
Concept explainers
For each of the following substituted benzenes: [1]
a. Does the substituent donate or withdraw electron density by an inductive effect?
b. Does the substituent donate or withdraw electron density by a resonance effect?
c. On balance, does the substituent make a benzene ring more or less electron rich than benzene itself?
d. Does the substituent activate or deactivate the benzene ring in electrophilic
(a)
Interpretation: The substituents present on the given benzene donate or withdraw electron density by an inductive effect is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.47P
The substituent in
Explanation of Solution
The inductive effect appears in a molecule due to the difference in electron negativity of atoms. The groups attached to benzene ring in the given compound are
The electron negativity of bromine is more than carbon atom. Hence, the substituent in
The electron negativity of nitrogen is more than carbon atom. Hence, the substituent in
The electron negativity of oxygen is more than carbon atom. Hence, the substituent in
The substituent in
(b)
Interpretation: The substituents present on the given benzene donate or withdraw electron density by a resonance effect is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.47P
The substituent in
Explanation of Solution
The positive resonance effect is observed when the substituent present on a benzene ring donates its lone pair of electrons. Whereas, the negative resonance effect is observed, when the substituents present on a benzene ring pull its electrons towards itself.
The bromine atom attached to a benzene ring in
The carbon atom of
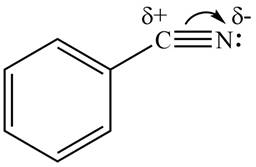
Figure 1
Therefore, the substituent in
The oxygen atom attached to a benzene ring in
The substituent in
(c)
Interpretation: The substituents make benzene ring more or less electron than benzene itself is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.47P
Substituents
Explanation of Solution
The electron donating groups or activating groups make benzene ring more electron rich than benzene itself, whereas the electron withdrawing groups or deactivating groups make benzene ring less electron rich than benzene itself.
The
Substituents
(d)
Interpretation: The substituents activate or deactivate the benzene ring in electrophilic aromatic substitution is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.47P
Substituents
Explanation of Solution
The electron donating groups activate the benzene ring in electrophilic aromatic substitution, whereas the electron withdrawing groups deactivate the benzene ring in electrophilic aromatic substitution.
The
Substituents
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Using reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NO2 (g) = N2O4(g) AGº = -5.4 kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 4.53 atm of dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) at 279. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2O4 tend to rise or fall? Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO2? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to '2' rise by adding NO2? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO 2 needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 00 rise ☐ x10 fall yes no ☐ atm G Ar 1arrow_forwardWhy do we analyse salt?arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. H H CH3OH, H+ H Select to Add Arrows H° 0:0 'H + Q HH ■ Select to Add Arrows CH3OH, H* H. H CH3OH, H+ HH ■ Select to Add Arrows i Please select a drawing or reagent from the question areaarrow_forward
- What are examples of analytical methods that can be used to analyse salt in tomato sauce?arrow_forwardA common alkene starting material is shown below. Predict the major product for each reaction. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the relative stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts H Šali OH H OH Select to Edit Select to Draw 1. BH3-THF 1. Hg(OAc)2, H2O =U= 2. H2O2, NaOH 2. NaBH4, NaOH + Please select a drawing or reagent from the question areaarrow_forwardWhat is the MOHR titration & AOAC method? What is it and how does it work? How can it be used to quantify salt in a sample?arrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this reaction. Cl₂ hv ? Draw only the major product or products in the drawing area below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. If there will be no products because there will be no significant reaction, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Note for advanced students: you can ignore any products of repeated addition. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 80 10 m 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility DII A F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 EO F11arrow_forwardGiven a system with an anodic overpotential, the variation of η as a function of current density- at low fields is linear.- at higher fields, it follows Tafel's law.Calculate the range of current densities for which the overpotential has the same value when calculated for both cases (the maximum relative difference will be 5%, compared to the behavior for higher fields).arrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) AGº = -34. KJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 8.06 atm of nitrogen (N2) and 2.58 atm of ammonia (NH3) at 106. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2 tend to rise or fall? ☐ x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding H2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding H₂? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. yes no ☐ atm Х ด ? olo 18 Ararrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
