
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17, Problem 14P
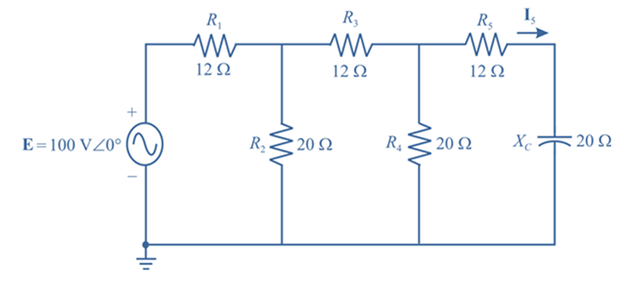
Find the current I5 for the network in Fig. 17.51. Note the effect of one reactive element on the resulting calculations.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Tutorial - Design of Common-Gate (CG) Amplifier
Design a common-gate NMOS amplifier with the following parameters:
Supply Voltage (VDD): 10 V
⚫Threshold Voltage (Vth): 2 V
•Overdrive Voltage (Vov) = VGS-Vth: 1 V
• Desired Voltage Gain Av: 10 V/V
• Transconductance gm: to be determined
•Ensure that the NMOS operates in the saturation region.
⚫ Design Vos to ensure saturation and enough voltage swing.
C₁
Vin
+VDD
RD
C₂ V
out
Rs
WI
RL
NEED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION DO NOT USE CHATGPT OR AI
Determine the response y(n), n≥0 of the system described by the second order
difference equation: y(n)-4y(n-1)+4y(n-2)=x(n)-x(n-1)
when the input is x(n)=(−1)" u(n) and the initial conditions are
y(-1)=y(-2)=0.
Chapter 17 Solutions
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Ch. 17 - For theseries-parallel network in Fig.17.38. a....Ch. 17 - For the network in Fig. 17.39: a. Find the total...Ch. 17 - For the network in FIg. 17.40: a. Find the total...Ch. 17 - For the network in Fig. 17.41: a. Find the total...Ch. 17 - For the network in Fig. 17.42: a. Find the current...Ch. 17 - For the network in Fig. 17.43: a. Find the current...Ch. 17 - For the network in Fig. 17.44: a. Find the current...Ch. 17 - For the network in Fig. 17.45: a. Find the source...Ch. 17 - For the network of Fig. 17.46: a. Find the voltage...Ch. 17 - For the network in Fig. 17.47: a. Find the total...
Ch. 17 - For the network in Fig. 17.48: a. Find the total...Ch. 17 - For the network of Fig. 17.49: a. Find the total...Ch. 17 - For the network of Fig. 17.50: a. Find the total...Ch. 17 - Find the current I5 for the network in Fig. 17.51....Ch. 17 - Find the average power delivered to R5 in Fig....Ch. 17 - For the ladder network of Fig. 17.53: a. Find the...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17PCh. 17 - PSpice or Multisim For Problems 15 through 18, use...Ch. 17 - PSpice or Multisim For Problems 15 through 18, use...Ch. 17 - PSpice or Multisim For Problems 15 through 18, use...Ch. 17 - PSpice or Multisim For Problems 15 through 18, use...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a Continuous- time LTI System described by y' (+)+ nycH) = x() find yet for a) x(+)o ē+4(H) b) X(+) = u(+). c) X(H= 5(+)arrow_forwardFind the Thevenin equivalent representation of the circuit given to the left of the nodes a and b. Find Vth and Rth and draw the equivalent Thevenin circuit. For Rth use a 1 volt test source as your method.arrow_forwardR(s) + E(s) 100(s+2)(s+6) s(s+3)(s+4) C(s)arrow_forward
- CONTROL SYSTEMS The system shown below has been tested with three different reference inputs 6u(t), 6tu(t), and 6tu(t). By using steady-state error calculation, identify which could give zero (0) steady state error. The function u(t) is the unit step. R(s) + E(s) 100(s+2)(s+6) s(s+3)(s+4) C(s)arrow_forwardEXAMPLE 3.8 Classify the following signals as energy signals or power signals or neither: a) f₁ (t) = e−t for t≥0 and f₁(t)=0 for t<0, b) f₂(t) = cos(t), and c) f³(t) = e¯†.arrow_forwardEXAMPLE 3.9 Classify the following systems as linear or nonlinear systems: a) y(t)=t2x(t) and b) y(t) = tx² (t). Solutionarrow_forward
- EXAMPLE 3.5 Suppose the signal c₁(t) is defined as follows: {−t+1, |||≤1 C₁(t): 0. |t|>1 Determine c₂(t)=c₁ (2t), c3(t)=c₁ (t/2), and c₁(t) = c₁(-2t).arrow_forwardDo problem 3.5darrow_forwardHomework Use graphical approach to find VGSQ, IDQ and use the mathematical approach to find VDS, VS, VG, VD. a. Rs b. Rs = = 100 Ω. 10 ΚΩ. 1 ΜΩ m 20 V 1 3.3 ΚΩ D G + VGS Rs IDss= 10 mA Vp= -4 V ID= IDSS | VGs=Vp/2 4 VDS =V DD-ID(RS+RD) Vs = IDRS V D=V +Vs DSarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Understanding Amplitude Modulation; Author: Rohde Schwarz;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I46eP8uZh_Y;License: Standard Youtube License