
Concept explainers
Transferred-in costs, FIFO method. Refer to the information in Problem 17-43. Suppose that Spelling Sports uses the FIFO method instead of the weighted-average method. Assume that all other information, including the cost of beginning WIP, is unchanged.
- 1. Using the FIFO process-costing method, complete Problem 17-43.
Required
- 2. If you did Problem 17-43, explain any difference between the cost of work completed and transferred out and the cost of ending work in process in the stitching department under the weighted-average method and the FIFO method.
17-43 Transferred-in costs, weighted-average method. Spelling Sports, which produces basketballs, has two departments: cutting and stitching. Each department has one direct-cost category (direct materials) and one indirect-cost category (conversion costs). This problem focuses on the stitching department.
Basketballs that have undergone the cutting process are immediately transferred to the stitching department. Direct material is added when the stitching process is 70% complete. Conversion costs are added evenly during stitching operations. When those operations are done, the basketballs are immediately transferred to Finished Goods.
Spelling Sports uses the weighted-average method of
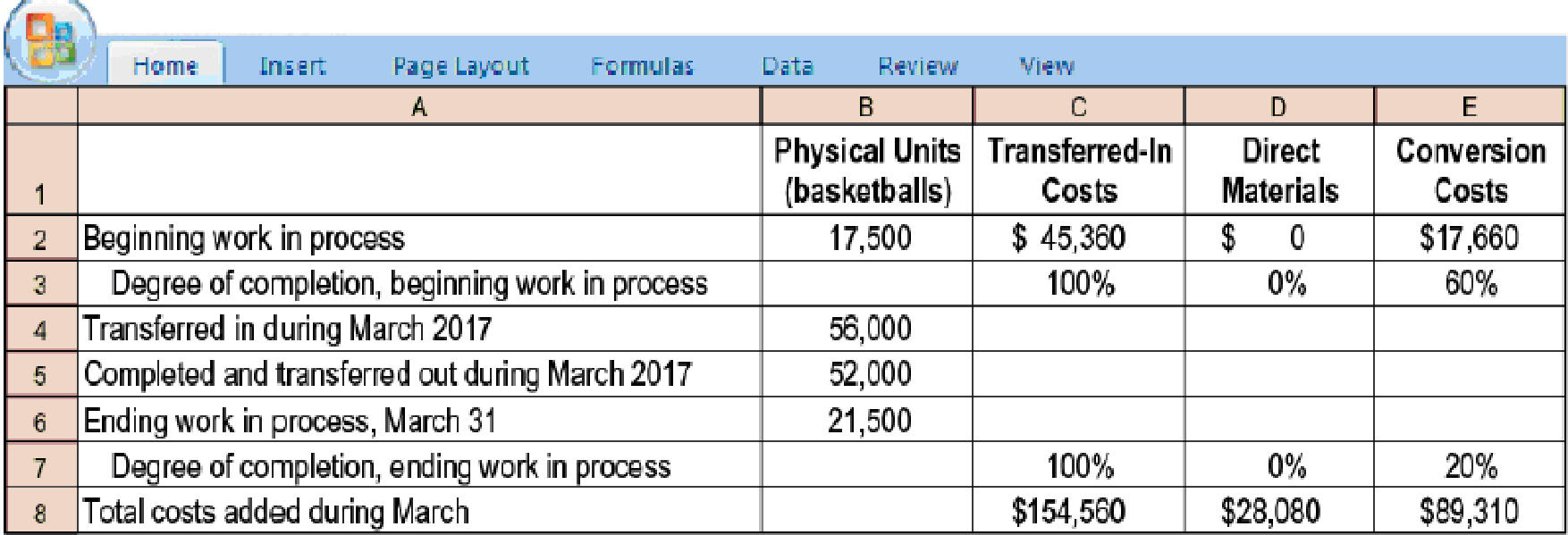
- 1. Summarize total stitching department costs for March 2017, and assign these costs to units completed (and transferred out) and to units in ending work in process.
Required
- 2. Prepare
journal entries for March transfers from the cutting department to the stitching department and from the stitching department to Finished Goods.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 17 Solutions
EBK HORNGREN'S COST ACCOUNTING
- Can you please give me true answer the general accounting question?arrow_forwardWhat is the amount of gross margin for this merchandise? General accountingarrow_forwardQuestion No. 14. (Financial Accounting): Suppose you sell a fixed asset for $153,000 when it's book value is $187,000. If your company's marginal tax rate is 42%, what will be the effect on cash flows of this sale (i.e., what will be the after-tax free cash flow of this sale)?arrow_forward
- Pasadena Candle Inc. budgeted production of 51,000 candles for the year. Each candle requires molding. Assume that 10 minutes are required to mold each candle. If molding labor costs $13.25 per hour, determine the direct labor cost budget for the year.arrow_forwardWhat is the net realizable value of account receivables?arrow_forwardProvide answer this financial accounting question please solvearrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning


