
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The given
Concept introduction:
Acid release hydrogen ion in water, Base release hydroxide ions in water.
An acid is a substance that produces hydronium ions,
Bronsted –Lowry definitions:
A Bronsted –Lowry acid is a proton donor, it donates a hydrogen ion (
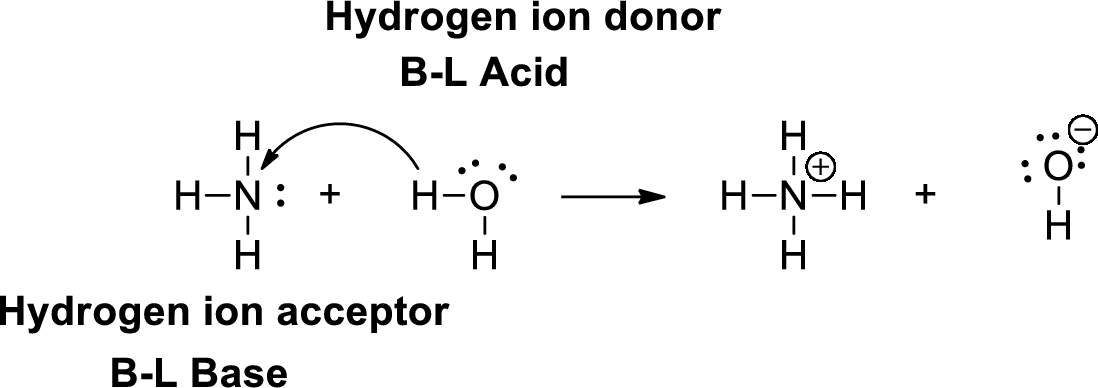
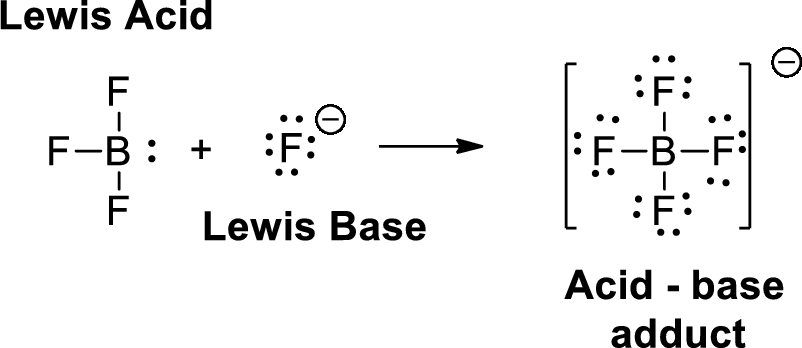
Lewis definition:
A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept and share an electron pair. A Lewis base is a substance that can donate and share an electron pair.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given
Concept introduction:
Arrhenius Acids and Bases:
Acid release hydrogen ion in water, Base release hydroxide ions in water.
An acid is a substance that produces hydronium ions,
Bronsted –Lowry definitions:
A Bronsted –Lowry acid is a proton donor, it donates a hydrogen ion (
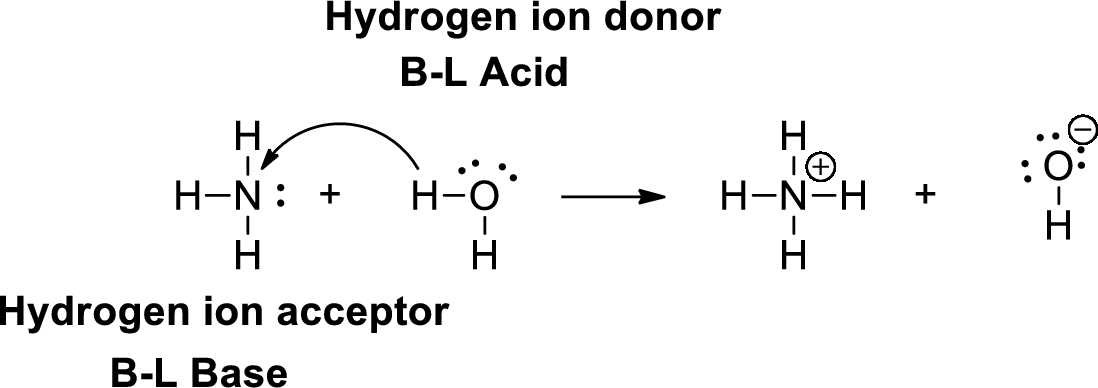
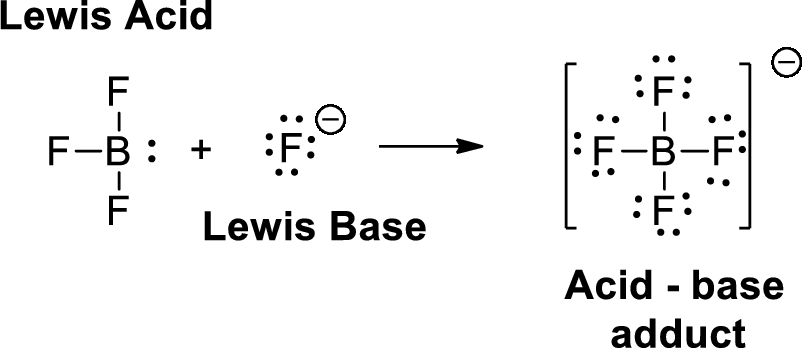
Lewis definition:
A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept and share an electron pair. A Lewis base is a substance that can donate and share an electron pair.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given
Concept introduction:
Arrhenius Acids and Bases:
Acid release hydrogen ion in water, Base release hydroxide ions in water.
