
Concept explainers
A phase diagram for carbon and platinum is shown. It is assumed the lines shown are linear, and the mixture has the following characteristics. The endpoints of the division line between these two phases are labeled on the diagram.
■ Below 1700 degrees Celsius, it is a mixture of solid platinum (Pt) and graphite (G).
■ Above 1700 degrees Celsius, there are two possible phases: a Liquid (L) phase and a Liquid (L) + phase (G).
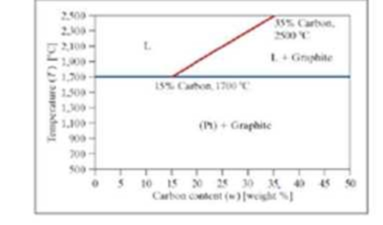
Write a program to determine the phase. The program should ask the user to enter the weight percent carbon and the temperature in degrees Celsius. Call the phases “Pt + G,” “L,” and “L + G,” for simplicity. If the point falls directly on the T = 1700°C line, include the point in the “Pt + G” phase. If the point falls directly on the L, L + Gline, include the point in the “L + G” phase.
Store the phase as text in a variable. The equation of the line dividing the L and L + G phases must be found in the program using polyfit. The program should produce a formatted output statement to the command window. Similar to “For X.XX weight percent carbon and a temperature of YYY degrees Celsius, the phase is PHASE” where x.xx, yyy and PHASE are replaced by the actual values formatted as shown.
The following partial code is designed to implement this program. You are to fill in the missing sections of code as appropriate to complete the program.

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
- subject: combustion please include complete solution, no rounding off, with diagram/explanation etc. In a joule cycle, intake of the compressor is 40,000 cfm at 0.3 psig and 90 deg F. The compression ratio is 6.0 and the inlet temperature at the turbine portion is 1900R while at the exit, it is 15 psi. Calculate for the back work ratio in percent.arrow_forwardsubject: combustion please include complete solution, no rounding off, with diagram/explanation etc. A gasoline engine, utilizing cold air, recorded a work of 431 BTU/lb at a maximum temperature of 3,273 K and 1112 deg F temperature at the beginning of constant volume heat addition. What is the compression ratio?arrow_forwardsubject: combustion please do step by step solution and no rounding off, complete solution with diagram/explanation if needed etc. thank you! Air enters the compressor at 101,320 Pascals, 305.15K, and leaves at a pressure of 0.808MPa. The air is heated to 990.15K in the combustion chamber. For a net output of 2,125,000 Watts, find the rate of flow of air per second.arrow_forward
- The link lengths and the value of 2 and offset for some fourbar crank-slide linkages are defined in Table 1. The linkage configuration and terminology are shown in Figure 1. For the rows assigned, find (a) all possible solutions for angle & and slider position d by vector loop method. (b) the transmission angle corresponding to angle 03. (Hint: Treat the vector R4 as virtual rocker) Show your work in details: vector loop, vector equations, solution procedure. Table 1 Row Link 2 Link 3 Offset Ө a 1.4 4 1 45° b 3 8 2 -30° C 5 20 -5 225° 03 slider axis B X offset Link 2 A R3 Link 3 R4 04 R2 02 R1 d Figure 1. Xarrow_forward4. Two links made of heat treated 6061 aluminum (Sy = 276 MPa, Sys = 160 MPa) are pinned together using a steel dowel pin (Sy = 1398 MPa, Sys = 806 MPa) as shown below. The links are to support a load P with a factor of safety of at least 2.0. Determine if the link will fail first by tearout, direct shear of the pin, bearing stress on the link, or tensile stress at section AA. (Hint: find the load P for each case and choose the case that gives the smallest load.) P 8 mm P 8 mm ¡+A 3 mm →A 10 mm Parrow_forward1. For a feature other than a sphere, circularity is where: A. The axis is a straight line B. The modifier is specified with a size dimension C. All points of the surface intersected by any plane perpendicular to an axis or spine (curved line) are equidistant from that axis or spine D. All points of the surface intersected by any plane passing through a common center are equidistant from that center 2. What type of variation is limited by a circularity toler- ance zone? A. Ovality B. Tapering C. Bending D. Warping 3. How does the Rule #1 boundary affect the application of a circularity tolerance? A. The modifier must be used. B. The feature control frame must be placed next to the size dimension. C. The circularity tolerance value must be less than the limits of size tolerance. D. Circularity cannot be applied where a Rule #1 boundary exists. 4. A circularity tolerance may use a modifier. A. Ø B. F C. M D. ℗ 5. A real-world application for a circularity tolerance is: A. Assembly (i.e.,…arrow_forward
- 3. A steel bar is pinned to a vertical support column by a 10 mm diameter hardened dowel pin, Figure 1. For P = 7500 N, find: a. the shear stress in the pin, b. the direct bearing stress on the hole in the bar, c. the minimum value of d to prevent tearout failure if the steel bar has a shear strength of 175 MPa. support column pin bar thickness of bar = 8 mm h d 150 mmarrow_forwardA press that delivers 115 strokes per minute, each stroke providing a force of 7826 N throughout a distance of 18 mm. The press efficiency is 90% and is driven by a 1749-rpm motor. Determine average torque that must be provided by the motor in the units of N-m.arrow_forward·3) find the force (P) for the figures (1) and (2) 15cm 10cm 15 h=10mm h2=6mm // Call = 90 N/2 P Agate Fig (i) Ans: 1)P=112614N 2) P=1956.5 N 25cm 25 cm الفترة أو الحجم تمر بالتي عثر اكو تورشن (ک Fig (2) h₁ = 10mm 42=6mm Cmarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





