
Concept explainers
Standard-costing method, spoilage. Refer to the information in Exercise 18-29. Suppose LogicCo determines standard costs of $215 per equivalent unit for direct materials and $92 per equivalent unit for conversion costs for both beginning work in process and work done in the current period.
- 1. Do Exercise 18-29 using the standard-costing method.
Required
- 2. What issues should the manager focus on when reviewing the equivalent units calculation?
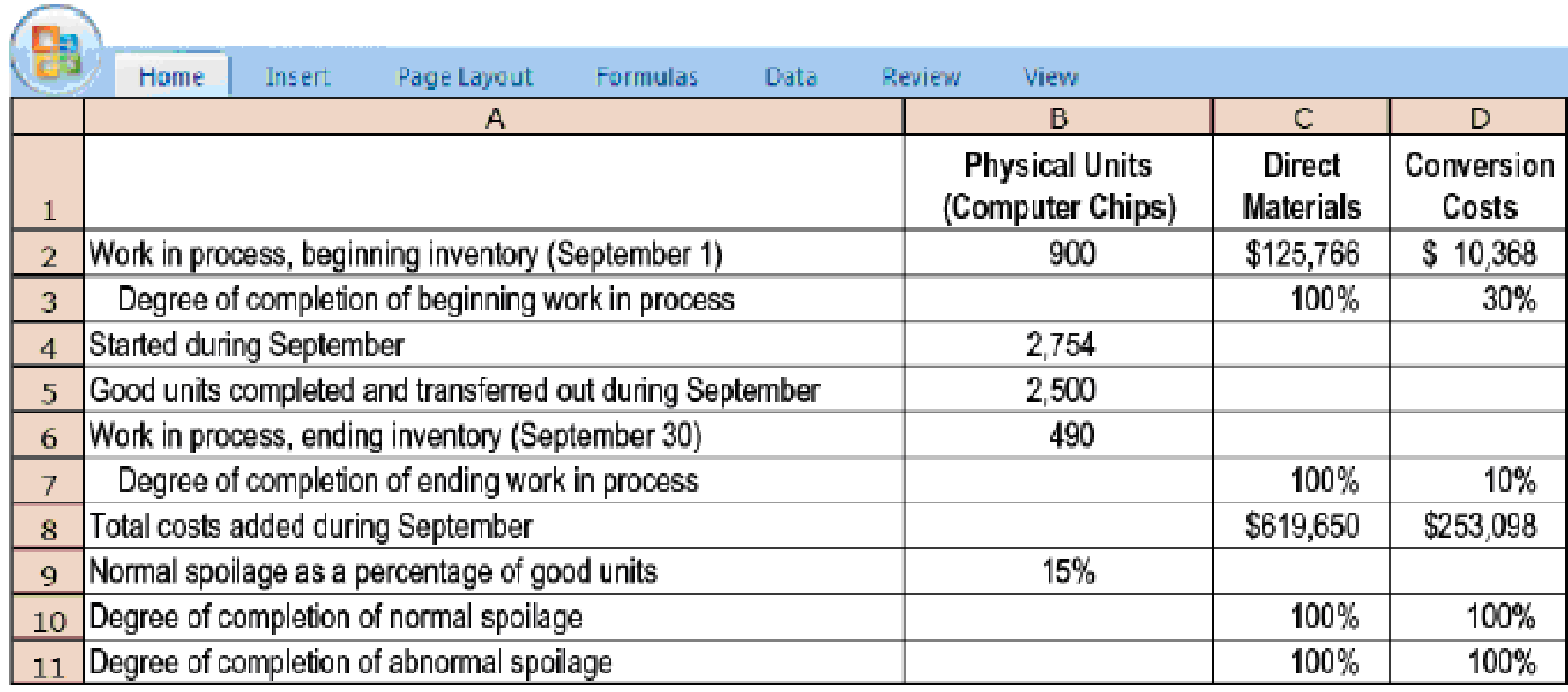
18-29 Weighted-average method, spoilage. LogicCo is a fast-growing manufacturer of computer chips. Direct materials are added at the start of the production process. Conversion costs are added evenly during the process. Some units of this product are spoiled as a result of defects not detectable before inspection of finished goods. Spoiled units are disposed of at zero net disposal value. LogicCo uses the weighted-average method of
Summary data for September 2017 are as follows:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting, Student Value Edition (16th Edition)
- Ansarrow_forwardWhat amount should be debited to the trademark account on these general accounting question?arrow_forwardColton Inc. is a merchandising company. Last month, the company's cost of goods sold was $85,600. The company's beginning merchandise inventory was $18,200, and its ending merchandise inventory was $30,500. What was the total amount of the company's merchandise purchases for the month?arrow_forward
- Willow Inc. has $310,000 in accounts receivable on February 1. Budgeted sales for February are $1,050,000. Willow Inc. expects to sell 25% of its merchandise for cash. Of the remaining 75% of sales on account, 80% are expected to be collected in the month of sale and the remainder the following month. The February cash collections from sales are: a. $1,202,500 b. $840,000 c. $1,090,000 d. $1,400,000arrow_forwardBeta Corporation began operations on January 1 with cash of $100,000. All of January's $200,000 sales were on account. During January, no customer collections occurred. The cost of goods sold was $70,000, and there were no ending inventories or accounts payable. Use this information to determine the ending balance of cash on hand for January.Solve this ?arrow_forwardCalculate Windsor Gear works total assets on these financial accounting questionarrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





