
Determine the input impedance Zin of the one-port shown in Fig. 16.51 if ω is equal to (a) 50 rad/s; (b) 1000 rad/s.
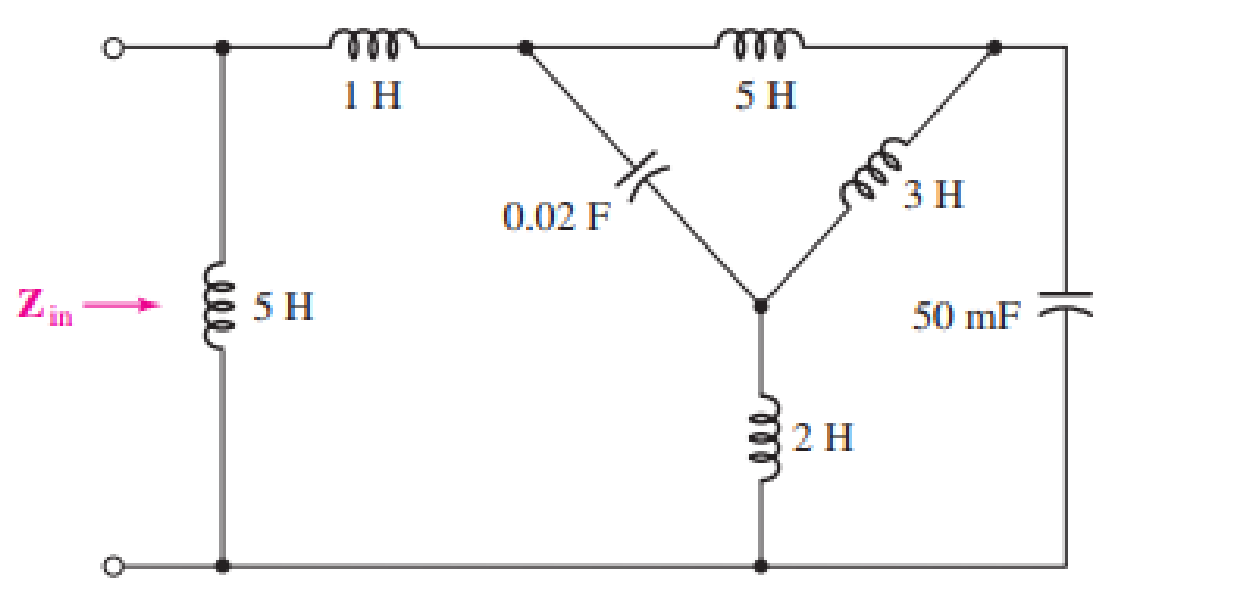
(a)
The value of the input impedance for
Answer to Problem 23E
The value of the input impedance is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The value of
The given diagram is shown in Figure 1.
Calculation:
Let the inductances be
Let the capacitance
The expression for the inductive impedance
The expression for the capacitive impedance
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The value of
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The conversion of
Substitute
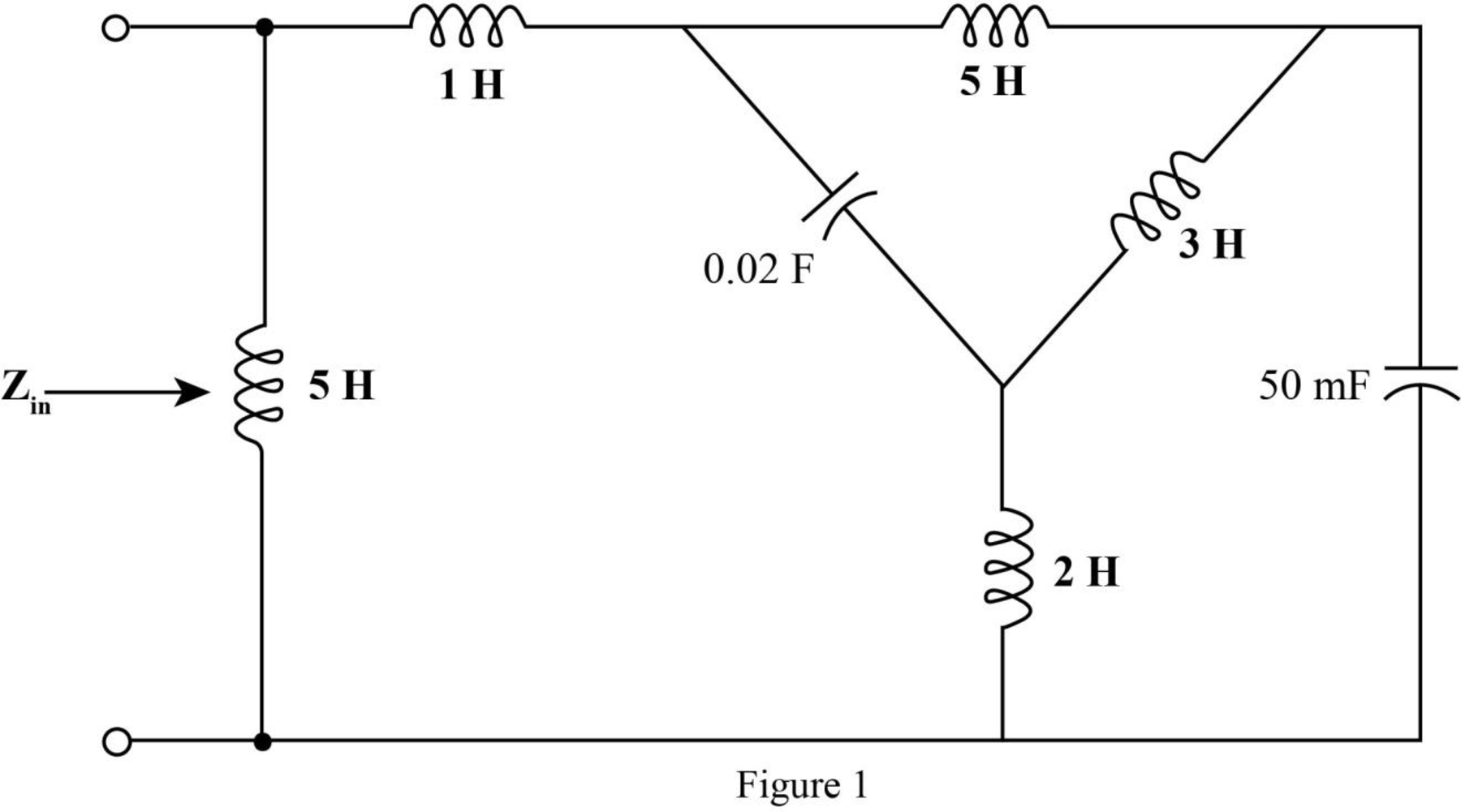
Mark the impedances and redraw the circuit.
The required diagram is shown in Figure 2
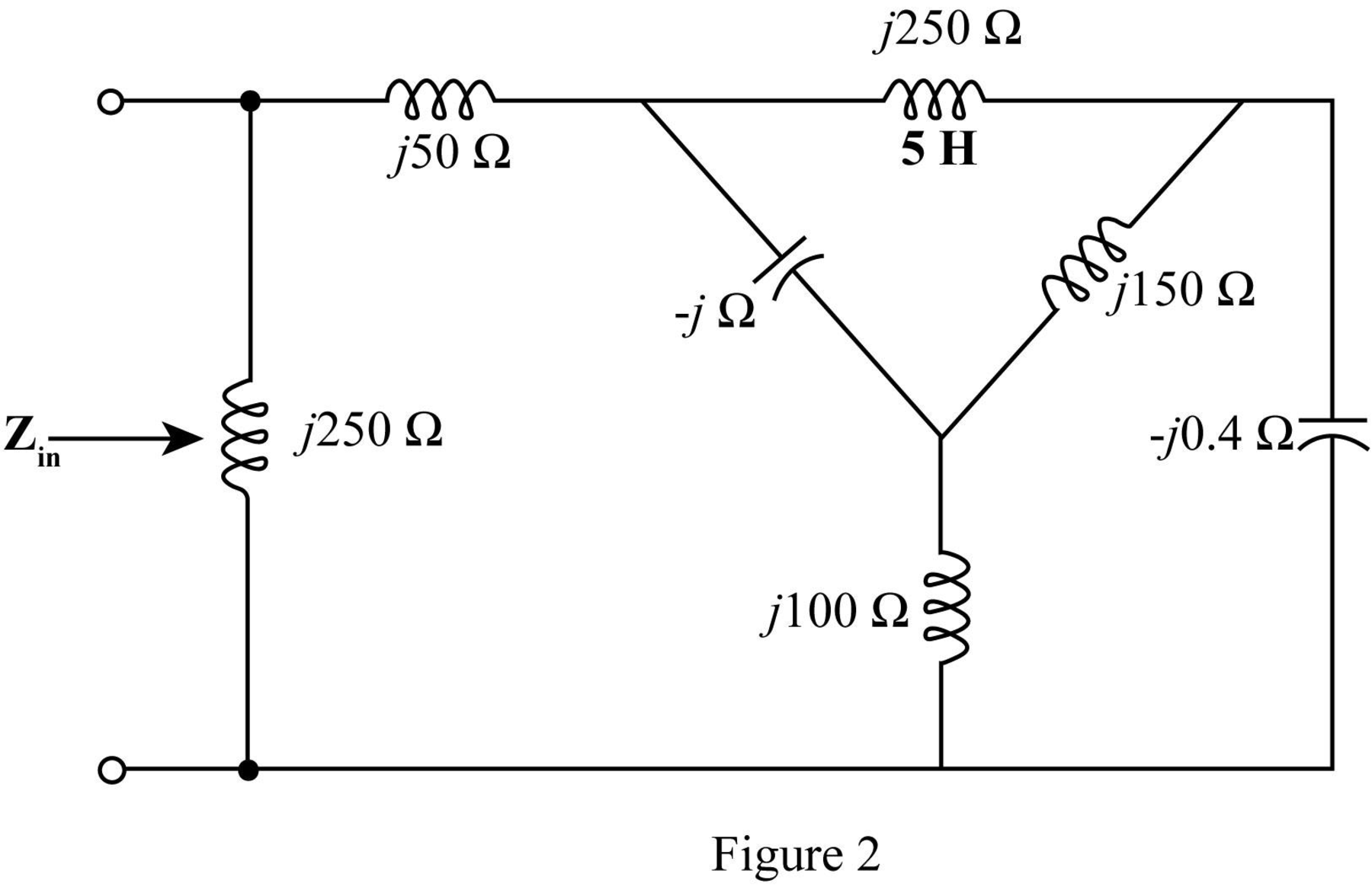
The
The required diagram is shown in the Figure 3.
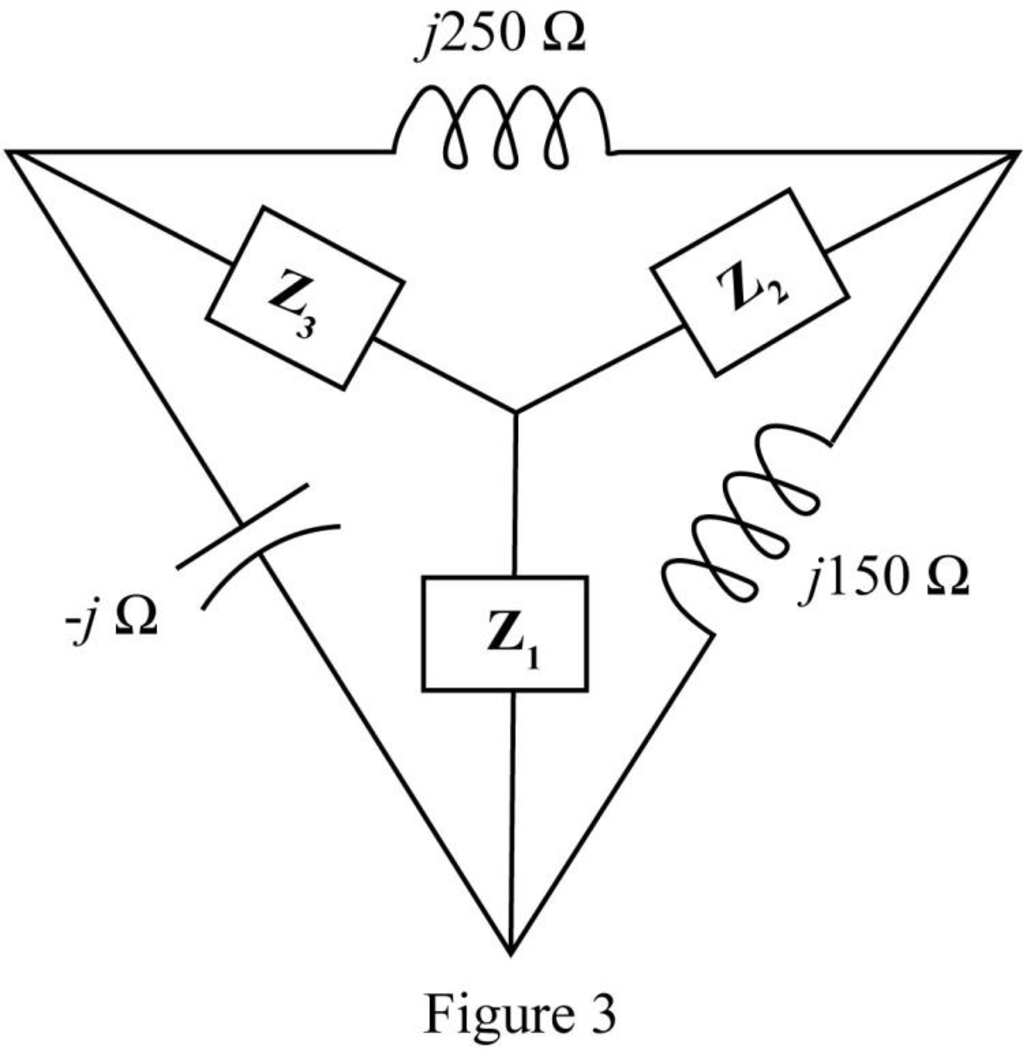
Here,
The impedance
The impedance
The impedance
The required diagram is shown in Figure 4.
