
Concept explainers
Four capacitors are connected as shown in Figure P16.48.
(a) Find the equivalent capacitance between points a and b.
(b) Calculate the charge on each capacitor, taking ΔVab = 15.0 V.
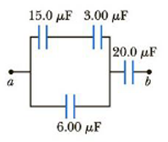
Figure P16.48
(a)
Answer to Problem 48P
Explanation of Solution
The capacitors
The capacitors
The capacitance
Substitute
Conclusion:
The equivalent capacitance is
(b)
Answer to Problem 48P
The charge on
The charge on
The charge on
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the charge on
Substitute
Formula to calculate the charge on
Therefore,
Substitute15.0 V for V,
Explanation:
Formula to calculate the charge on charge on
Therefore,
Substitute15.0 V for V,
Conclusion:
The charge on
The charge on
The charge on
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Bundle: College Physics, Loose-Leaf Version, 10th, + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Serway/Vuille's College Physics, 10th Edition, Multi-Term
- Page 2 SECTION A Answer ALL questions in Section A [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-A sub question.] Question A1 SPA6308 (2024) Consider Minkowski spacetime in Cartesian coordinates th = (t, x, y, z), such that ds² = dt² + dx² + dy² + dz². (a) Consider the vector with components V" = (1,-1,0,0). Determine V and V. V. (b) Consider now the coordinate system x' (u, v, y, z) such that u =t-x, v=t+x. [2 marks] Write down the line element, the metric, the Christoffel symbols and the Riemann curvature tensor in the new coordinates. [See the Appendix of this document.] [5 marks] (c) Determine V", that is, write the object in question A1.a in the coordinate system x'. Verify explicitly that V. V is invariant under the coordinate transformation. Question A2 [5 marks] Suppose that A, is a covector field, and consider the object Fv=AAμ. (a) Show explicitly that F is a tensor, that is, show that it transforms appropriately under a coordinate transformation. [5 marks] (b)…arrow_forwardHow does boiling point of water decreases as the altitude increases?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 14 Z In figure, a closed surface with q=b= 0.4m/ C = 0.6m if the left edge of the closed surface at position X=a, if E is non-uniform and is given by € = (3 + 2x²) ŷ N/C, calculate the (3+2x²) net electric flux leaving the closed surface.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardsuggest a reason ultrasound cleaning is better than cleaning by hand?arrow_forward
- Checkpoint 4 The figure shows four orientations of an electric di- pole in an external electric field. Rank the orienta- tions according to (a) the magnitude of the torque on the dipole and (b) the potential energy of the di- pole, greatest first. (1) (2) E (4)arrow_forwardWhat is integrated science. What is fractional distillation What is simple distillationarrow_forward19:39 · C Chegg 1 69% ✓ The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take F=1700 lb. (Figure 1) Figure 800 lb ||-5- F 600 lb بتا D E C BO 10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft- Solved Part A The compound beam is fixed at E and... Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm Problem A-12 % Chia sẻ kip 800 lb Truy cập ) D Lưu of C 600 lb |-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft D E 5 ft- Trying Cheaa Những kết quả này có hữu ích không? There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!) Chegg Solved The compound b... Có Không ☑ ||| Chegg 10 וחarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





