
(a)
Interpretation:
The principal organic compound that is expected when
Concept introduction:
The addition reaction of the
Answer to Problem 17.23AP
The principal organic compound that is formed when
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
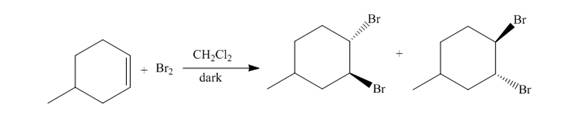
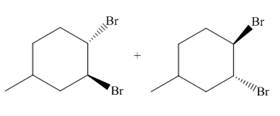
Figure 1
The addition of the bromine molecule on the double bond of the alkene takes place to give the dibromo product. The addition of bromine to the double bond is the anti-addition.
The principal organic compound that is formed when
(b)
Interpretation:
The principal organic compound that is expected when
Concept introduction:
The addition reactions of the alkene are very well known reactions. The electron density on the alkene double bond makes it nucleophilic. The alkene undergoes varieties of addition reaction via different mechanisms.
Answer to Problem 17.23AP
The principal organic compound that is formed when
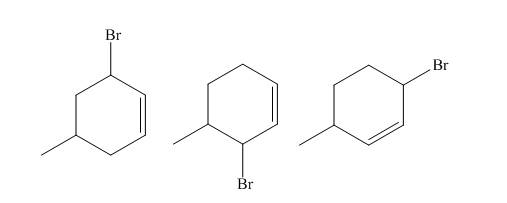
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
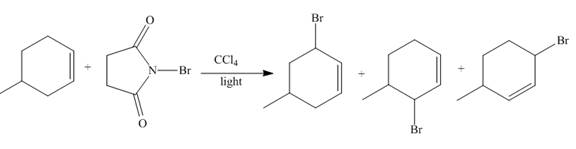
Figure 2
The reaction of an alkene with N-bromosuccinimide in the presence is the free-radical reaction. In this reaction, allylic bromination is observed instead of an addition to the alkene. The N-bromosuccinimide acts as radical initiator. This molecule breaks the
The principal organic compound that is formed when
(c)
Interpretation:
The principal organic compound that is expected when product(s) of part (b) undergo solvolysis in aqueous acetone is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The nucleophilic substitution reactions are the reactions in which a nucleophile attacks at the electrophilic carbon and eliminates another group. The
The
Answer to Problem 17.23AP
The principal organic compounds that are formed when product(s) of part (b) undergo solvolysis in aqueous acetone are shown below.
Explanation of Solution
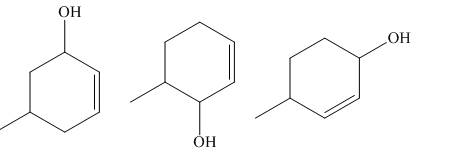
The products of part (b) are shown below.
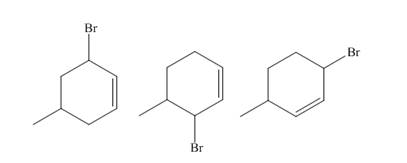
Figure 3
The reaction of product(s) of part (b) on solvolysis in aqueous acetone is shown below.
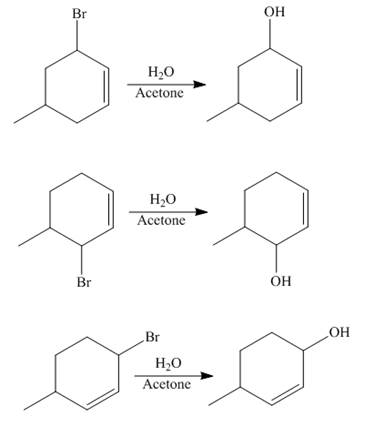
Figure 4
The nucleophilic substitution reaction takes place when solvolysis of products of part (b) is done. The bromine group is substituted by the hydroxyl group giving rise to the formation of an allylic alcohol.
The principal organic compound that is formed when product(s) of part (b) undergo solvolysis in aqueous acetone is shown in Figure 4.
(d)
Interpretation:
The principal organic compound that is expected when product(s) of part (b) are reacted with
Concept introduction:
The reaction of an
Answer to Problem 17.23AP
The principal organic compounds that are formed when product(s) of part (b) are reacted with
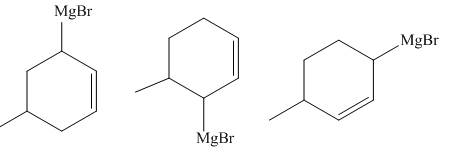
Explanation of Solution
The products of part (b) are shown below.

