
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics Study (Book and Pearson eText)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780134116990
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17.3, Problem 28P
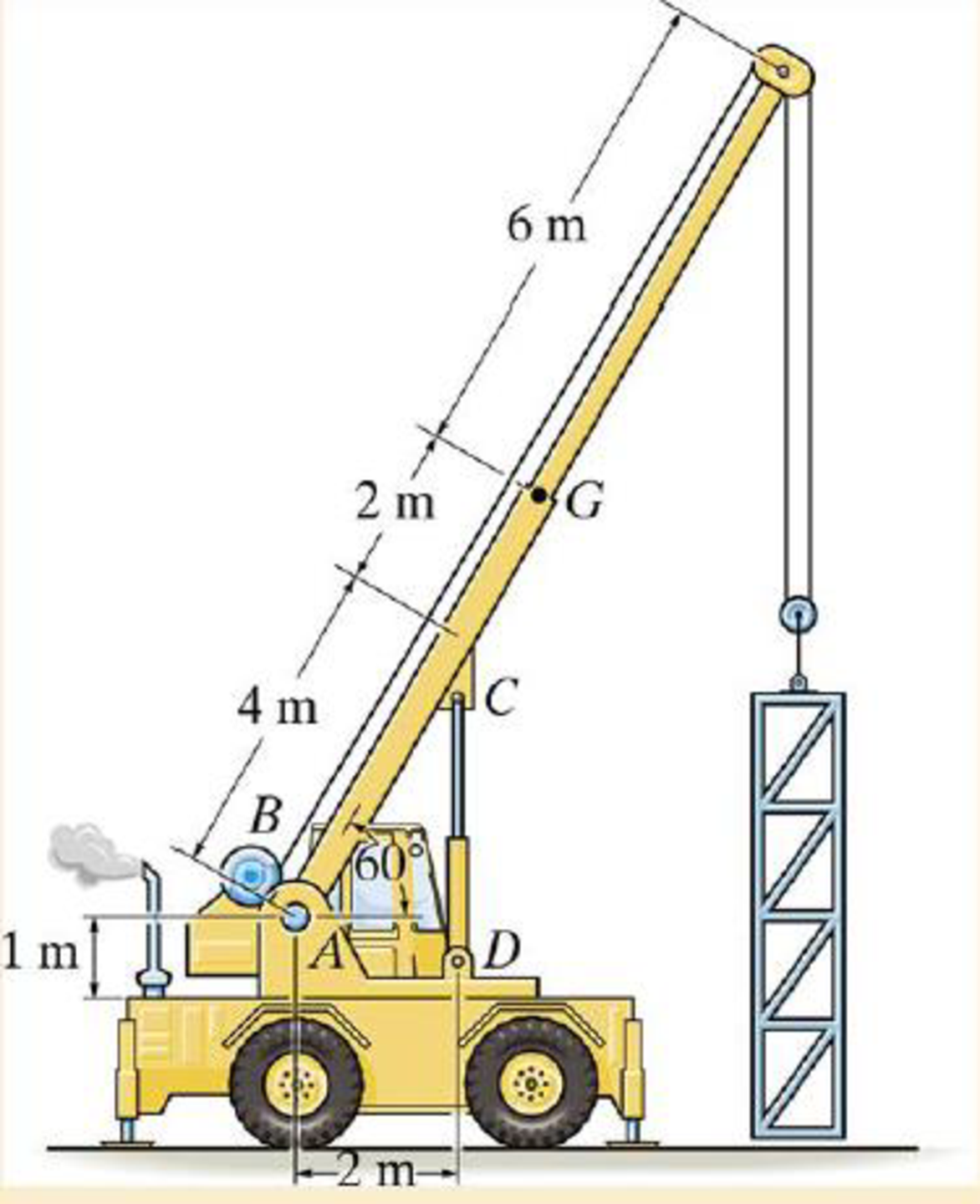
If the winch at B draws in the cable with an acceleration of 2 m/s2, determine the compressive force in the hydraulic cylinder needed to support the boom. The boom has a mass of 2 Mg and mass center at G.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The fallowing question is from a reeds book on applied heat i am studying. Although the answer is provided, im struggling to understand the whole answer and the formulas and the steps theyre using. Also where some ov the values such as Hg and Hf come from in part i for example. Please explain step per step in detail thanks
In an NH, refrigerator, the ammonia leaves the evaporatorand enters the cornpressor as dry saturated vapour at 2.68 bar,it leaves the compressor and enters the condenser at 8.57 bar with50" of superheat. it is condensed at constant pressure and leavesthe condenser as saturated liquid. If the rate of flow of the refrigerantthrough the circuit is 0.45 kglmin calculate
(i) the compressorpower,
(ii) the heat rejected to the condenser cooling water in kJ/s,an (iii) the refrigerating effect in kJ/s.
