
Concept explainers
The following table contains information concerning four jobs that are awaiting processing at a work center.
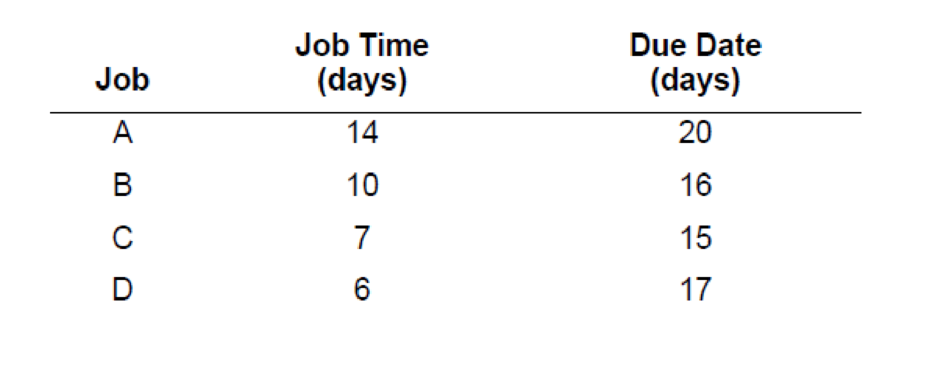
Sequence the jobs using (1) FCFS, (2) SPT, (3) EDD, and (4) CR. Assume the list is by order of arrival.
b. For each of the methods in part a, determine (1) the average job flow time, (2) the average tardiness, and (3) the average number of jobs at the work center.
c. Is one method superior to the others? Explain.
a)
1)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule First Come First Served (FCFS).
Introduction: First Come First Served is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, the first come would be served first.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) |
| A | 14 | 20 |
| B | 10 | 16 |
| C | 7 | 15 |
| D | 6 | 17 |
Determine the sequence using FCFS:
According to FCFS, the first come would be served first. Hence, the jobs should be sequenced in the order as per its arrival.
Hence, the sequence of jobs using FCFS is A-B-C-D.
1)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule First Come First Served (FCFS).
Introduction: First Come First Served is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, the first come would be served first.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) |
| A | 14 | 20 |
| B | 10 | 16 |
| C | 7 | 15 |
| D | 6 | 17 |
Determine the sequence using FCFS:
According to FCFS, the first come would be served first. Hence, the jobs should be sequenced in the order as per its arrival.
Hence, the sequence of jobs using FCFS is A-B-C-D.
2)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule Shortest Processing Time (SPT).
Introduction: Shortest Processing Tine is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, job with the shortest duration would be served first. Then, the process would be going on from shortest to largest duration.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) |
| A | 14 | 20 |
| B | 10 | 16 |
| C | 7 | 15 |
| D | 6 | 17 |
Determine the sequence using SPT:
According to SPT, the job that has the shortest processing would be served first and it goes on as the processing time increase. Duration should be assembled in the ascending order
Hence, the sequence of jobs using SPT is D-C-B-A.
3)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule Earliest Due Date (EDD).
Introduction: Earliest Due Date is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, job with the earliest due date would be served first. Then, the process would be going on from earliest due date to latest due date.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) |
| A | 14 | 20 |
| B | 10 | 16 |
| C | 7 | 15 |
| D | 6 | 17 |
Determine the sequence using EDD:
According to EDD, the job that has the earliest due date would be served first and it goes on as the due date increases. The job should be arranged based on due date. Due date should be assembled in the ascending order
Hence, the sequence of jobs using EDD is C-B-D-A.
4)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule critical ratio.
Introduction: Critical ratio is kind of scheduling rule that helps to identify that, the task or job is on the correct track. It would help to identify if the task is behind or ahead of the schedule.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) |
| A | 14 | 20 |
| B | 10 | 16 |
| C | 7 | 15 |
| D | 6 | 17 |
Determine the sequence using critical ratio:
Initial critical ratio should be determined at day 0:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Critical ratio |
| A | 14 | 20 | 1.43 |
| B | 10 | 16 | 1.6 |
| C | 7 | 15 | 2.14 |
| D | 6 | 17 | 2.83 |
Critical ratio for Job A:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of previous job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Critical ratio for Job B:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of previous job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Critical ratio for Job C:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of previous job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Critical ratio for Job D:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of previous job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Job A has the lowest critical ratio. Thus, it will be completed first. Hence, Job A would be completed first in the sequence of jobs.
Determine the critical ratio after the completion of Job A:
As the processing time of job A is 14 days, completion day of completed day would be 14.
