
Find Data for Profit
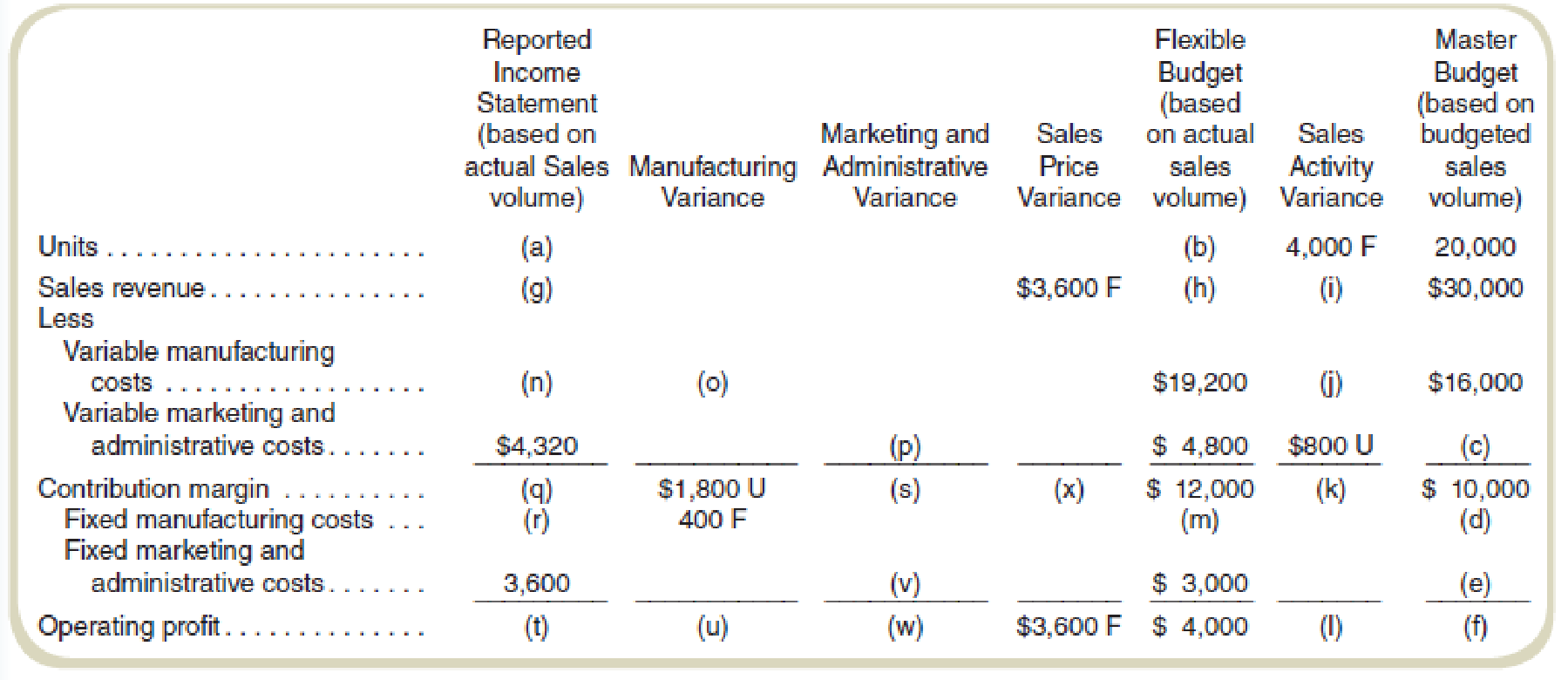
Required
Find the values of the missing items (a) through (x). Assume that actual sales volume equals actual production volume. (There are no inventory level changes.)
Find the missing data to prepare profit variance analysis.
Explanation of Solution
Profit variance analysis:
The analysis that studies the difference between the actual operating profit and the standard operating profit is called the profit variance analysis.
Prepare profit variance analysis:
| Actual Revenue & Costs | Manufacturing variance | Marketing and administrative variance | Sales price variance | Flexible budget | Sales Activity Variance | Master budget | |
| Units Produced | 24,000(1) | 24,000 | 4,000F(2) | 20,000 | |||
| Sales revenue | $39,600(7) | $3,600F | $36,000(6) | $6,000F(8) | $30,000 | ||
| Less: Variable costs | |||||||
| Manufacturing | $21,000(10) | $1,800U(9) | $19,200 | $3,200U | $16,000 | ||
| Marketing &administrative costs | $4,320 | $480F(11) | $4,800 | $800U | $4,000 | ||
| Contribution margin | $14,280(12) | $1,800U | $480F | $3,600F | $12,000 | $2,000F | $10,000 |
| Less: Fixed Costs | |||||||
| Manufacturing | $4,600(13) | $400F | $5,000(3) | $5,000 | |||
| Marketing &administrative costs | $3,600 | $600U(16) | $3,000(4) | $3,000 | |||
| Operating Profits | $6,080(14) | $1,400U(15) | $120U(17) | $3,600F | $4,000 | $2,000F | $2,000(5) |
Table: (1)
Working Note 1:
Actual units and fixed budget units:
Working Note 2:
Budgeted variable marketing and administrative cost:
Working Note 3:
Flexible budget fixed manufacturing cost:
Working Note 4:
Master budget fixed marketing and administrative cost:
Fixed cost in the master budget will be the same as given in the flexible budget which is $3,000.
Working Note 5:
Master budget operating profit:
Working Note 6:
Flexible budget sales revenue:
Working Note 7:
Actual sales revenue:
Working Note 8:
Sales activity variance:
Working Note 9:
Manufacturing variance will be equal to the total manufacturing variance which is $1,800U.
Working Note 10:
Actual variable manufacturing cost:
Working Note 11:
Marketing and administrative variance:
Working Note 12:
Contribution margin:
Working Note 13:
Actual fixed manufacturing cost:
Working Note 14:
Operating profit:
Working Note 15:
Total manufacturing variance:
Working Note 16:
Fixed marketing and administrative variance:
Working Note 17:
Total marketing and administrative variance:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
COST ACCOUNTING W/CONNECT
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub





