.arrow_forward
- In Section 13.1 of your text, it is mentioned that equilibrium is reached in a closed system. What is meant by the term closed system. and why is it necessary to have a closed system in order for a system to reach equilibrium? Explain why equilibrium is not reached in an open system.arrow_forwardIn the figure, orange fish are placed in one aquarium and green fish in an adjoining aquarium. The two tanks are separated by a removable partition that is initially closed. (a) Describe what happens in the first few minutes after the partition is opened. (b) What would you expect to see several hours later? (c) How is this system analogous to dynamic chemical equilibrium?arrow_forward. Explain what it means that a reaction has reached a state of chemical equilibrium. Explain why equilibrium is a dynamic state: Does a reaction really “stop” when the system reaches a state of equilibrium? Explain why, once a chemical system has reached equilibrium, the concentrations of all reactants remain constant with time. Why does this constancy of concentration not contradict our picture of equilibrium as being dynamic? What happens to the rates of the forward and reverse reactions as a system proceeds to equilibrium from a starting point where only reactants are present?arrow_forward
- Tell what will happen to each equilibrium concentration in the following when the indicated stress is applied and a new equilibrium position is established. a. H+(aq)+HCO3(aq)H2O(l)+CO2(g); HCO3is added. b. CO2(g)+H2O(l)H2CO3(aq)+heat; CO2is removed. c. CO2(g)+H2O(l)H2CO3(aq)+heat; The system is cooled.arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant expression for a given reaction depends on how the equilibrium equation is written. Explain the meaning of that statement. You may, if you wish, use the equilibrium equation N2(g)+3H2(g)2NH3(g) to illustrate your explanation.arrow_forwardFor the generalized chemical reaction A(g)+B(g)C(g)+D(g) determine whether the concentration of A in an equilibrium mixture will (1) increase, (2) decrease, or (3) not change when each of the following changes is effected. a. concentration of B is increased b. concentration of C is decreased c. concentration of D is increased d. concentration of D is decreasedarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





