
a.
Interpretation:
Name the given compound.
Concept introduction:
The nomenclature of
Naming Aldehydes:
Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
The IUPAC naming of an aldehydes is obtained by replacing the final "e" on the name of the parent hydrocarbon with "al".
The common name of the aldehyde is substituted for "oic acid" at the end of parent hydrocarbon chain.
For example:
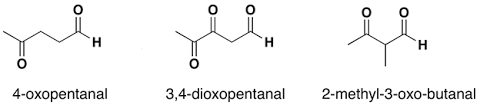
Naming Ketones:
Carbonyl carbon atom attached to the two oxygen atoms.
The IUPAC name of a ketones are obtained by replacing the "e" on the end of the parent hydrocarbon with "one".
Only few ketones have common name.
For example:
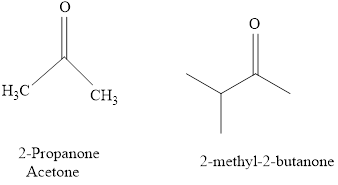
b.
Interpretation:
Name the given compound.
Concept introduction:
Naming Aldehydes:
Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
The IUPAC naming of an aldehydes is obtained by replacing the final "e" on the name of the parent hydrocarbon with "al".
The common name of the aldehyde is substituted for "oic acid" at the end of parent hydrocarbon chain.
For example:

Naming Ketones:
Carbonyl carbon atom attached to the two oxygen atoms.
The IUPAC name of a ketones are obtained by replacing the "e" on the end of the parent hydrocarbon with "one".
Only few ketones have common name.
For example:

c.
Interpretation:
Name the given compound.
Concept introduction:
Naming Aldehydes:
Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
The IUPAC naming of an aldehydes is obtained by replacing the final "e" on the name of the parent hydrocarbon with "al".
The common name of the aldehyde is substituted for "oic acid" at the end of parent hydrocarbon chain.
For example:

Naming Ketones:
Carbonyl carbon atom attached to the two oxygen atoms.
The IUPAC name of a ketones are obtained by replacing the "e" on the end of the parent hydrocarbon with "one".
Only few ketones have common name.
For example:

d.
Interpretation:
Name the given compound.
Concept introduction:
Naming Aldehydes:
Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
The IUPAC naming of an aldehydes is obtained by replacing the final "e" on the name of the parent hydrocarbon with "al".
The common name of the aldehyde is substituted for "oic acid" at the end of parent hydrocarbon chain.
For example:

Naming Ketones:
Carbonyl carbon atom attached to the two oxygen atoms.
The IUPAC name of a ketones are obtained by replacing the "e" on the end of the parent hydrocarbon with "one".
Only few ketones have common name.
For example:

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions Manual, Books a la Carte Edition (8th Edition)
- Select all molecules which are chiral. Brarrow_forwardUse the reaction coordinate diagram to answer the below questions. Type your answers into the answer box for each question. (Watch your spelling) Energy A B C D Reaction coordinate E A) Is the reaction step going from D to F endothermic or exothermic? A F G B) Does point D represent a reactant, product, intermediate or transition state? A/ C) Which step (step 1 or step 2) is the rate determining step? Aarrow_forward1. Using radii from Resource section 1 (p.901) and Born-Lande equation, calculate the lattice energy for PbS, which crystallizes in the NaCl structure. Then, use the Born-Haber cycle to obtain the value of lattice energy for PbS. You will need the following data following data: AH Pb(g) = 196 kJ/mol; AHƒ PbS = −98 kJ/mol; electron affinities for S(g)→S¯(g) is -201 kJ/mol; S¯(g) (g) is 640kJ/mol. Ionization energies for Pb are listed in Resource section 2, p.903. Remember that enthalpies of formation are calculated beginning with the elements in their standard states (S8 for sulfur). The formation of S2, AHF: S2 (g) = 535 kJ/mol. Compare the two values, and explain the difference. (8 points)arrow_forward
- In the answer box, type the number of maximum stereoisomers possible for the following compound. A H H COH OH = H C Br H.C OH CHarrow_forward7. Magnesium is found in nature in the form of carbonates and sulfates. One of the major natural sources of zinc is zinc blende (ZnS). Use relevant concepts of acid-base theory to explain this combination of cations and anions in these minerals. (2 points)arrow_forward6. AlF3 is insoluble in liquid HF but dissolves if NaF is present. When BF3 is added to the solution, AlF3 precipitates. Write out chemical processes and explain them using the principles of Lewis acid-base theory. (6 points)arrow_forward
- 5. Zinc oxide is amphoteric. Write out chemical reactions for dissolution of ZnO in HCl(aq) and in NaOH(aq). (3 points)arrow_forwardDraw the product(s) formed when alkene A is reacted with ozone, followed by Zn and H₂O. If no second product is formed, do not draw a structure in the second box. Higher Molecular Weight Product A Lower Molecular Weight Product draw structure ... draw structure ...arrow_forwardRank A - D in order of increasing rate of reaction with H2 and Pd/C. ب ب ب ب A B с Which option correctly ranks the alkenes in order of increasing rate of reaction with H₂ and Pd/C? О Barrow_forwardDraw the product of the following Sharpless epoxidation, including stereochemistry. Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. -OH (CH3)3C-OOH Ti[OCH(CH3)2]4 (+)-DET draw structure ... Guidarrow_forwardWhat alkyne (or diyne) yields the following oxidative cleavage products? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ... CO₂ + OHarrow_forwardlighting discharges in the atmosphere catalyze the conversion of nitrogen to nitric oxide. How many grams of nitrogen would be required to make 25.0 g of nitric oxide in this way ?arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
 EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





