
Weighted-average method, spoilage, equivalent units. (CMA, adapted) Consider the following data for November 2017 from MacLean Manufacturing Company, which makes silk pennants and uses a process-costing system. All direct materials are added at the beginning of the process, and conversion costs are added evenly during the process. Spoilage is detected upon inspection at the completion of the process. Spoiled units are disposed of at zero net disposal value. MacLean Manufacturing Company uses the weighted-average method of
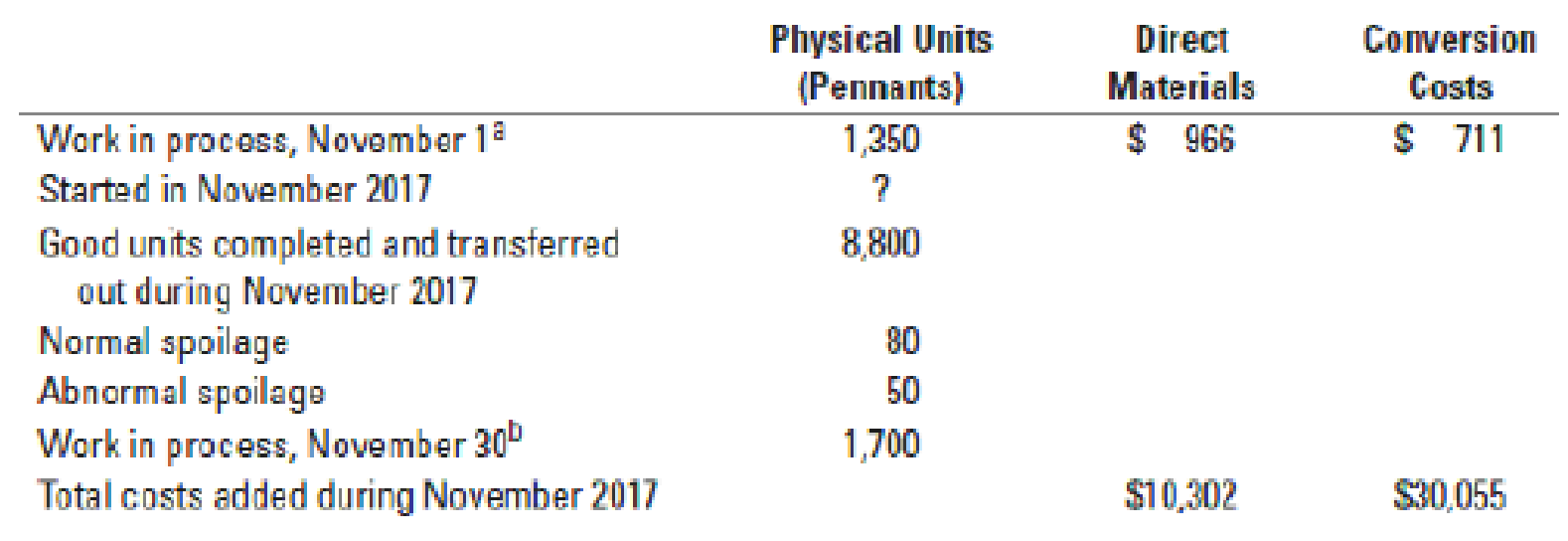
a Degree of completion: direct materials, 100%; conversion costs, 45%.
b Degree of completion: direct materials, 100%; conversion costs, 35%.