From tables page 12, NH,:2.68 bar, hg= 1430.58.57 bar, hf = 275.1 h supht 50" = 1597.2Mass flow of refrigerant--- - - 0.0075 kgls 60Enthalpy gain per kg of refrigerant in…
state the formulas for calculating work done by gas
Exercises
Find the solution of the following Differential Equations
1) y" + y = 3x²
3)
"+2y+3y=27x
5) y"+y=6sin(x)
7) y"+4y+4y = 18 cosh(x)
9) (4)-5y"+4y = 10 cos(x)
11) y"+y=x²+x
13) y"-2y+y=e*
15) y+2y"-y'-2y=1-4x³
2) y"+2y' + y = x²
4) "+y=-30 sin(4x)
6) y"+4y+3y=sin(x)+2 cos(x)
8) y"-2y+2y= 2e* cos(x)
10) y+y-2y=3e*
12) y"-y=e*
14) y"+y+y=x+4x³ +12x²
16) y"-2y+2y=2e* cos(x)
Chapter 17 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics Study (Book and Pearson eText)
Ch. 17.1 - The rod's density end cross-sectional area. A are...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the mass of the cylinder end its moment...Ch. 17.1 - The nag has a mass m.Ch. 17.1 - Determine the radius of gyration kx. The density...Ch. 17.1 - The specific weight of the material is = 380...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia Iz and express the...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia Ix and express the...Ch. 17.1 - Defending the moment of inertia Iy and express the...Ch. 17.1 - Express the result in terms of the mass m of the...Ch. 17.1 - Determine me radius of gyration of the pendulum...
Ch. 17.1 - Determine the mass moment of inertia of the...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia of the solid steel...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the wheels moment of inertia about an...Ch. 17.1 - If the large ring, small ring and each of the...Ch. 17.1 - The thin plate has a hole in its center its...Ch. 17.1 - The material has a mass per unit area of 20 kg/m2.Ch. 17.1 - The block has a mass of 3 kg and the semicylinder...Ch. 17.1 - The block has a mass of 3 kg and the semicylinder...Ch. 17.1 - The material has a specific weight = 90 lb/ft3.Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 20PCh. 17.1 - Determine the location y of the center of mass G...Ch. 17.1 - The material is steel having a density of = 7.85...Ch. 17.1 - The material is steel having a density of = 7.85...Ch. 17.3 - Draw the free-body and kinetic diagrams of the...Ch. 17.3 - Draw the free-body and kinetic diagrams of the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the acceleration of the can and the...Ch. 17.3 - If the 80-kg cabinet is allowed to roll down the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the maximum acceleration of the frame...Ch. 17.3 - Also what is the corresponding normal reaction on...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the tension developed in the rods and...Ch. 17.3 - If it is subjected to a couple moment M = 450 N ...Ch. 17.3 - Determine how far the door moves in 25, starting...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the constant force F that must be...Ch. 17.3 - Initially at take-off the engines provide a thrust...Ch. 17.3 - If it starts from rest it causes the rear wheels...Ch. 17.3 - If the winch at B draws in the cable with an...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the greatest acceleration of the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the internal axial, shear, and...Ch. 17.3 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the reactions at both the wheels at A...Ch. 17.3 - Also, what is the acceleration of the cart? The...Ch. 17.3 - If it is subjected to a horizontal force of P =...Ch. 17.3 - Determine its initial acceleration if a man pushes...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the initial acceleration of a desk when...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 17.3 - If it is released from rest, determine the...Ch. 17.3 - It is carried on a truck as shown. Determine the...Ch. 17.3 - It is carried on a truck as shown. If the truck...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the smallest acceleration that will...Ch. 17.3 - The coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.3 - If the collar is given a constant acceleration of...Ch. 17.3 - If it is supported by the cable AB and hinge at C,...Ch. 17.3 - If it is supported by the cable AB and hinge at C,...Ch. 17.3 - If the acceleration is a = 20 ft/s2, determine the...Ch. 17.3 - If h = 3 ft, determine the snowmobiles maximum...Ch. 17.3 - If the carts mass is 30 kg and it is subjected to...Ch. 17.3 - The uniform rod BC has a mass of 15 kg.Ch. 17.3 - If the acceleration of the truck is at = 0.5 m/s2,...Ch. 17.3 - If the angle = 30, determine the acceleration of...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the largest initial angular acceleration...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the initial friction and normal force of...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the largest initial angular acceleration...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the normal force NE, shear force VE, and...Ch. 17.4 - If the wheel starts from rest determine its...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the angular velocity of the disk when t...