
Concept explainers
a)
Find the angular velocity of the bar after the impact.
a)
Answer to Problem 17.130P
The angular velocity of the bar after the impact is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight
The radius
The weight
The length
The angular velocity
The velocity
Calculation:
Consider G is the mass center of rod AB.
Find the mass
Substitute 2 lb for
Find the moment of inertia
Substitute
Consider C be the mass center of the sphere.
Find the mass of the sphere
Substitute 3 lb for
Find the moment of inertia
Substitute
The rod and sphere have same angular velocity
Sketch the geometry of the sphere and the uniform rod as shown in Figure (1).
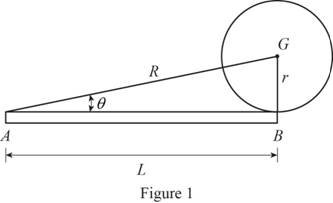
Refer Figure (1),
Find the distance R.
Substitute 10 in. for L and 3 in. for r.
Find the angle
Substitute 10 in. for L and 3 in. for r.
Find the velocity
Substitute 10 in. for L and
Write the velocity
Write the velocity
Consider the conservation of momentum principle.
Sketch the impulse and momentum diagram of the system as shown in Figure (2).
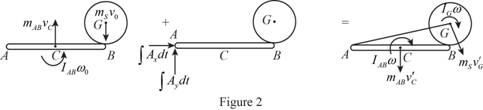
Refer Figure (2).
Take moment about A (positive sign in clockwise direction).
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the angular velocity of the bar after the impact is
b)
Find the components of the reactions at A.
b)
Answer to Problem 17.130P
The horizontal component of the reactions at A is
The vertical component of the reactions at A is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Find the normal acceleration
Substitute 10 in. for L and
Write the equation of tangential acceleration
Here,
Substitute 10 in. for L.
Find the normal acceleration
Substitute 0.8700 ft for R and
Write the equation of tangential acceleration
Substitute 0.8700 ft for R.
Sketch the free body diagram of the uniform rod and sphere as shown in Figure (1).
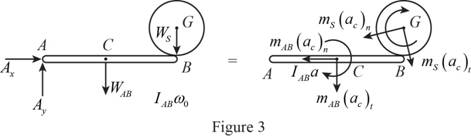
Refer Figure (3).
Take moment about A (positive sign in clockwise direction).
Substitute
Substitute 2 lb for
Find the tangential acceleration
Substitute
Find the tangential acceleration
Substitute
Refer Figure (3),
Consider the horizontal component forces.
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the horizontal component of the reactions at A is
Consider vertical components of forces.
Here,
Substitute 2 lb for
Thus, the vertical component of the reactions at A is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
- Correct answers are written below. Detailed and correct solution only with fbd. I will upvote. 1: A 3 m alloy shaft fixed at one end has a torsional shearing stress capacity of 55 MPa. Due to improper fabrication, its cross-sectionalarea has become irregularly shaped. Its effective polar moment of inertia has become 2 x10-7 m4, and the maximum torque stress acts at 7.5 cm fromthe center of the shaft.[1]: If the shaft is to be replaced by a properly manufactured solid circular shaft that has a maximumshearing stress capacity of 70 MN/m2, what is the minimum diameter required so it can withstand the sameload? [2]: Calculate the thickness of a hollow circular shaft with the same outside diameter calculated initem [1] that can carry the same load. Limit the maximum shearing stress of the hollow circular shaft to0.09 GPa.Determine the angle of twist on the free end of the shaft. Use G = 150 x103 GPa. [3]: Use the solidcircular shaft from [1] and use the hollow circular shaft from [2].…arrow_forwardPlease can you assist me with the attached question. Many thanks.arrow_forwardPlease can you assist me with the attached question. Many thanks.arrow_forward
- Please can you assist me with the attached question. Many thanks.arrow_forwardIn using the bolt cutter shown, a worker applies two forces P to the handles. If the magnitude ofP is 500 N, determine the magnitude of the forces exerted by the cutter on the boltarrow_forwardArterioles bifurcate (i.e., split) into capillaries in the circulatory system. Blood flows at a velocity of 20 cm/s through an arteriole with a diameter of 0.20 cm. This vessel bifurcates into two vessels: one with a diameter of 0.17 cm and a blood flow velocity of 18 cm/sec, and one with a diameter of 0.15 cm. Each of these two vessels splits again. The 0.17-cm diameter vessel splits into two vessels, each with a diameter of 0.15 cm. The 0.15-cm diameter vessel splits into two vessels, each with a diameter of 0.12 cm. Determine the mass flow rate and velocity of blood in each of the four vessels at the end of the arteriole bifurcations. You may need to set up several systems, each with a different system boundary, in order to solve this problem.arrow_forward
- Suppose that a steel of eutectoid composition is cooled to 675°C (1250°F) from 760°C (1400°F) in less than 0.5 s and held at this temperature. (a) How long will it take for the austenite-topearlite reaction to go to 50% completion? To 100% completion? (b) Estimate the hardness of the alloy that has completely transformed to pearlite.arrow_forwardProblem 2: Determine the components of the reaction at point B (Please use paper sheet + FBD ,don't use chatgpt) MECHANICAL ENGGarrow_forwardARL040_AE_Kn_2of3... Dor Question 4. A two-throw crankshaft has masses distributed as shown: RAH 90 rpm A TRAV B Re Rev M₁ = 15kg; M₂ = 12kg L = 950mm; 1, 350mm; 1₁ = 600mm; 0₁ = 90°; 02=0°; r₁ = 300mm; r250mm The crankshaft is to be balanced by attaching masses at radii of 300 mm and rotating in planes 150 mm outside the planes of number one and number two cranks. Determine the magnitude and angular position of the balance masses. Answer 4.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