An acid is a substance that produces hydronium ions,
Bronsted –Lowry definitions:
A Bronsted –Lowry acid is a proton donor, it donates a hydrogen ion (
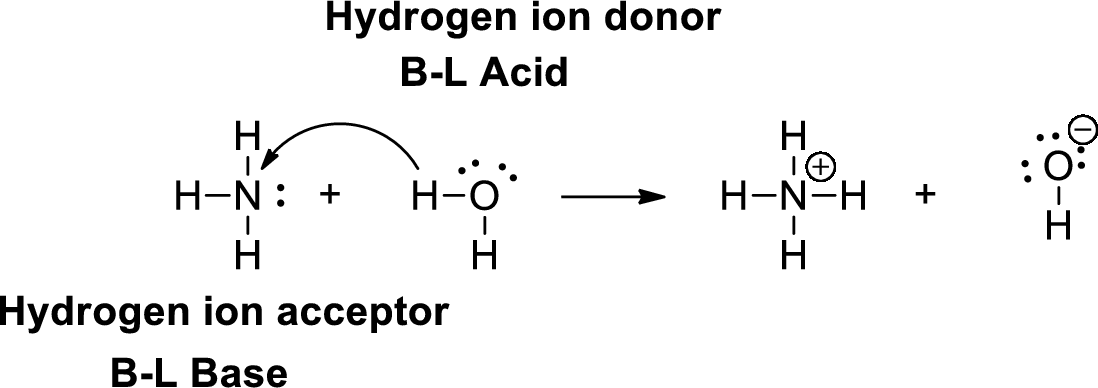
Lewis definition:
A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept and share an electron pair. A Lewis base is a substance that can donate and share an electron pair.
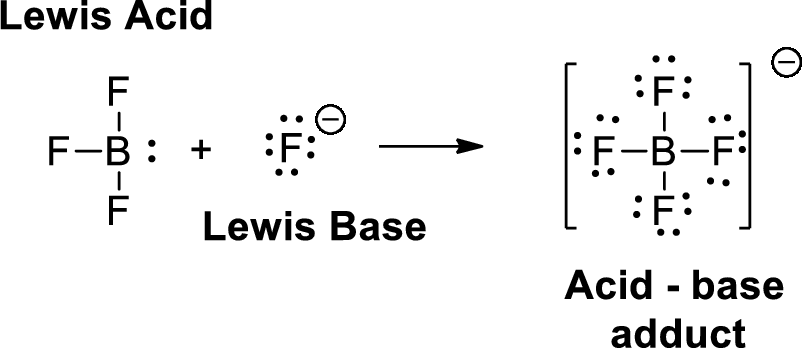
(d)
Interpretation:
The given
Concept introduction:
Arrhenius Acids and Bases:
Acid release hydrogen ion in water, Base release hydroxide ions in water.
An acid is a substance that produces hydronium ions,
Bronsted –Lowry definitions:
A Bronsted –Lowry acid is a proton donor, it donates a hydrogen ion (
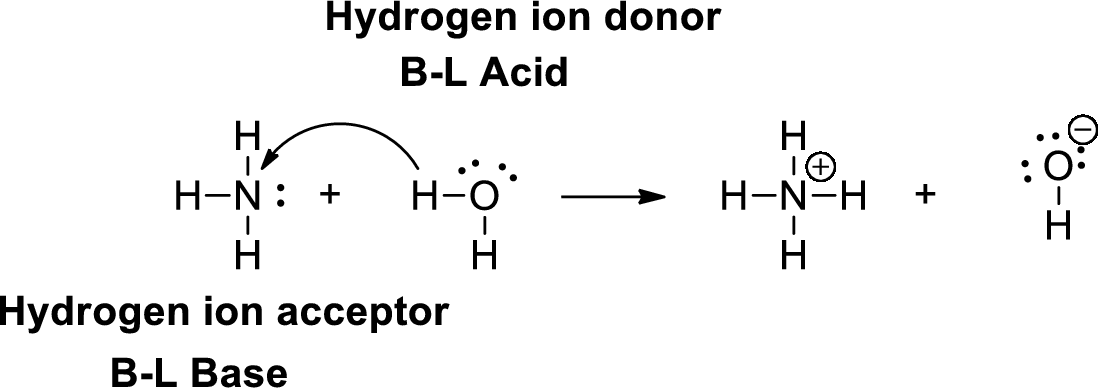
Lewis definition:
A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept and share an electron pair. A Lewis base is a substance that can donate and share an electron pair.
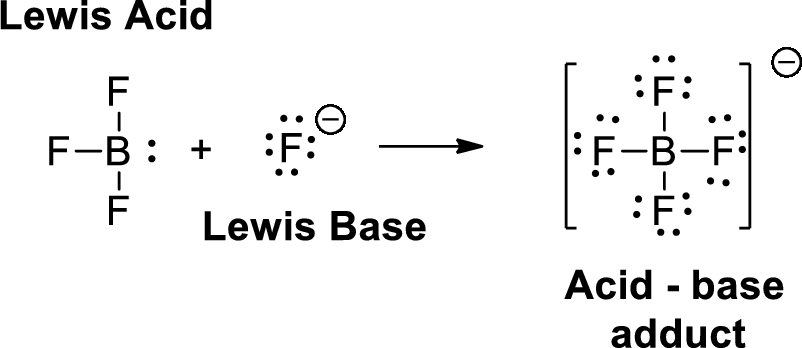
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
CHEMISTRY: MOLECULAR...(LL) W/ALEKS
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





