
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound needs to be determined.
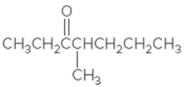
Concept Introduction:
In
A carbonyl group is a group composed of carbon and oxygen atoms, which are double-bonded to each other. Any compound comprising
In order to give the name to the carbonyl compound following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest) continuous carbon chain containing a carbonyl group (=CO) is selected.
2. While writing the name of aldehyde, the suffix "e" of the corresponding
3. Name should be written in alphabetical order and numbering should be done in such a way that the multiple bond and substituent group gets the lowest number.
4. Hyphen is used to connect the number to the name.
For number of carbons atoms in alkane chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound needs to be determined.
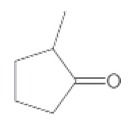
Concept Introduction:
In organic chemistry, IUPAC naming is a systematic method of naming organic molecules. The IUPAC is termed as the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, which makes the set of rules for naming the molecules in chemistry. IUPAC naming is sometimes easier than the older name, such that ethanol is IUPAC name and ethyl alcohol is the older name.
A carbonyl group is a group composed of carbon and oxygen atoms, which are double-bonded to each other. Any compound comprising aldehyde group is termed as a carbonyl molecule. In organic chemistry, there are various carbonyl compounds, such as aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, carboxylate ester, and amide.
In order to give the name to the carbonyl compound following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest) continuous carbon chain containing a carbonyl group (=CO) is selected.
2. While writing the name of aldehyde, the suffix "e" of the corresponding alkane is replaced by "-al", and while writing the name of ketone, the suffix "e" of the corresponding alkane is replaced by "-one"
3. The name should be written in alphabetical order and numbering should be done in such a way that the multiple bond and substituent group gets lowest number.
4. Hyphen is used to connect the number to the name.
For number of carbons atoms in alkane chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound needs to be determined.
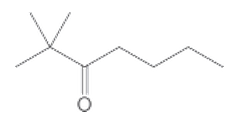
Concept Introduction:
In organic chemistry, IUPAC naming is a systematic method of naming organic molecules. The IUPAC is termed as the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, which makes the set of rules for naming the molecules in chemistry. IUPAC naming is sometimes easier than the older name, such that ethanol is IUPAC name and ethyl alcohol is older name.
A carbonyl group is a group composed of carbon and oxygen atoms, which are double-bonded to each other. Any compound comprising aldehyde group is termed as a carbonyl molecule. In organic chemistry, there are various carbonyl compounds, such as aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, carboxylate ester, and amide.
In order to give the name to the carbonyl compound following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest) continuous carbon chain containing a carbonyl group (=CO) is selected.
2. While writing the name of aldehyde, the suffix "e" of the corresponding alkane is replaced by "-al", and while writing the name of ketone, the suffix "e" of the corresponding alkane is replaced by "-one"
3. The name should be written in alphabetical order and numbering should be done in such a way that the multiple bond and substituent group gets the lowest number.
4. Hyphen is used to connect the number to the name.
For number of carbons atoms in alkane chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Loose Leaf for General, Organic and Biological Chemistry with Connect 2 Year Access Card
- Three pure compounds are formed when 1.00 g samples of element x combine with, respectively, 0.472 g, 0.630 g, and 0.789 g of element z. The first compound has the formula x2Z3. find the empricial formula of the other two compoundsarrow_forwardDraw the product and the mechanism A. excess H*; 人 OH H*; B. C. D. excess OH ✓ OH H*; H₂O 1. LDA 2. H*arrow_forwardIn reactions whose kinetic equation is v = k[A]m, the rate coefficient k is always positive. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- If the concentration of A decreases exponentially with time, what is the rate equation? (A). -d[A] (B). dt d[A] = k[A] e-kt dtarrow_forwardGiven the first-order reaction: aA → products. State its kinetic equation.arrow_forwardDetermine the symmetry of the combination of atomic orbitals for bf 4-arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning




