
Draw the structure for each of the following:
a. phenol
b. benzyl phenyl ether
c. benzonitrile
d. benzaldehyde
e. anisole
f. styrene
g. toluene
h. tert-buty lbenzene
i. benzyl chloride
a)
Interpretation:
The structure of phenol is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Phenols are defined as those compounds in which hydroxy group is attached directly to the benzene ring. Phenols and alcohols have so many similar properties.
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of phenol is shown below.
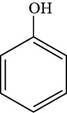
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
The structure of phenol is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of phenol is shown below.
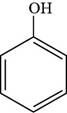
Figure 1
b)
Interpretation:
The structure of benzyl phenyl ether is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of benzyl phenyl ether is shown below.
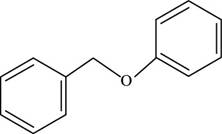
Figure 2
Explanation of Solution
The structure of benzyl phenyl ether is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of benzyl phenyl ether is shown below.

Figure 2
c)
Interpretation:
The structure of benzonitrile is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of benzonitrile is shown below.
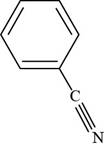
Figure 3
Explanation of Solution
The structure of benzonitrile is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of benzonitrile is shown below.
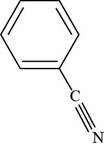
Figure 3
d)
Interpretation:
The structure of benzaldehyde is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of benzaldehyde is shown below.
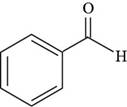
Figure 4
Explanation of Solution
The structure of benzaldehyde is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of benzaldehyde is shown below.
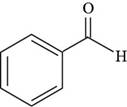
Figure 4
e)
Interpretation:
The structure of anisole is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of anisole is shown below.
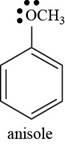
Figure 5
Explanation of Solution
The structure of anisole is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of anisole is shown below.
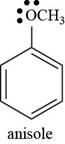
Figure 5
f)
Interpretation:
The structure of styrene is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of styrene is shown below.
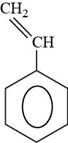
Figure 6
Explanation of Solution
The structure of styrene is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of styrene is shown below.
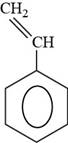
Figure 6
g)
Interpretation: The structure of toluene is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of toluene is shown below.
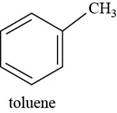
Figure 7
Explanation of Solution
The structure of toluene is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of toluene is shown below.
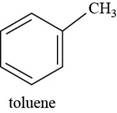
Figure 7
h)
Interpretation: The structure of tert-butyl benzene is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of tert-butyl benzene is shown below.
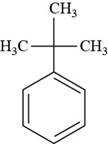
Figure 8
Explanation of Solution
The structure of tert-butyl benzene is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of tert-butyl benzene is shown below.

Figure 8
i)
Interpretation:
The structure of benzyl chloride is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of benzyl chloride is shown below.
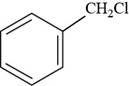
Figure 9
Explanation of Solution
The structure of benzyl chloride is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of benzyl chloride is shown below.

Figure 9
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Student's Study Guide and Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry
- Indicate one aspect that benefits and another that makes it difficult to use the hydroquinone electrode to measure pH.arrow_forwardAt an electrified interface according to the Gouy-Chapman model, what types of interactions do NOT occur between the ions and the solvent according to this theory?arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions. Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry (syn- vs anti- or both). If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please draw all the enantiomers. Hint: In this case you must choose the best answer to demonstrate the stereochemistry of H2 addition. 1.03 2. (CH3)2S BIZ CH₂OH 2. DMS KMnO4, NaOH ΖΗ Pd or Pt (catalyst) HBr 20 1 HBr ROOR (peroxide) HO H-SO HC 12 11 10 BH, THE 2. H2O2, NaOH Brz cold HI 19 18 17 16 MCPBA 15 14 13 A Br H₂O BH3⚫THF Brz EtOH Pd or Ni (catalyst) D₂ (deuterium) 1. Os04 2. H2O2 CH3CO3H (peroxyacid) 1. MCPBA 2. H₂O* H B + H H H "H C H H Darrow_forward
- Explain how Beer’s Law can be used to determine the concentration in a selected food sample. Provide examples.arrow_forwardExplain the importance of having a sampling plan with respect to food analysis. Explain the importance of having a sampling plan with respect to food analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions. Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry (syn- vs anti- or both). If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please draw all the enantiomers. cold KMnO4, NaOH 2. DMS 1. 03 CH3OH Br2 1. 03 2. (CH3)2S H₂ Pd or Pt (catalyst) HBr 18 19 20 1 HBr ROOR (peroxide) H₂O H₂SO4 HCI HI 17 16 6 15 MCPBA 1. BH3 THF 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. OsO4 2. H₂O₂ 110 CH3CO₂H (peroxyacid) 1. MCPBA 2. H₂O* Br2 H₂O BH3 THF B12 EtOH Pd or Ni (catalyst) D₂ (deuterium) Bra A B C D H OH H OH OH H OH α α α OH H OH OH фон d H "Harrow_forward
- Briefly indicate the models that describe the structure of the interface: Helmholtz-Perrin, Gouy-Chapman, Stern and Grahame models.arrow_forwardElectrochemistry. Briefly describe the Gibbs model and the Gibbs absorption equation.arrow_forwardThermodynamic analysis of electrified interfaces.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning