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Critical ratio |
| A | - | - | - |
| B | 10 | 16 | 0.20 |
| C | 7 | 15 | 0.14 |
| D | 6 | 17 | 0.50 |
Critical ratio for Job B:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Critical ratio for Job C:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Critical ratio for Job D:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Job C has the lowest critical ratio. Hence, Job C would be completed next in the sequence of jobs after Job A.
Determine the critical ratio after the completion of Job A and Job C:
As the processing time of job A is 14 days and Job C is 7, completion day of completed day would be 21 (14+7).
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Critical ratio |
| A | - | - | - |
| B | 10 | 16 | -0.50 |
| C | |||
| D | 6 | 17 | -0.67 |
Critical ratio for Job B:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Critical ratio for Job D:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Job D has the lowest critical ratio. Hence, Job D would be completed next in the sequence of jobs after Job A and Job C.
As Job B is the remaining job, it will be completed next.
Hence, the sequence of jobs using critical ratio is A-C-D-B.
b)
To determine: Average flow time, average tardiness, and average number of jobs for each method.
Introduction: Rules that are framed for providing the order in which the jobs need to be performed are termed as priority rules. These rules are more suitable for process-oriented facilities. The main purpose of priority rules are on-time completion of jobs, efficient utilization of services, and the maximizing the customer services.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) |
| A | 14 | 20 |
| B | 10 | 16 |
| C | 7 | 15 |
| D | 6 | 17 |
First Come First Served:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Flow time | Tardiness |
| A | 14 | 20 | 14 | 0 |
| B | 10 | 16 | 24 | 8 |
| C | 7 | 15 | 31 | 16 |
| D | 6 | 17 | 37 | 20 |
| Total | 37 | 68 | 106 | 44 |
| Average | 9.3 | 17.0 | 26.5 | 11.0 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job A:
Flow time of Job A is less than its respective due date. Hence, there would be no tardiness.
Tardiness of Job B:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job B is 8.
Tardiness of Job C:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job C is 16.
Tardiness of Job D:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job D is 20.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 26.5 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 11.0 days
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 2.86 jobs.
Shortest processing time:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Flow time | Tardiness |
| D | 6 | 17 | 6 | |
| C | 7 | 15 | 13 | |
| B | 10 | 16 | 23 | 7 |
| A | 14 | 20 | 37 | 17 |
| Total | 37 | 68 | 79 | 24 |
| Average | 9.3 | 17.0 | 19.8 | 12.0 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job D and Job C:
Flow time of Job D and Job C is less than its respective due date. Hence, there would be no tardiness.
Tardiness of Job B:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job B is 7.
Tardiness of Job A:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job A is 17.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 19.75 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 6.0 days
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 2.14 jobs.
Earliest Due Date:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Flow time | Tardiness |
| C | 7 | 15 | 7 | |
| B | 10 | 16 | 17 | 1 |
| D | 6 | 17 | 23 | 6 |
| A | 14 | 20 | 37 | 17 |
| Total | 37 | 68 | 84 | 24 |
| Average | 9.3 | 17.0 | 21.0 | 8.0 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job C:
Flow time of Job C is less than its respective due date. Hence, there would be no tardiness.
Tardiness of Job B:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job B is 1.
Tardiness of Job D:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job D is 6.
Tardiness of Job A:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job A is 17.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 21.00 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 6.0 days
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 2.27 jobs.
Critical ratio:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Flow time | Tardiness |
| A | 14 | 20 | 14 | 0 |
| C | 7 | 15 | 21 | 6 |
| D | 6 | 17 | 27 | 10 |
| B | 10 | 16 | 37 | 21 |
| Total | 37 | 68 | 99 | 37 |
| Average | 9.3 | 17.0 | 24.8 | 9.3 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job A:
Flow time of Job A is less than its respective due date. Hence, there would be no tardiness.
Tardiness of Job C:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job C is 6.
Tardiness of Job D:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job D is 10.
Tardiness of Job B:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job B is 21.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 24.75 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 9.25 days
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 2.68 jobs.
c)
To determine: The method which is superior to others.
