
The initial trial asphalt content for different blends.
Answer to Problem 16P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Nominal maximum sieve of each aggregate blend = 19 mm.
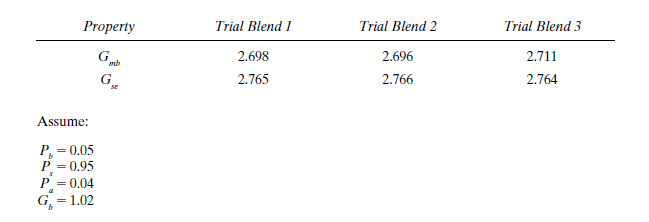
Calculation:
For trial blend 1, we have:
The amount of asphalt binder absorbed by the aggregates is estimated
from Eq. 18.18 as
Where,
Substitute the values in the required equation, we have
Estimate the percent of effective asphalt binder by volume using theempirical expression given as follows:
Where,
gradation (mm).
Substitute the values in the required equation, we have
Now, calculate the mass of aggregate by using the following formula:
Where,
Substitute the values, we have
A trial percentage of asphalt binder then is determined for each trial
aggregate blend using the following equation.
Where,
Substitute the values, we have
For trial blend 2, we have:
The amount of asphalt binder absorbed by the aggregates is estimated
from Eq. 18.18 as
Where,
Substitute the values in the required equation, we have
Estimate the percent of effective asphalt binder by volume using the empirical expression given as follows:
Where,
gradation (mm).
Substitute the values in the required equation, we have
Now, calculate the mass of aggregate by using the following formula:
Where,
Substitute the values, we have
A trial percentage of asphalt binder then is determined for each trial
aggregate blend using the following equation.
Where,
Substitute the values, we have
For trial blend 3, we have:
The amount of asphalt binder absorbed by the aggregates is estimated
from Eq. 18.18 as
Where,
Substitute the values in the required equation, we have
Estimate the percent of effective asphalt binder by volume using the empirical expression given as follows:
Where,
gradation (mm).
Substitute the values in the required equation, we have
Now, calculate the mass of aggregate by using the following formula:
Where,
Substitute the values, we have
A trial percentage of asphalt binder then is determined for each trial
aggregate blend using the following equation.
Where,
Substitute the values, we have
Conclusion:
Therefore, the initial trial asphalt content for1st, 2nd and 3rd blends is as follows
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Traffic and Highway Engineering - With Mindtap
- ٢٥ ٠٥:٤٠١٠ 2025 ChatGPT VivaCut Onet Puzzle مسلم X Excel JPG I❤> PDF Copilot Chat Bot PDF2IMG iLovePDF NokoPrint O.O StudyX ☑ W CapCut Candy Crush DeepSeek Word ☐ Saga 啡 AcadAl ل TikTokarrow_forwardRefer to the figure below. Given: L = 7 m, y = 16.7 kN/m², and ø' = 30°. L L3 ση Sand γ $' D T LA L σε σε IN P Sand 1. Calculate the theoretical depth of penetration, D. (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) D= m 2. Calculate the maximum moment. (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) Mmax kN-m/marrow_forwardWhy is it important for construction project managers to be flexible when dealing with the many variable factors that pop up in a project?arrow_forward
- What are some reasons for why a company would accelerate a construction project?arrow_forwardFor the design of a shallow foundation, given the following: Soil: ' = 20° c' = 52 kN/m² Unit weight, y = 15 kN/m³ Modulus of elasticity, E, = 1400 kN/m² Poisson's ratio, μs = 0.35 Foundation: L=2m B=1m Df = 1 m Calculate the ultimate bearing capacity. Use the equation: 1 - qu = c' NcFcs Fcd Fcc +qNqFqsFqdFqc + ½√BN√Fãs F√dƑxc 2 For '=20°, Nc = 14.83, N₁ = 6.4, and N₁ = 5.39. (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) qu = kN/m²arrow_forwardA 2.0 m wide strip foundation carries a wall load of 350 kN/m in a clayey soil where y = 15 kN/m³, c' = 5.0 kN/m² and ' = 23°. The foundation depth is 1.5 m. For ' = 23°: Nc = 18.05; N₁ = 8.66; Ny = = = 8.20. Determine the factor of safety using the equation below. qu= c' NcFcs FcdFci+qNqFqsFq 1 F + gd. 'qi 2 ·BN√· FF γί Ysyd F (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) FS =arrow_forward
- 2P -1.8 m- -1.8 m- -B Wo P -1.8 m- Carrow_forwardPart F: Progressive activity week 7 Q.F1 Pick the rural location of a project site in Victoria, and its catchment area-not bigger than 25 sqkm, and given the below information, determine the rainfall intensity for ARI 5, 50, 100 year storm event. Show all the details of the procedure. Each student must propose different length of streams and elevations. Use fig below as a sample only. Pt. E-nt 950 200 P: D-40, PC-92.0 300m 300m 000m PL.-02.0 500m HI-MAGO PLA-M 91.00 To be deemed satisfactory the solution must include: Q.F1.1.Choice of catchment location Q.F1.2. A sketch displaying length of stream and elevation Q.F1.3. Catchment's IFD obtained from the Buro of Metheorology for specified ARI Q.F1.4.Calculation of the time of concentration-this must include a detailed determination of the equivalent slope. Q.F1.5.Use must be made of the Bransby-Williams method for the determination of the equivalent slope. Q.F1.6.The graphical display of the estimation of intensities for ARI 5,50, 100…arrow_forwardI need help finding: -The axial deflection pipe in inches. -The lateral deflection of the beam in inches -The total deflection of the beam like structure in inches ?arrow_forward
- A 2.0 m wide strip foundation carries a wall load of 350 kN/m in a clayey soil where y = 17 kN/m³, c' = 5.0 kN/m² and 23°. The foundation depth is 1.5 m. For o' = 23°: Nc = 18.05; N = 8.66; N = 8.20. Determine the factor of safety using the equation below. 1 qu = c' NcFcs Fed Fci +qNqFqs FqdFqi + ½ BN F√s 1 2 (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) s Fyd Fi FS =arrow_forward1.2 m BX B 70 kN.m y = 16 kN/m³ c' = 0 6'-30° Water table Ysat 19 kN/m³ c' 0 &' = 30° A square foundation is shown in the figure above. Use FS = 6, and determine the size of the foundation. Use the Prakash and Saran theory (see equation and figures below). Suppose that F = 450 kN. Qu = BL BL[c′Nc(e)Fcs(e) + qNg(e)Fcs(e) + · 1 YBN(e) F 2 7(e) Fra(e)] (Enter your answer to two significant figures.) B: m Na(e) 60 40- 20- e/B=0 0.1 0.2 0.3 .0.4 0 0 10 20 30 40 Friction angle, ' (deg) Figure 1 Variation of Na(e) with o' Ny(e) 60 40 20 e/B=0 0.3 0.1 0.2 0.4 0 0 10 20 30 40 Friction angle, ' (deg) Figure 2 Variation of Nye) with o'arrow_forwardK/S 46. (O المهمات الجديدة 0 المنتهية 12 المغـ ۱۱:۰۹ search ليس لديك اي مهمات ☐ ○ ☑arrow_forward
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage,
Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage,





