
Electrostatic precipitator (esp) Electrostatic precipitators are a common form of air-cleaning device ESPs are used to remove particle emissions from smoke moving up smokestacks in coal and oil-fired electricity-generating plants and pollutants from the boilers in oil refineries. You can buy portable ESPs of whole-house ESPs that connect to the cold-air return on the furnace. These devices remove about 95% of dirt and 85% of microscopic particles from the air.
A basic electrostatic precipitator contains a negatively charged horizontal metal grid (made of thin wires) and a stack of large flat, vertically oriented metal collecting plates, with the plates typically spaced about 1 cm apart (only two plates are shown in Figure 18.30). Air flows across the charged grid of wires and then passes between the plates. A large negative potential difference (tens of thousands of volts) is applied between the wires and the plates, creating a strong electric field that ionizes particles in the air around the thin wires. Negatively charged smoke particles flow upward between the plates. The charged particles are attracted to and stick to the oppositely charged plates and are thus removed from the moving gas.
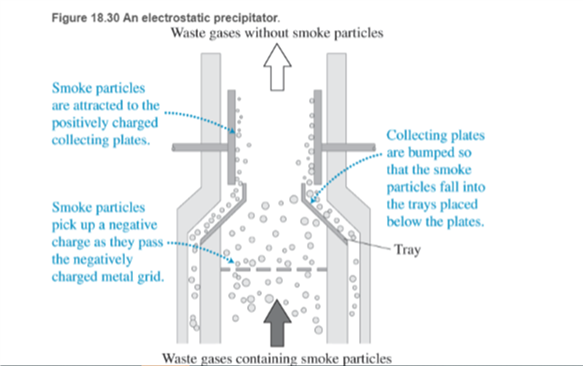
What is the purpose of giving a negative charge to the particles collected by the precipitator?
a. The particles are then attracted to the positively charged plates while moving upward.
b. The particles are then repelled from the positively charged plates while moving upward.
c. The extra mass slows the upward movement of the particles.
d. The negative charge cancels the positive charge the particles have when entering the precipitator.
e. a and c
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
College Physics: Explore And Apply, Volume 2 (2nd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answer .arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next question. Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of 42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below: A Incident ray at A Note: This diagram is not to scale. Air (n = 1.00) Water (n = 1.34) Barrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next question. Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of 42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below: A Incident ray at A Note: This diagram is not to scale. Air (n = 1.00) Water (n = 1.34) Barrow_forward
- Good explanation it sure experts solve it.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Asaparrow_forwardA satellite has a mass of 100kg and is located at 2.00 x 10^6 m above the surface of the earth. a) What is the potential energy associated with the satellite at this loction? b) What is the magnitude of the gravitational force on the satellite?arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardCorrect answer No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardStatistical thermodynamics. The number of imaginary replicas of a system of N particlesa) cannot be greater than Avogadro's numberb) must always be greater than Avogadro's number.c) has no relation to Avogadro's number.arrow_forward
- Lab-Based Section Use the following information to answer the lab based scenario. A student performed an experiment in an attempt to determine the index of refraction of glass. The student used a laser and a protractor to measure a variety of angles of incidence and refraction through a semi-circular glass prism. The design of the experiment and the student's results are shown below. Angle of Incidence (°) Angle of Refraction (º) 20 11 30 19 40 26 50 31 60 36 70 38 2a) By hand (i.e., without using computer software), create a linear graph on graph paper using the student's data. Note: You will have to manipulate the data in order to achieve a linear function. 2b) Graphically determine the index of refraction of the semi-circular glass prism, rounding your answer to the nearest hundredth.arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next two questions. A laser is directed at a prism made of zircon (n = 1.92) at an incident angle of 35.0°, as shown in the diagram. 3a) Determine the critical angle of zircon. 35.0° 70° 55 55° 3b) Determine the angle of refraction when the laser beam leaves the prism.arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next two questions. A laser is directed at a prism made of zircon (n = 1.92) at an incident angle of 35.0°, as shown in the diagram. 3a) Determine the critical angle of zircon. 35.0° 70° 55 55° 3b) Determine the angle of refraction when the laser beam leaves the prism.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