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the tangential and normal components of...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the tangential and normal components or...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 17.4 - If the rod has a counterclockwise angular velocity...Ch. 17.4 - If the wheel is subjected to a moment M = (5t) N ...Ch. 17.4 - Determine its initial angular acceleration and the...Ch. 17.4 - If it is released from rest when = 0. determine...Ch. 17.4 - If it is released from rest in the position shown,...Ch. 17.4 - The reel rests on rollers at A and B and has a...Ch. 17.4 - The spring has a stiffness k = 5 lb ft/rad, so...Ch. 17.4 - The spring has a stiffness k = 5 lb ft/rad, so...Ch. 17.4 - If a force of F=(142)N, where is in radians, is...Ch. 17.4 - If no slipping occurs between them determine the...Ch. 17.4 - Show that IG may be eliminated by moving the...Ch. 17.4 - Treat the beam as a uniform slender rod.Ch. 17.4 - It consists of a 100-kg steel plate AC and a...Ch. 17.4 - It is pin supported at both ends by two brackets...Ch. 17.4 - It is pin supported at both ends by two brackets...Ch. 17.4 - Determine its angular velocity when t = 2 s...Ch. 17.4 - If it is placed on the ground for which the...Ch. 17.4 - Compute the time needed to unravel 5 m of cable...Ch. 17.4 - If the rotor always maintains a constant clockwise...Ch. 17.4 - It is originally spinning at = 40 rad/s. If it is...Ch. 17.4 - It is pin supported at both ends by two brackets...Ch. 17.4 - Disk E has a weight of 60 lb and is initially at...Ch. 17.4 - If the cylinders are released from rest, determine...Ch. 17.4 - If the pulley can be treated as a disk of mass 3...Ch. 17.4 - If the pulley can be treated as a disk of mass M,...Ch. 17.4 - Assume that the board is uniform and rigid, and...Ch. 17.4 - At the instant the rolor is horizontal it has an...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the initial tending moment at the fixed...Ch. 17.4 - Movement is controlled by the electromagnet E,...Ch. 17.4 - If it is rotating in the vertical plane at a...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the angular acceleration of the rod and...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 17.5 - If the powder burns at a constant rate of 20 g/s...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the acceleration of the bars mass center...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the acceleration of its mass center and...Ch. 17.5 - When the wheel is subjected to the couple moment,...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the angular acceleration of the sphere...Ch. 17.5 - If the couple moment is applied to the spool and...Ch. 17.5 - If the rod is released from rest at = 0,...Ch. 17.5 - rolls without slipping, show that when moments are...Ch. 17.5 - If it is initially at rest and is subjected to a...Ch. 17.5 - The uniform 150-lb beam is initially at rest when...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - Solve Prob.17-96 if the cord and force P = 50 N...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - If a horizontal force of F = 80 N is applied to...Ch. 17.5 - If slipping does not occur, determine the rings...Ch. 17.5 - Neglect the thickness of the ring.Ch. 17.5 - Using a collar of negligible mass, its end A is...Ch. 17.5 - If the pin is connected to a track which is giver...Ch. 17.5 - Assume the roller to be a uniform cylinder and...Ch. 17.5 - Also, find the angular acceleration of the roller....Ch. 17.5 - Determine the bars initial angular acceleration...Ch. 17.5 - Solve Prob.17-106 if the roller is removed and the...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficient of static friction at A is s, =...Ch. 17.5 - If the truck has an acceleration of 3 m/s2...Ch. 17.5 - A cord is wrapped around the periphery of the disk...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficient of static friction at A is s =...Ch. 17.5 - At this instant the center of gravity of the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the initial angular acceleration of the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the time before it starts to roll...Ch. 17.5 - If they are released from rest determine the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the normal force which the path exerts...Ch. 17.5 - If it is originally at rest while being supported...Ch. 17.5 - If the pin support at A suddenly fails, determine...Ch. 17.5 - Determine its angular acceleration.Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the normal reactions at each of the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the internal axial force Ex, shear force...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the maximum acceleration it can have if...Ch. 17.5 - The roil rest against a wall for which the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the magnitude of force F and the initial...Ch. 17.5 - Compute the reaction at the pin O just after the...Ch. 17.5 - if the coefficient of kinetic friction at the...Ch. 17.5 - The coefficient of kinetic friction is A = 0.3.
