
(a)
Interpretation:
The validation corresponding to the fact that aspartame is chiral is to be stated. If aspartame is chiral, then the possible number of stereoisomers for aspartame is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
A compound that contains a chiral carbon is known as chiral compound. Carbon atom that contains all the four different atoms or group of atoms attached to it is referred as the chiral atom. This carbon is also known as stereocenter.
The possible number of stereoisomers is calculated by the expression
Answer to Problem 10P
Aspartame is a chiral compound. The possible number of stereoisomers for aspartame is
Explanation of Solution
The aspartame is a chiral compound. The structure of aspartame which contains chiral carbon atoms is shown as,
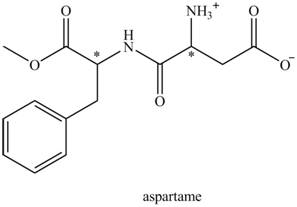
There are two chiral carbon atoms present in aspartame which are marked with asterisk sign. In the structure of aspartame, one carbon atom is directly bonded to
Thus, the possible number of stereoisomers in aspartame is,
Where,
- is the number of stereocenter.
Thus, the possible stereoisomers of aspartame is
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of each functional group present in aspartame is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as
Answer to Problem 10P
The name of each functional group present in aspartame is ester group
Explanation of Solution
According to the structure of aspartame shown in Figure 1, there are four functional groups present in the structure of aspartame.
The name of all the functional group of aspartame is ester group
(c)
Interpretation:
The net charge on aspartame molecule in an aqueous solution at
Concept Introduction:
The negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration of the solution is known as
Answer to Problem 10P
The net charge on aspartame molecule in an aqueous solution at
Explanation of Solution
In an aqueous solution of
Hence, there is no change of charge takes place in aspartame and it possesses zero net charge.
(d)
Interpretation:
The validation corresponding to the fact that aspartame is whether soluble in water or not is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
According to the concept of solubility, it is mentioned that like dissolves like. Generally, polar compound can only be dissolved in polar solvents and non-polar or weakly polar compounds can only be dissolved in non-polar solvents or weakly polar solvents.
Answer to Problem 10P
Aspartame is soluble in water.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure of asparatame is present in zwitterion form which suggests that it is a polar molecule. According to the concept of like dissolves like, aspartame is soluble in water because water is also a polar molecule.
(e)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
Concept Introduction:
An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as functional groups. The functional group is the most reactive part present in the molecule. The main functional groups are
The addition of water molecule to the compound is known as hydrolysis that compound.
Answer to Problem 10P
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
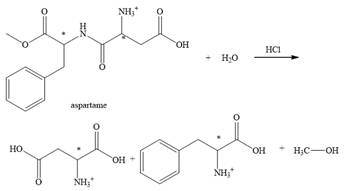
Explanation of Solution
The hydrolysis of aspartame in the presence of aqueous
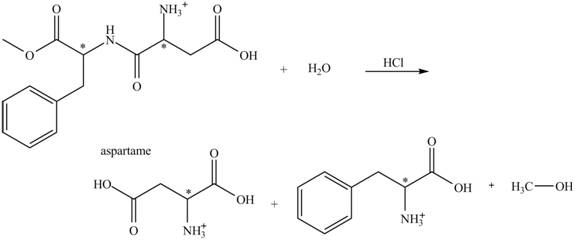
Figure 2.
The reaction of aspartame with aqueous
(f)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
Concept Introduction:
An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as functional groups. The functional group is the most reactive part present in the molecule. The main functional groups are
The addition of water molecule to the compound is known as hydrolysis that compound.
Answer to Problem 10P
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
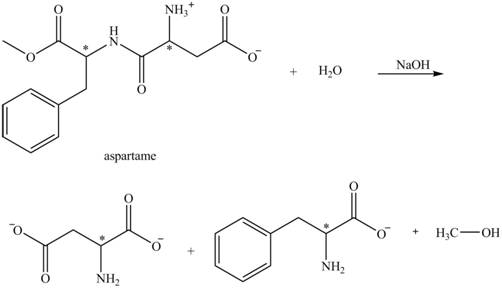
Explanation of Solution
The hydrolysis of aspartame in the presence of aqueous
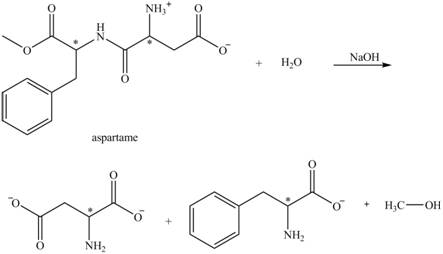
Figure 3.
The reaction of aspartame with aqueous
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
EP INTRO.TO GENERAL,ORGANIC...-OWL ACCE
- 8 00 6 = 10 10 Decide whether each of the molecules in the table below is stable, in the exact form in which it is drawn, at pH = 11. If you decide at least one molecule is not stable, then redraw one of the unstable molecules in its stable form below the table. (If more than unstable, you can pick any of them to redraw.) Check OH stable HO stable Ounstable unstable O OH stable unstable OH 80 F6 F5 stable Ounstable X Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C ཀྭ་ A F7 매 F8 F9 4 F10arrow_forwardJust try completing it and it should be straightforward according to the professor and TAs.arrow_forwardThe grading is not on correctness, so if you can just get to the correct answers without perfectionism that would be great. They care about the steps and reasoning and that you did something. I asked for an extension, but was denied the extension.arrow_forward
- Show your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers. Something that looks reasonable or correct would be sufficient. If you can get many of them correct that would be great!arrow_forwardShow your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers. Something that looks reasonable or correct would be sufficient. If you can get many of them correct that would be great!arrow_forwardTake a look at the following molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. (You can click the other tab to see the molecule without the colored regions.) with colored region plain 0= CH2-0-C-(CH2)16-CH3 =0 CH-O-C (CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)5-CH3 D CH3 | + OMPLO CH3-N-CH2-CH2-0-P-O-CH2 B CH3 A Try again * 000 Ar 8 0 ?arrow_forward
- Show your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers.arrow_forwardShow your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers.arrow_forward= 1 = 2 3 4 5 6 ✓ 7 8 ✓ 9 =10 Devise a synthesis to prepare the product from the given starting material. Complete the following reaction scheme. Part 1 of 3 -Br Draw the structure for compound A. Check Step 1 Step 2 A Click and drag to start drawing a structure. × ↓m + OH Save For Later S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privaarrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reduction: 田 Check AP + + H2 Lindlar catalyst Click an drawing 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rigarrow_forward70 Suppose the molecule below is in acidic aqueous solution. Is keto-enol tautomerization possible? • If a keto-enol tautomerization is possible, draw the mechanism for it. Be sure any extra reagents you add to the left-hand sid available in this solution. • If a keto-enol tautomerization is not possible, check the box under the drawing area. : ☐ Add/Remove step Click and drag to st drawing a structure Check Save For Late. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardThe problem will not be graded for correctness, but you have to get a reasonable answer something that is either correct or very closer to the correct answer. The instructor professor wants us to do something that shows the answer but everything does not have to be correct. Ideally, yes, it has to be correct. Give it your best shot.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co