Figure 3
The reaction that occurs when product(s) of part (b) are reacted with
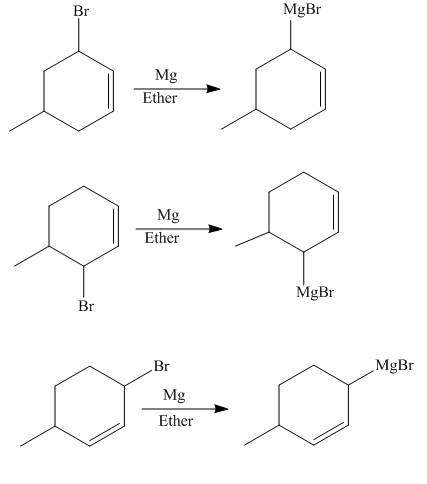
Figure 5
The allylic halide also undergoes the same kind of reactions as the alkyl halide with magnesium metal in dry ether. They also lead to the formation of Grignard reagent but this time with the allylic group.
The principal organic compounds that are formed when product(s) of part (b) are reacted with
(e)
Interpretation:
The principal organic compound that is expected when product(s) of part (d) are reacted with
Concept introduction:
The nucleophilic substitution reactions are the reactions in which a nucleophile attacks at the electrophilic carbon and eliminates another group. The rate of reaction depends upon the nucleophilicity and concentration of the nucleophile.
The
Answer to Problem 17.23AP
The principal organic compounds that are formed when product(s) of part (d) are reacted with
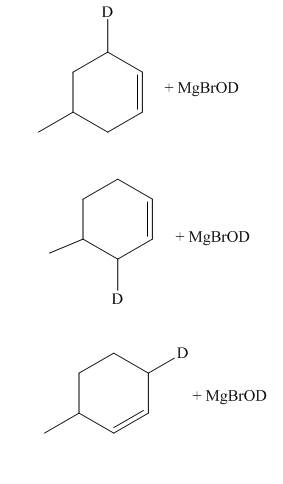
Explanation of Solution
The products of part (d) are shown below.

Figure 6
The reaction of product(s) of part (d) with
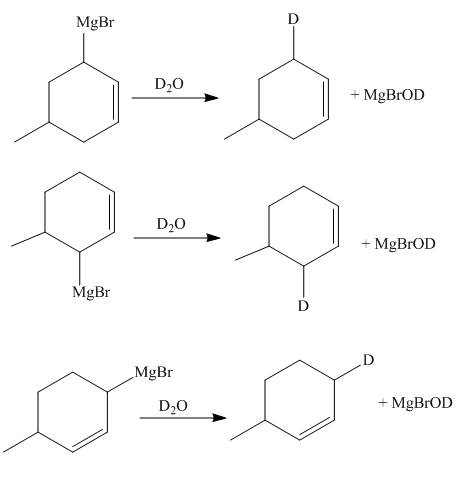
Figure 7
The Grignard reagents are highly reactive towards moisture. The carbon chain on the Grignard reagent gets the hydrogen in place of
The principal organic compounds that are formed when product(s) of part (d) are reacted with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- One liter of chlorine gas at 1 atm and 298 K reacts completely with 1.00 L of nitrogen gas and 2.00 L of oxygen gas at the same temperature and pressure. A single gaseous product is formed, which fills a 2.00 L flask at 1.00 atm and 298 K. Use this information to determine the following characteristics of the product:(a) its empirical formula;(b) its molecular formula;(c) the most favorable Lewis formula based on formal charge arguments (the central atom is N);(d) the shape of the molecule.arrow_forwardHow does the square root mean square velocity of gas molecules vary with temperature? Illustrate this relationship by plotting the square root mean square velocity of N2 molecules as a function of temperature from T=100 K to T=300 K.arrow_forwardDraw product B, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CF3 NH2 Me O .N. + B OMearrow_forward
- Benzimidazole E. State its formula. sState the differences in the formula with other benzimidazoles.arrow_forwardDraw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CN CF3 K2CO3, DMSO, H₂O2 Aarrow_forward19) Which metal is most commonly used in galvanization to protect steel structures from oxidation? Lead a. b. Tin C. Nickel d. Zinc 20) The following molecule is an example of a: R₁ R2- -N-R3 a. Secondary amine b. Secondary amide c. Tertiary amine d. Tertiary amidearrow_forward
- pls helparrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward35) Complete the following equation by drawing the line the structure of the products that are formed. Please note that in some cases more than one product is possible. You must draw all possible products to recive full marks! a. ethanol + 2-propanol + H2SO4 → b. OH conc. H2SO4 CH2 H3C CH + K2Cr2O7 C. d. H3C A pressure CH3 + H2 CH Pt catalystarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