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The state of stress at a point is σ = -4.00 kpsi, σy = 16.00 kpsi, σ = -14.00 kpsi, Try = 11.00 kpsi, Tyz = 8.000 kpsi, and T = -14.00 kpsi. Determine the principal stresses. The principal normal stress σ₁ is determined to be [ The principal normal stress σ2 is determined to be [ The principal normal stress σ3 is determined to be kpsi. kpsi. The principal shear stress 71/2 is determined to be [ The principal shear stress 7½ is determined to be [ The principal shear stress T₁/, is determined to be [ kpsi. kpsi. kpsi. kpsi.arrow_forwardRepeat Problem 28, except using a shaft that is rotatingand transmitting a torque of 150 N * m from the left bearing to the middle of the shaft. Also, there is a profile keyseat at the middle under the load. (I want to understand this problem)arrow_forwardProb 2. The material distorts into the dashed position shown. Determine the average normal strains &x, Ey and the shear strain Yxy at A, and the average normal strain along line BE. 50 mm B 200 mm 15 mm 30 mm D ΕΙ 50 mm x A 150 mm Farrow_forward
- Prob 3. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the shear strain, Yxy, at A. Prob 4. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the average normal strain & along the x axis. Prob 5. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the average normal strain &x along the x' axis. x' 45° 800 mm 45° 45% 800 mm 5 mmarrow_forwardAn airplane lands on the straight runaway, originally travelling at 110 ft/s when s = 0. If it is subjected to the decelerations shown, determine the time t' needed to stop the plane and construct the s -t graph for the motion. draw a graph and show all work step by steparrow_forwarddny dn-1y dn-1u dn-24 +a1 + + Any = bi +b₂- + +bnu. dtn dtn-1 dtn-1 dtn-2 a) Let be a root of the characteristic equation 1 sn+a1sn- + +an = : 0. Show that if u(t) = 0, the differential equation has the solution y(t) = e\t. b) Let к be a zero of the polynomial b(s) = b₁s-1+b2sn−2+ Show that if the input is u(t) equation that is identically zero. = .. +bn. ekt, then there is a solution to the differentialarrow_forward
- B 60 ft WAB AB 30% : The crane's telescopic boom rotates with the angular velocity w = 0.06 rad/s and angular acceleration a = 0.07 rad/s². At the same instant, the boom is extending with a constant speed of 0.8 ft/s, measured relative to the boom. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of point B at this instant.arrow_forwardThe motion of peg P is constrained by the lemniscate curved slot in OB and by the slotted arm OA. (Figure 1) If OA rotates counterclockwise with a constant angular velocity of 0 = 3 rad/s, determine the magnitude of the velocity of peg P at 0 = 30°. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of peg P at 0 = 30°. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 0 (4 cos 2 0)m² B Aarrow_forward5: The structure shown was designed to support a30-kN load. It consists of a boom AB with a 30 x 50-mmrectangular cross section and a rod BC with a 20-mm-diametercircular cross section. The boom and the rod are connected bya pin at B and are supported by pins and brackets at A and C,respectively.1. Calculate the normal stress in boom AB and rod BC,indicate if in tension or compression.2. Calculate the shear stress of pins at A, B and C.3. Calculate the bearing stresses at A in member AB,and in the bracket.arrow_forward
- 4: The boom AC is a 4-in. square steel tube with a wallthickness of 0.25 in. The boom is supported by the 0.5-in.-diameter pinat A, and the 0.375-in.-diameter cable BC. The working stresses are 25ksi for the cable, 18 ksi for the boom, and 13.6 ksi for shear in the pin.Neglect the weight of the boom.1. Calculate the maximum value of P (kips) based on boom compression and the maximum value of P (kips) based on tension in the cable.2. Calculate the maximum value of P (kips) based on shear in pin.arrow_forward3: A steel strut S serving as a brace for a boat hoist transmits a compressive force P = 54 kN to the deck of a pier as shown in Fig. STR-08. The strut has a hollow square cross section with a wall thickness t =12mm and the angle θ between the strut and the horizontal is 40°. A pin through the strut transmits the compressive force from the strut to two gusset plates G that are welded to the base plate B. Four anchor bolts fasten the base plate to the deck. The diameter of the pin is 20mm, the thickness of the gusset plates is 16mm, the thickness of the base plate is 8mm, and the diameter of the anchor bolts is 12mm. Disregard any friction between the base plate and the deck.1. Determine the shear stress in the pin, in MPa and the shear stress in the anchor bolts, in MPa.2. Determine the bearing stress in the strut holes, in MPa.arrow_forward1. In the figure, the beam, W410x67, with 9 mm web thicknesssubjects the girder, W530x109 with 12 mm web thickness to a shear load,P (kN). 2L – 90 mm × 90 mm × 6 mm with bolts frame the beam to thegirder.Given: S1 = S2 = S5 = 40 mm; S3 = 75 mm; S4 = 110 mmAllowable Stresses are as follows:Bolt shear stress, Fv = 125 MPaBolt bearing stress, Fp = 510 MPa1. Determine the allowable load, P (kN), based on the shearcapacity of the 4 – 25 mm diameter bolts (4 – d1) and calculate the allowable load, P (kN), based on bolt bearing stress on the web of the beam.2. If P = 450 kN, determine the minimum diameter (mm) of 4 – d1based on allowable bolt shear stress and bearing stress of thebeam web.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY