1 Introduction To Physics 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics 3 Vectors In Physics 4 Two-Dimensional Kinematics 5 Newton’s Laws Of Motion 6 Applications Of Newton’s Laws 7 Work And Kinetic Energy 8 Potential Energy And Conservation Of Energy 9 Linear Momentum And Collisions 10 Rotational Kinematics And Energy 11 Rotational Dynamics And Static Equilibrium 12 Gravity 13 Oscillations About Equilibrium 14 Waves And Sound 15 Fluids 16 Temperature And Heat 17 Phases And Phase Changes 18 The Laws Of Thermodynamics 19 Electric Charges, Forces, And Fields 20 Electric Potential And Electric Potential Energy 21 Electric Current And Direct-Current Circuits 22 Magnetism 23 Magnetic Flux And Faraday’s Law Of Induction 24 Alternating-Current Circuits 25 Electromagnetic Wave 26 Geometrical Optics 27 Optical Instruments 28 Physical Optics: Interference And Diffraction 29 Relativity 30 Quantum Physics 31 Atomic Physics 32 Nuclear Physics And Nuclear Radiation expand_more
16.1 Temperature And The Zeroth Law Of Thermodynamics 16.2 Temperature Scales 16.3 Thermal Expansion 16.4 Heat And Mechanical Work 16.5 Specific Heats 16.6 Conduction, Convection, And Radiation Chapter Questions expand_more
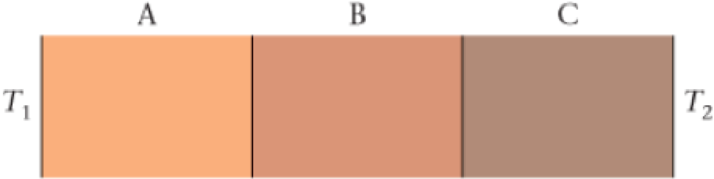
Problem 1CQ Problem 2CQ Problem 3CQ Problem 4CQ: If the glass in a glass thermometer had the same coefficient of volume expansion as mercury, the... Problem 5CQ Problem 6CQ: Sometimes the metal lid on a glass jar has been screwed on so tightly that it is very difficult to... Problem 7CQ Problem 8CQ: The specific heat of concrete is greater than that of soil. Given this fact, would you expect a... Problem 9CQ: When you touch a piece of metal and a piece of wood that are both at room temperature the metal... Problem 10CQ: The rate of heat flow through a slab does not depend on which of the following? (a) The temperature... Problem 11CQ Problem 12CQ: Updrafts of air allow hawks and eagles to glide effortlessly, all the while gaining altitude. What... Problem 13CQ: BIO The fur of polar bears consists of hollow fibers. (Sometimes algae will grow in the hollow... Problem 14CQ: Object 2 has twice the emissivity of object 1, though they have the same size and shape. If the two... Problem 1PCE Problem 2PCE Problem 3PCE: Incandescent lightbulbs heat a tungsten filament to a temperature of about 4580 F, which is almost... Problem 4PCE: Normal body temperature for humans is 98.6 F. What is the corresponding temperature in (a) degrees... Problem 5PCE: The temperature at the surface of the Sun is about 6000 K. Convert this temperature to the (a)... Problem 6PCE: One day you notice that the outside temperature increased by 17F between your early morning jog and... Problem 7PCE: The gas in a constant-volume gas thermometer has a pressure of 93.5 kPa at 105 C. (a) What is the... Problem 8PCE Problem 9PCE: Greatest Change in Temperature A world record for the greatest change in temperature was set in... Problem 10PCE Problem 11PCE Problem 12PCE: When the bulb of a constant-volume gas thermometer is placed in a beaker of boiling water at 100 C,... Problem 13PCE: Bimetallic strip A is made of copper and steel; bimetallic strip B is made of aluminum and steel.... Problem 14PCE Problem 15PCE: Predict/Explain A brass plate has a circular hole whose diameter is slightly smaller than the... Problem 16PCE: Figure 16-25 shows five metal plates, all at the same temperature and all made from the same... Problem 17PCE: Longest Suspension Bridge The worlds longest suspension bridge is the Akashi Kaikyo Bridge in Japan.... Problem 18PCE: A vinyl siding panel for a house is installed on a day when the temperature is 15.6 C. If the... Problem 19PCE: A cylinder bore in an aluminum engine block has a diameter of 96.00 mm at 20.00 C. (a) What is the... Problem 20PCE Problem 21PCE: At 18.75 C a brass sleeve has an inside diameter of 2.21988 cm and a steel shaft has a diameter of... Problem 22PCE: Early in the morning, when the temperature is 5.5 C, gasoline is pumped into a cars 53-L steel gas... Problem 23PCE: Some cookware has a stainless steel interior ( = 17.3 106 K1) and a copper bottom ( = 17.0 106 K1)... Problem 24PCE: Predict/Calculate You construct two wire-frame cubes, one using copper wire, the other using... Problem 25PCE: A metal ball that is 1.2 m in diameter expands by 2.2 mm when the temperature is increased by 95 C.... Problem 26PCE: A copper ball with a radius of 1.7 cm is heated until its diameter has increased by 0.16 mm.... Problem 27PCE: Predict/Calculate An aluminum saucepan with a diameter of 23 cm and a height of 6.0 cm is filled to... Problem 28PCE Problem 29PCE: BIO An exercise machine indicates that you have worked off 2.1 Calories in a minute-and-a-half of... Problem 30PCE: BIO A certain sandwich cookie contains 53 C of nutritional energy. (a) For what amount of time must... Problem 31PCE: BIO During a workout, a person repeatedly lifts a 16-lb barbell through a distance of 1.1 ft. How... Problem 32PCE Problem 33PCE: BIO It was shown in Example 16-18 that a typical person radiates about 62 W of power at room... Problem 34PCE: Predict/Explain Two objects are made of the same material but have different temperatures. Object 1... Problem 35PCE Problem 36PCE Problem 37PCE Problem 38PCE: A 9.7-g lead bullet is fired into a fence post. The initial speed of the bullet is 720m/s, and when... Problem 39PCE Problem 40PCE Problem 41PCE: A 225-g