
Core Skill: Modeling The goal of this modeling challenge is to predict the outcome of meiosis if one pair of chromosomes does not separate properly during meiosis II.
Modeling Challenge: In Figure 16.13, the starting cell in meiosis I has 3 homologous pairs of chromosomes that differ in length: short, medium, and long. Let’s suppose that during meiosis I, the segregation of the long chromosomes into the two daughter cells occurs abnormally, and both of the long chromosomes go into the same daughter cell. Draw a model showing the chromosomal composition of the four daughter cells at the end of meiosis II. For each pair of homologs, draw one red and the other blue, as in the figure. You do not need to include crossovers in your model.
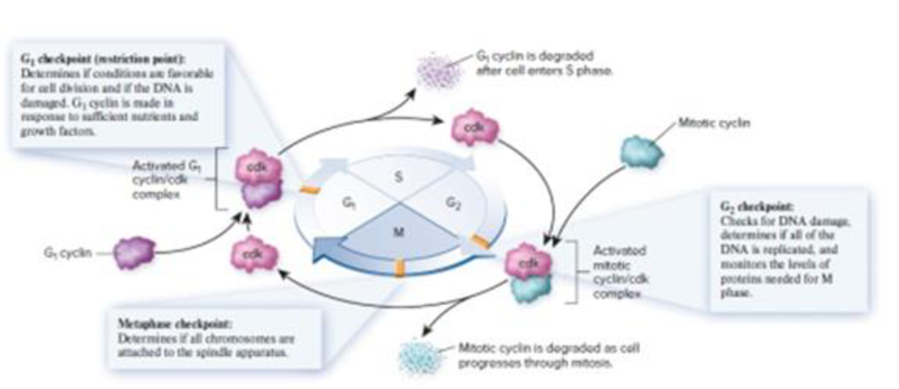
Figure 16.3 Checkpoints in the cell cycle. This is a general diagram of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Advancement through the cell cycle requires the formation of activated cyclin/cdk complexes. Cells make different types of cyclin proteins, which are typically degraded after the cell has advanced to the next phase. The formation of activated cyclin/cdk complexes is regulated by checkpoint proteins.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Biology
- Give examples of fat soluble and non-fat soluble hormonesarrow_forwardJust click view full document and register so you can see the whole document. how do i access this. following from the previous question; https://www.bartleby.com/questions-and-answers/hi-hi-with-this-unit-assessment-psy4406-tp4-report-assessment-material-case-stydu-ms-alecia-moore.-o/5e09906a-5101-4297-a8f7-49449b0bb5a7. on Google this image comes up and i have signed/ payed for the service and unable to access the full document. are you able to copy and past to this response. please see the screenshot from google page. unfortunality its not allowing me attch the image can you please show me the mathmetic calculation/ workout for the reult sectionarrow_forwardIn tabular form, differentiate between reversible and irreversible cell injury.arrow_forward
- 1.)What cross will result in half homozygous dominant offspring and half heterozygous offspring? 2.) What cross will result in all heterozygous offspring?arrow_forward1.Steroids like testosterone and estrogen are nonpolar and large (~18 carbons). Steroids diffuse through membranes without transporters. Compare and contrast the remaining substances and circle the three substances that can diffuse through a membrane the fastest, without a transporter. Put a square around the other substance that can also diffuse through a membrane (1000x slower but also without a transporter). Molecule Steroid H+ CO₂ Glucose (C6H12O6) H₂O Na+ N₂ Size (Small/Big) Big Nonpolar/Polar/ Nonpolar lonizedarrow_forwardwhat are the answer from the bookarrow_forward
- what is lung cancer why plants removes liquid water intead water vapoursarrow_forward*Example 2: Tracing the path of an autosomal dominant trait Trait: Neurofibromatosis Forms of the trait: The dominant form is neurofibromatosis, caused by the production of an abnormal form of the protein neurofibromin. Affected individuals show spots of abnormal skin pigmentation and non-cancerous tumors that can interfere with the nervous system and cause blindness. Some tumors can convert to a cancerous form. i The recessive form is a normal protein - in other words, no neurofibromatosis.moovi A typical pedigree for a family that carries neurofibromatosis is shown below. Note that carriers are not indicated with half-colored shapes in this chart. Use the letter "N" to indicate the dominant neurofibromatosis allele, and the letter "n" for the normal allele. Nn nn nn 2 nn Nn A 3 N-arrow_forwardI want to be a super nutrition guy what u guys like recommend mearrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning





