
(a)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Concept introduction: Friedel-Crafts alkylation permits the synthesis of alkylated products by the reaction of arenes with alkyl chlorides in the presence of aluminium chloride (Lewis acid). This alkylation reaction comes under the category of electrophilic aromatic substitution.
(a)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
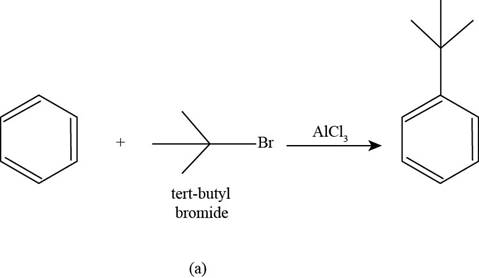
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with
(b)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Concept introduction: Friedel-Crafts alkylation permits the synthesis of alkylated products by the reaction of arenes with alkyl chlorides in the presence of aluminium chloride (Lewis acid). This alkylation reaction comes under the category of electrophilic aromatic substitution.
(b)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
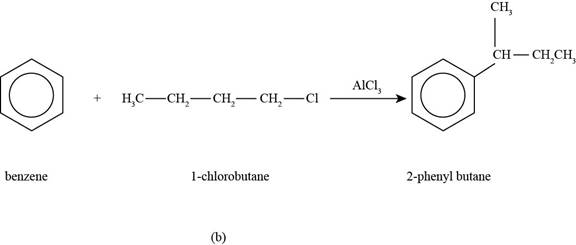
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with
(c)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutyl alcohol in the presence of
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutyl alcohol in the presence of
Concept introduction: Friedel-Crafts alkylation permits the synthesis of alkylated products by the reaction of arenes with alcohol in the presence of
(c)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutyl alcohol in the presence of
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutyl alcohol in the presence of
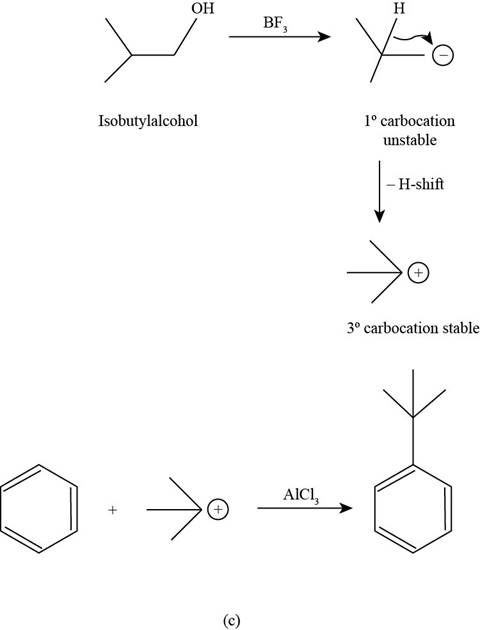
Figure
In the above reaction, the primary carbocation that is generated by the protonation of isobutyl alcohol by
In the second step, this electrophilic carbocation reacts with benzene in the presence of
(d)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with bromine in the presence of a nail.
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with bromine in the presence of a nail is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The reaction that includes the addition of one or more bromine atoms in a compound is known as bromination reaction. Bromination reaction is a type of halogenation reaction.
(d)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with bromine in the presence of a nail is shown as follows.
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with bromine in the presence of a nail is shown in Figure
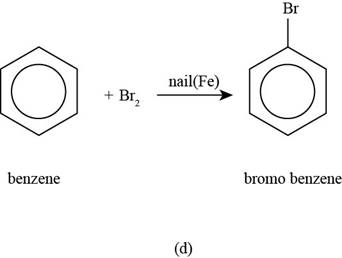
Figure
In the above reaction, bromination of benzene ring occurs to form bromobenzene as the desired product.
(e)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutylene in the presence of
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutylene in the presence of
Concept introduction: Friedel-Crafts alkylation permits the synthesis of alkylated products by the reaction of arenes with
(e)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutylene in the presence of
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with isobutylene in the presence of
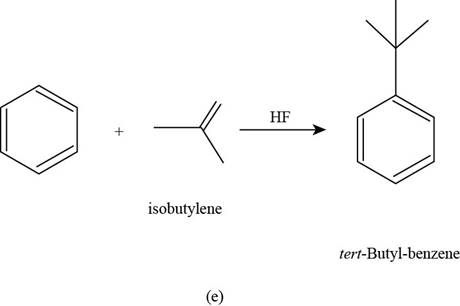
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with isobutylene in the presence of
(f)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with fuming sulphuric acid.
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with fuming sulphuric acid is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The process of attaching
(f)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with fuming sulphuric acid is shown as follows.