lead ball at a temperature of 81.2 C is placed in a light calorimeter containing 155 g of... Problem 42PCE: If 2200 J of heat are added to a 190-g object, its temperature increases by 12C. (a) What is the... Problem 43PCE: Chips by the Ton Tortilla chips are manufactured by submerging baked and partially cooled masa at 41... Problem 44PCE Problem 45PCE: To determine the specific heat of an object, a student heats it to 100 C in boiling water. She then... Problem 46PCE: Predict/Calculate A student drops a 0.33-kg piece of steel at 42 C into a container of water at 22... Problem 47PCE Problem 48PCE: Predict/Explain In a popular lecture demonstration, a sheet of paper is wrapped around a rod that is... Problem 49PCE: Figure 16-27 shows a composite slab of three different materials with equal thickness but different... Problem 50PCE: Figure 16-28 Problem 50 50. CE Heat is transferred from an area where the temperature is 20 C to an... Problem 51PCE: Predict/Explain Two identical bowls of casserole need to be kept warm. The cook covers bowl 1 with... Problem 52PCE: Two bowls of soup with identical temperatures are placed on a table. Bowl 1 has a metal spoon in it;... Problem 53PCE: A glass window 0.33 cm thick measures 81 cm by 39 cm. How much heat flows through this window per... Problem 54PCE: BIO Assuming your skin temperature is 37.2 C and the temperature of your surroundings is 20.0 C,... Problem 55PCE: Find the heat that flows in 1.0 s through a lead brick 25 cm long if the temperature difference... Problem 56PCE: Consider a double-paned window consisting of two panes of glass, each with a thickness of 0.500 cm... Problem 57PCE: Predict/Calculate Two metal rods of equal lengthone aluminum, the other stainless steelare connected... Problem 58PCE: Two cylindrical metal rodsone copper, the other leadare connected in parallel with a temperature of... Problem 59PCE Problem 60PCE: Predict/Calculate Consider two cylindrical metal rods with equal cross sectionone lead, the other... Problem 61PCE: A copper rod 85 cm long is used to poke a fire. The hot end of the rod is maintained at 115 C and... Problem 62PCE: Two identical objects are placed in a room at 24 C. Object 1 has a temperature of 99 C, and object 2... Problem 63PCE: A block has the dimensions L, 2L, and 3L. When one of the L 2L faces is maintained at the... Problem 64GP Problem 65GP: CE A copper ring stands on edge with a metal rod placed inside it, as shown in Figure 16-30. As this... Problem 66GP: CE Referring to the copper ring in the previous problem, imagine that initially the ring is hotter... Problem 67GP Problem 68GP: Making Steel Sheets In the continuous-caster process, steel sheets 25.4 cm thick, 2.03 m wide and... Problem 69GP: The Coldest Place in the Universe The Boomerang nebula holds the distinction of having the lowest... Problem 70GP: BIO The Hottest Living Things From the surreal realm of deep-sea hydrothermal vents 200 miles... Problem 71GP: Thermal energy is added to 180 g of water at a constant rate for 3.5 min, resulting in an increase... Problem 72GP Problem 73GP: BIO Brain Power As you read this problem, your brain is consuming about 22 W of power. (a) If your... Problem 74GP: BIO Brain Food Your brain consumes about 22 W of power, and avocados have been shown to promote... Problem 75GP: BIO The Cricket Thermometer The rate of chirping of the snowy tree cricket (Oecanthus fultoni... Problem 76GP: Predict/Calculate A pendulum consists of a large weight suspended by a steel wire that is 0.9500 m... Problem 77GP Problem 78GP: A256-kg rock sits in full sunlight on the edge of a cliff 5.75 m high. The temperature of the rock... Problem 79GP Problem 80GP: Thermal Storage Solar heating of a house is much more efficient if there is a way to store the... Problem 81GP: Pave It Over Suppose city 1 leaves an entire block (100 m 100 m) as a park with trees and grass... Problem 82GP Problem 83GP: You turn a crank on a device similar to that shown in Figure 16-12 and produce a power of 0.16 hp.... Problem 84GP Problem 85GP: The Solar Constant The surface of the Sun has a temperature of 5500 C. (a) Treating the Sun as a... Problem 86GP: Bars of two different metals are bolted together, as shown in Figure 16-31. Show that the distance D... Problem 87GP: A grandfather clock has a simple brass pendulum of length L. One night, the temperature in the house... Problem 88GP Problem 89GP: A layer of ice has formed on a small pond. The air just above the ice is at 5.4 C, the water-ice... Problem 90GP: A Double-Paned Window An energy-efficient double-paned window consists of two panes of glass seen... Problem 91PP: Cool Medicine In situations in which the brain is deprived of oxygen, such as in a heart attack or... Problem 92PP: Cool Medicine In situations in which the brain is deprived of oxygen, such as in a heart attack or... Problem 93PP: Cool Medicine In situations in which the brain is deprived of oxygen, such as in a heart attack or... Problem 94PP Problem 95PP: Referring to Example 16-12 Suppose the mass of the block is to be increased enough to make the final... Problem 96PP: Referring to Example 16-12 Suppose the initial temperature of the block is to be increased enough to... Problem 97PP Problem 98PP: Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 16-16 Suppose the temperature of the hot plate is to be... format_list_bulleted


 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