Required
Compute equivalent units for direct materials and conversion costs. Show physical units in the first column of your schedule.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 18 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting, Student Value Edition (16th Edition)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Horngren's Accounting (11th Edition)
Financial Accounting (11th Edition)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (4th Edition)
Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Intermediate Accounting
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, The Financial Chapters (6th Edition)
- The total cost of spoilage chargeable to Revenue is (recognized as expenses):arrow_forwardFor E2-17, prepare any journal entries that would have been different if the only trigger points had been the purchase of materials and the sale of finished goods. Davis Co. uses backflush costing to account for its manufacturing costs. The trigger points are the purchase of materials, the completion of goods, and the sale of goods. Prepare journal entries to account for the following: a. Purchased raw materials, on account, 70,000. b. Requisitioned raw materials to production, 70,000. c. Distributed direct labor costs, 15,000. d. Factory overhead costs incurred, 45,000. (Use Various Credits for the account in the credit part of the entry.) e. Completed all of the production started. f. Sold the completed production for 195,000, on account. (Hint: Use a single account for raw materials and work in process.)arrow_forwardOverstitch Textiles Company makes silk banners and uses the FIFO method of process costing. Direct materials are added at the beginning of the process, and conversion costs are added evenly during the process. Spoilage is detected upon inspection at the completion of the process. Spoiled units are disposed of at zero net disposal value. (Click the icon to view the process costing data.) Determine the equivalent units of work done in July, and calculate the cost of units completed and transferred out (including normal spoilage), the cost of abnormal spoilage, and the cost of units in ending inventory. For each cost category, compute equivalent units. Enter the physical units in first, then calculate the equivalent units. (Complete all input fields. Enter a "0" for any zero amounts.) Physical Data table Flow of Production Units Work in process beginning Physical Units Direct Conversion Started during current period (Banners) Materials Costs To account for 2,000 $9,000 $1,200 Work in…arrow_forward
- The total costs of goods allocated to units transferred out is:arrow_forward(a) Prepare a statement of equivalent production to determine the equivalent units for direct materials(From Moulding & Direct Material Added), and conversion costs and the cost per equivalent unit fordirect materials and conversion costs. (b) Calculate the:- Total cost of units completed and transferred to the Spraying Department- Cost of abnormal losses- Cost of ending work-in-process inventory in the Baking Department(c) Prepare Michael Pottery’s Work-In-Process Inventory – Baking Department T-account, clearly showingthe ending balance.arrow_forward[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Victory Company uses weighted average process costing. The company has two production processes. Conversion cost is added evenly throughout each process. Direct materials are added at the beginning of the first process. Additional information for the first process follows. Beginning work in process inventory Units started this period Units completed and transferred out Ending work in process inventory. Beginning work in process inventory. Direct materials Conversion Costs added this period Direct materials Conversion Total costs to account for Cost per equivalent unit of production Units Total costs + Equivalent units of production (from part 1) Cost per equivalent unit of production 78,000 876,000 760,000 194,000 $ 496,080 87,640 3,319,920 1,665, 160 Direct Materials. Percent Complete 100% 100% 2. Compute cost per equivalent unit of production for both direct materials and conversion. Costs EUP $ 583,7: 4,985,0…arrow_forward
- Please show your computations using good accounting form through excel. Thank you! Problem: By products In Department III of SAMCIS Company, a portion of the materials (a by-product) is removed further processed and sold. The Company uses the reversal cost method to account for the by-product. Data for June include: Amount of by-product removed is 2000 units; Estimated sales price of by-product after processing further is P1.20/unit. Estimated processing cost after separation is P0.30 per unit and estimated selling expenses is 10% of the sales price. The estimated profit margin is 5% of the sales price. What is the total cost of the by-product?arrow_forwarda) What are the normal and abnormal spoilage units, respectively, for March when using FIFO? b) Using above problem, what costs would be associated with normal and abnormal spoilage, respectively, using the FIFO method of process costing?arrow_forward[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Victory Company uses weighted average process costing. The company has two production processes. Conversion cost is added evenly throughout each process. Direct materials are added at the beginning of the first process. Additional information for the first process follows. Beginning work in process inventory Units started this period Units completed and transferred out Ending work in process inventory Beginning work in process inventory Direct materials Conversion Costs added this period Direct materials Conversion Total costs to account for Cost assignment-Weighted average Completed and transferred out Direct materials Conversion Ending work in process Direct materials Conversion Total costs accounted for Units EUP 78,000 876,000 760,000 194,000 $ 496,080 87,640 3,319,920 1,665, 160 Direct Materials. Percent Complete 100% 3. Assign costs to the department's output-specifically, to the units transferred out and to…arrow_forward
- ii) Assign total cost to:a. Units completed and transferred out to the Drying Departmentb. Units rejected as abnormal spoilagec. Units in the Molding department work in process inventory.arrow_forwardCalculate the manufacturing cost per unit of HJ6 in 2016.arrow_forwardSummarize the total costs to account for; calculate the cost per equivalent unit for each cost category; and assign costs to units completed and transferred out (including normal spoilage), to abnormal spoilage, and to units in ending work in process.arrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