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with fuming sulphuric acid is shown in Figure
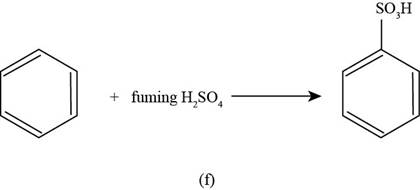
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with fuming sulphuric acid to form as the desired sulfonated product.
(g)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Concept introduction: Friedel-Crafts alkylation permits the synthesis of alkylated products by the reaction of arenes with alkyl chlorides in the presence of aluminium chloride (Lewis acid). This alkylation reaction comes under the category of electrophilic aromatic substitution.
(g)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
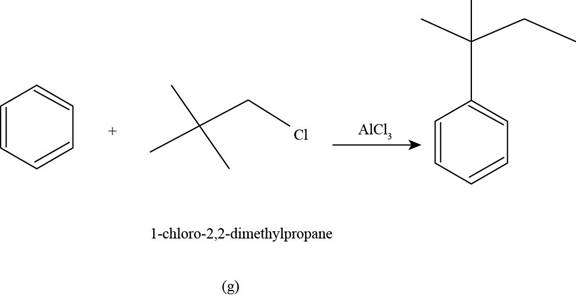
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with
(h)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of
Concept introduction: Friedel-Crafts alkylation permits the synthesis of alkylated products by the reaction of arenes with alkyl chlorides in the presence of aluminium chloride (Lewis acid). This alkylation reaction comes under the category of electrophilic aromatic substitution.
(h)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of
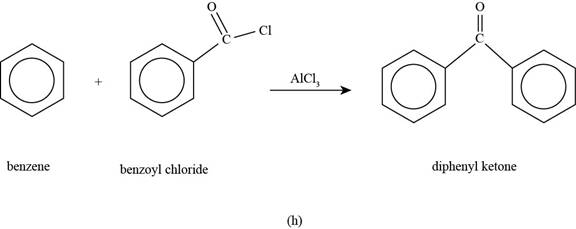
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with benzoyl chloride in the presence of
(i)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with iodine molecule in the presence of
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with iodine molecule in the presence of
Concept introduction: The reaction that includes the addition of one or more than one halogen atoms in a compound is known as halogenation reaction.
(i)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with iodine molecule in the presence of
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with iodine molecule in the presence of
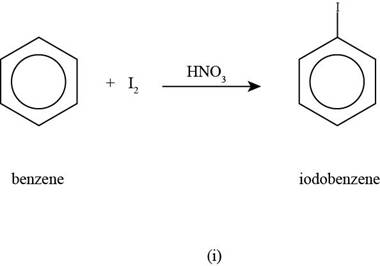
Figure
In the above halogenations reaction, benzene reacts with iodine molecule in the presence of
(j)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with nitric acid and sulphuric acid.
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with nitric acid and sulphuric acid is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The reaction that involves the addition of a nitro group on an alkyl or an aromatic compound in the presence of concentrated nitric acid and sulphuric acid is known as nitration reaction.
(j)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with nitric acid and sulphuric acid is shown as follows.
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene benzene with nitric acid and sulphuric acid is shown in Figure
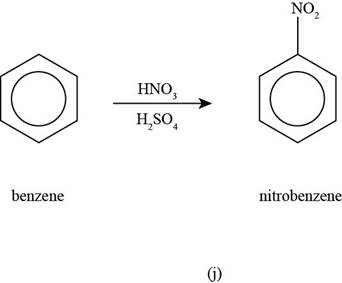
Figure
In the above nitration reaction, benzene reacts with concentrated nitric acid and sulphuric acid that forms nitrobenzene as the desired product.
(k)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with carbon monoxide in the presence of
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with carbon monoxide in the presence of
Concept introduction: The synthesis in which
(k)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with carbon monoxide in the presence of
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with carbon monoxide in the presence of
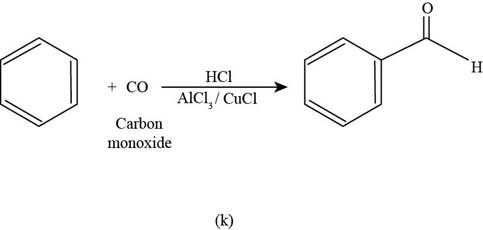
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with benzoyl carbon monoxide in the presence of
(l)
To determine: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Interpretation: The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Concept introduction: Friedel-Crafts acylation permits the synthesis of acylated products by the reaction of arenes with acyl chlorides in the presence of
(l)
Answer to Problem 17.50SP
The major product that is formed by reaction of benzene with
Explanation of Solution
The major product that is formed by reaction benzene with
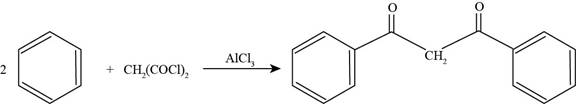
Figure
In the above reaction, benzene reacts with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
EP ORGANIC CHEMISTRY -MOD.MASTERING 18W
- What is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forward
- What would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





