
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of carbonyl-containing compound that is obtained when the given amide undergoes acidic hydrolysis has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are derivatives of
Acidic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid and
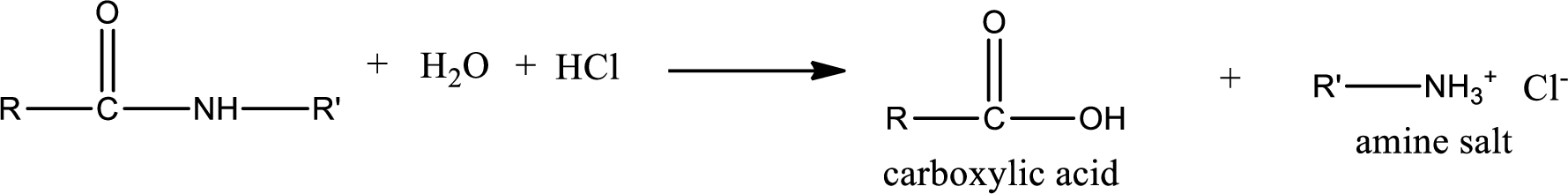
Basic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid salt and amine. Carboxylic acid salt is obtained because in basic conditions the carboxylic acid is converted into carboxylic acid salt.
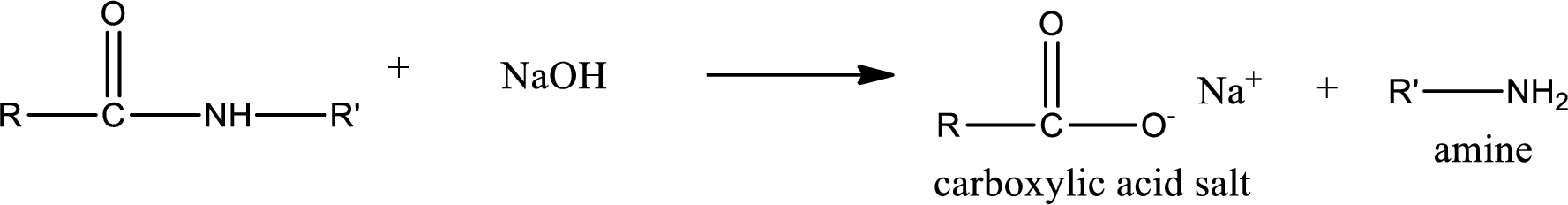
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of carbonyl-containing compound that is obtained when the given amide undergoes acidic hydrolysis has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are derivatives of carboxylic acid. Amides are not much reactive as of carboxylic acids. They are also stable relatively in aqueous solution. But under strenuous conditions amides undergo hydrolysis. The conditions are presence of acid, base or enzymes.
Acidic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid and amine salt. Amine salt is obtained because in acidic conditions the amine is converted into amine salt.
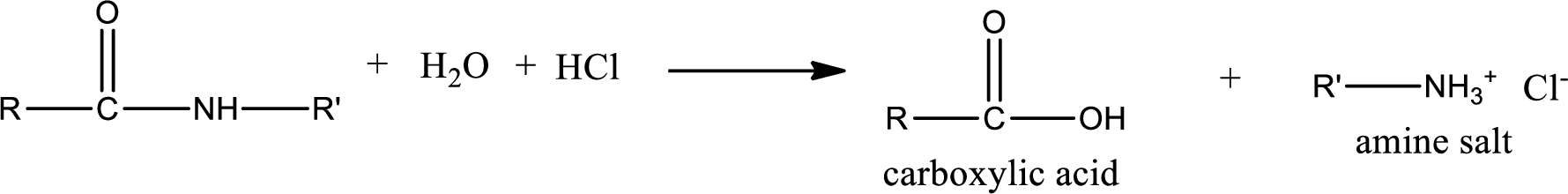
Basic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid salt and amine. Carboxylic acid salt is obtained because in basic conditions the carboxylic acid is converted into carboxylic acid salt.