Introduction: Rules that are framed for providing the order in which the jobs need to be performed are termed as priority rules. These rules are more suitable for process-oriented facilities. The main purpose of priority rules are on-time completion of jobs, efficient utilization of services, and the maximizing the customer services.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) |
| A | 14 | 20 |
| B | 10 | 16 |
| C | 7 | 15 |
| D | 6 | 17 |
Determine the method which is superior to other:
Shortest Processing Time (SPT) is the method which is superior to other, as it is the method which would provide lowest value when compare to others.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Operations Management (Comp. Instructor's Edition)
- Your company is considering investing in a Human Resource Information System (HRIS).Briefly explain the strategies for justifying HRIS investments.arrow_forwardPresent the criteria you would utilize to determine if a right should be extended to an employee or if it would unnecessarily impact a manager’s ability to manage. Additionally, assess how you would balance the need for management rights against the need for employee rights, and how greater employee rights positively and negatively affect the future of the organization.arrow_forwardprovide schoarly research and references as to how internal and exteral audit is a risk management strategy to mitigate risk in a financial institutionarrow_forward
- Learning Activity 4: Strategic Sales Management How has the advent and rapid evolution of digital technology transformed traditional sales management strategies, and what do you think are the most significant challenges and opportunities this transformation brings? In addition, please select and describe an example of company that has embraced change and implemented a unique and effective sales strategy.arrow_forward1) View the two video excerpts (Ctrl+Click on the two links), Preview 1 to the Goal Movie (Goldratt) (11.17 minutes), https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2RVMgV37O_k and Preview 2 to the Goal Movie – How to Version (Goldratt) (9.40 minutes) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t_oM9LvK0rU and answer the following questions: a) What problems is UniCo facing and how are they tackling these problems currently? b) What advice did Jonah give to Rogo, and what lessons did Rogo learn from “Herbie’s Hike”? c) How do you think Rogo can leverage Jonah’s advice (as well as the lessons learnt from “Herbie’s Hike”) to solve UniCo’s problems? 2) A business program has the facilities and faculty to handle an enrollment of 2,000 new students per semester. However, in an effort to limit class sizes to a “reasonable” level the business dean, placed a ceiling on enrollment of 1,500 new students. Although there was ample demand for business courses last semester, conflicting schedules allowed only 1,450 new…arrow_forwardThe global marketplace has undergone a dramatic transformation, demanding that businesses adapt their supply chain management and implement new strategies to ensure the reliable sourcing of materials and goods. Please choose an organisation that you are currently working for or you are familiar with where its procurement operations has been greatly affected. You may pick a commercial or public institution as a choice for your study. You will need to briefly describe the institution and explain its category management structure which support the strategic procurement. You are required to provide an overview and discuss how spend are identified along with the types of categories purchased Briefly describe the organisation that you have chosen. Analyse the criticality of both the category management and strategic sourcing that will impact the business needs of the institution that you have chosen. Laing oxemples from the institution you have selected appraise and recommend COarrow_forward
- The Ideal Spot in the Segment Circles So, where should you try to position your product in the segment circles? As a basic rule, the 'Ideal Spot' will help guide you. The ideal spot represents the position with the highest point of demand for each consumer base – or segment. The ideal spot is made up by the product’s performance (speed) and size. As the perceptual map drifts down and to the right each year, the ideal spot will change as customers demand sensors with decreased size (smaller) and increased performance (faster). Although it would seem that the Ideal Spot would be in the center of the segment circle, the positioning actually varies due to the customer focus of each segment. For example, in the High End segment, the Ideal Spot is at the leading edge of the segment because those customers want the best possible product. Each segment’s ideal spot is represented by the pink dots on the Perceptual Map. Ideal Spots offset from segment center Calculating the Ideal Spot To…arrow_forwardIn Ecuador, cut roses are one of the country’s leading exports. Prior to advancements in the air transportation industry, this would have been impossible as roses must be sold within three to five days once cut. Today Ecuador is one of the world’s top producers of roses.arrow_forwardThe World Trade Organization is the only global trade organization and has 164 member nations representing 98 percent of world trade. How does the WTO help nations improve trade relations? What are some of the major challenges facing the WTO today?arrow_forward
- What is a good example of a letter of recommendation for a 5th grade Language Arts Teaching Position at an elementary school from a school principal?arrow_forwardProblem 1 (10 Points) Davison Electronics manufactures three LED television monitors, identified as Model A, Model B, and Model C. Davison Electronics four manufacturing plants. Each model has its lowest possible production cost when produced at Plant 1. However, Plant 1 does not have the capacity to handle the total production of all three models. As a result, at least some of the production must be routed to the other manufacturing plants. The following table shows the minimum production requirements for next month, the plant capacities in units per month, and the production cost per unit at each plant: Model Production Cost per Unit Minimum Production Requirements Plant 1 Plant 2 Plant 3 Plant 4 A $25 $28 $37 $34 48,000 B $26 $35 $36 $41 75,000 C $20 $31 $26 $23 60,000 Production Capacity 65,000 50,000 32,000 43,000 Davison’s objective is to determine the cost-minimizing production plan. We have…arrow_forwardLead Story: Identify the key story or insight based on your visualizations. Shaffer’s 4C Framework: Describe how you applied Shaffer’s 4C principles in the design of your charts. Gestalt Principles or Preattentive Attributes: Explain how you applied at least one Gestalt principle or preattentive attribute in your chartarrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing

