
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
If the given compound is hemiacetal, acetal, or ether should be determined.
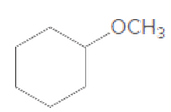
Concept Introduction:
The combination of two
(b)
Interpretation:
If the given compound is hemiacetal, acetal, or ether should be determined.
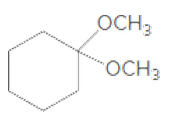
Concept Introduction:
The combination of two functional groups results in the formation of a hemiacetal. In a hemiacetal, a carbon atom is bonded to an alcohol group and an ether group. It is derived from the aldehyde. When two ether and one alcohol group is bonded to a carbon atom, then it results in the formation of acetal. It is derived from hemiacetal.
(c)
Interpretation:
If the given compound is hemiacetal, acetal, or ether should be determined.
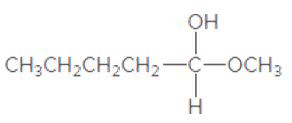
Concept Introduction:
The combination of two functional groups results in the formation of a hemiacetal. In a hemiacetal, a carbon atom is bonded to an alcohol group and an ether group. It is derived from the aldehyde. When two ether and one alcohol group is bonded to a carbon atom, then it results in the formation of acetal. It is derived from hemiacetal.
(d)
Interpretation:
If the given compound is hemiacetal, acetal, or ether should be determined.
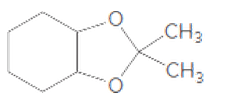
Concept Introduction:
The combination of two functional groups results in the formation of a hemiacetal. In a hemiacetal, a carbon atom is bonded to an alcohol group and an ether group. It is derived from the aldehyde. When two ether and one alcohol group is bonded to a carbon atom, then it results in the formation of acetal. It is derived from hemiacetal.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Loose Leaf for General, Organic and Biological Chemistry with Connect 2 Year Access Card
- consider the rate of the reaction below to be r. Whats the rate after each reaction? Br + NaCN CN + NaBr a. Double the concentration of alkyl bromide b. Halve the concentration of the electrophile & triple concentration of cyanide c. Halve the concentration of alkyl chloridearrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant that is involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forward
- What is the organic molecule X of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Without using graphs, calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/(mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forward
- Predict the organic products that form in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat are the products of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- What would happen if you added the HCI to the Grignard reagent before adding benzophenone? Draw a reaction mechanism to support your answer.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/ (mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forwardWrite the correct IUPAC names of the molecules in the picturearrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning