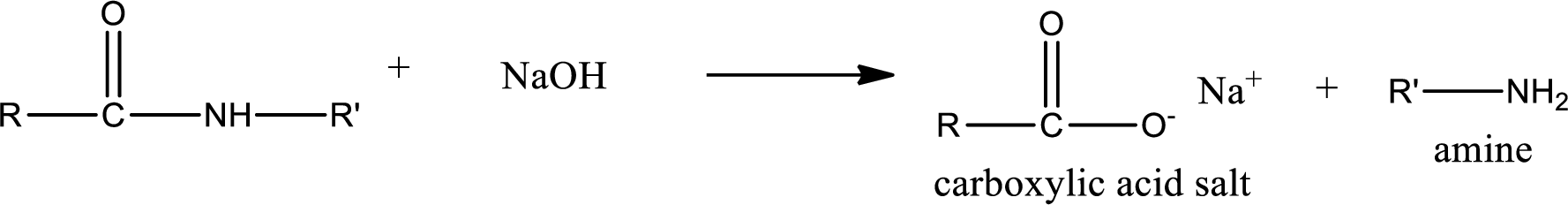
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of carbonyl-containing compound that is obtained when the given amide undergoes acidic hydrolysis has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are derivatives of carboxylic acid. Amides are not much reactive as of carboxylic acids. They are also stable relatively in aqueous solution. But under strenuous conditions amides undergo hydrolysis. The conditions are presence of acid, base or enzymes.
Acidic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid and amine salt. Amine salt is obtained because in acidic conditions the amine is converted into amine salt.
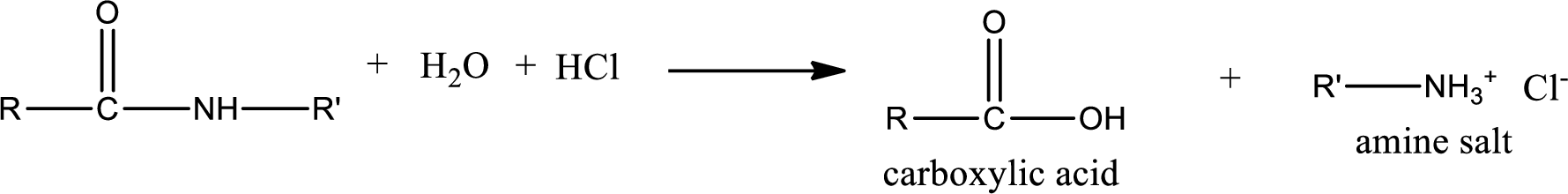
Basic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid salt and amine. Carboxylic acid salt is obtained because in basic conditions the carboxylic acid is converted into carboxylic acid salt.
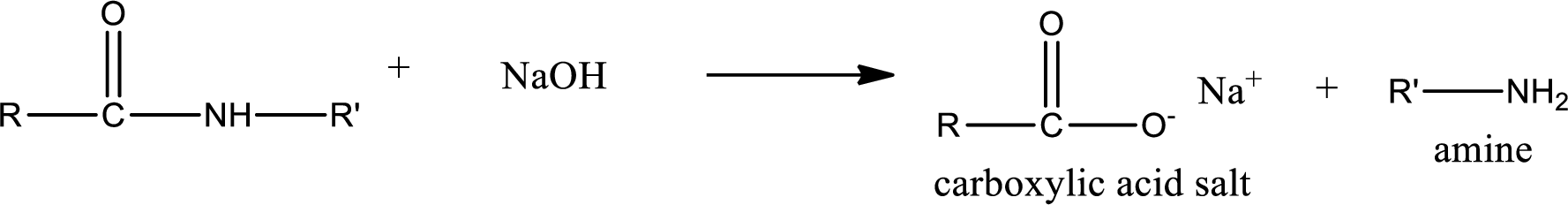
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of carbonyl-containing compound that is obtained when the given amide undergoes acidic hydrolysis has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are derivatives of carboxylic acid. Amides are not much reactive as of carboxylic acids. They are also stable relatively in aqueous solution. But under strenuous conditions amides undergo hydrolysis. The conditions are presence of acid, base or enzymes.
Acidic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid and amine salt. Amine salt is obtained because in acidic conditions the amine is converted into amine salt.
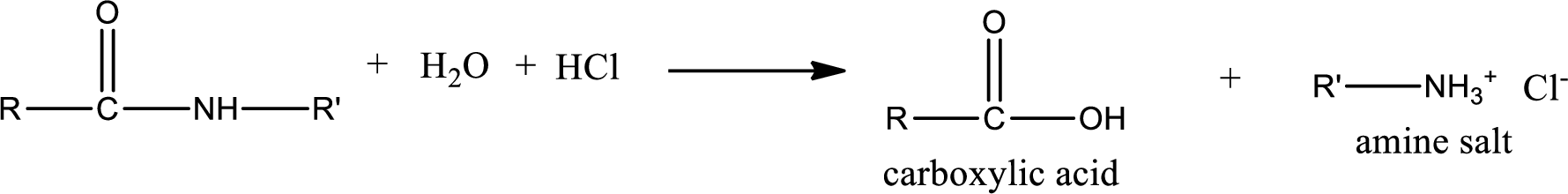
Basic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid salt and amine. Carboxylic acid salt is obtained because in basic conditions the carboxylic acid is converted into carboxylic acid salt.
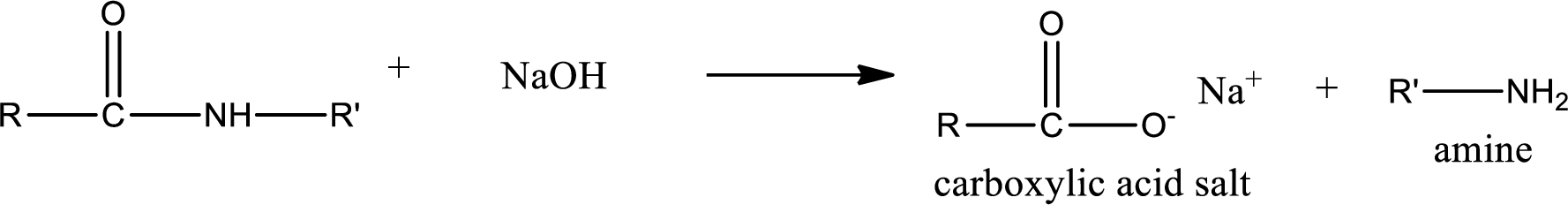
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
General, Organic, And Biological Chemistry, Hybrid (with Owlv2 Quick Prep For General Chemistry Printed Access Card)
- Assign the functional group bands on the IR spectra.arrow_forwardFind the pH of a 0.120 M solution of HNO2. Find the pH ignoring activity effects (i.e., the normal way). Find the pH in a solution of 0.050 M NaCl, including activityarrow_forwardPlease help me answer these three questions. Required info should be in data table.arrow_forward
- Draw the major organic substitution product or products for (2R,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane reacting with the given nucleophile. Clearly drawn the stereochemistry, including a wedged bond, a dashed bond and two in-plane bonds at each stereogenic center. Omit any byproducts. Bri CH3CH2O- (conc.) Draw the major organic product or products.arrow_forwardTartaric acid (C4H6O6) is a diprotic weak acid. A sample of 875 mg tartaric acid are dissolved in 100 mL water and titrated with 0.994 M NaOH. How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the first equivalence point? How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the second equivalence point?arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forward
- Order the following series of compounds from highest to lowest reactivity to electrophilic aromatic substitution, explaining your answer: 2-nitrophenol, p-Toluidine, N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide, 4-methylbenzonitrile, 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile.arrow_forwardOrdene la siguiente serie de compuestos de mayor a menor reactividad a la sustitución aromática electrofílica, explicando su respuesta: ácido bencenosulfónico, fluorobenceno, etilbenceno, clorobenceno, terc-butilbenceno, acetofenona.arrow_forwardCan I please get all final concentrations please!arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