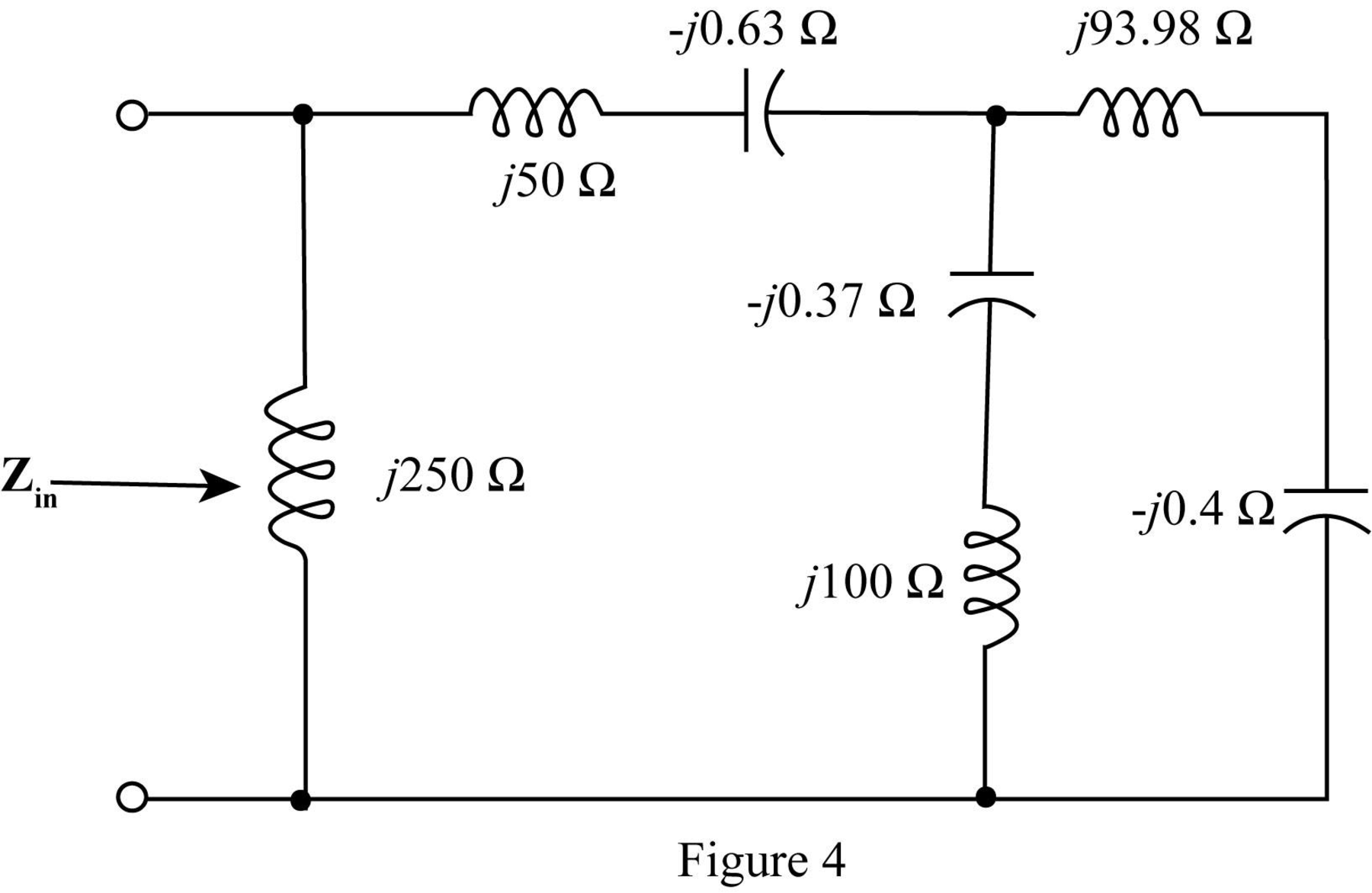
Add the impedances in series in the above network and redraw the network.
The required diagram is shown in Figure 5.
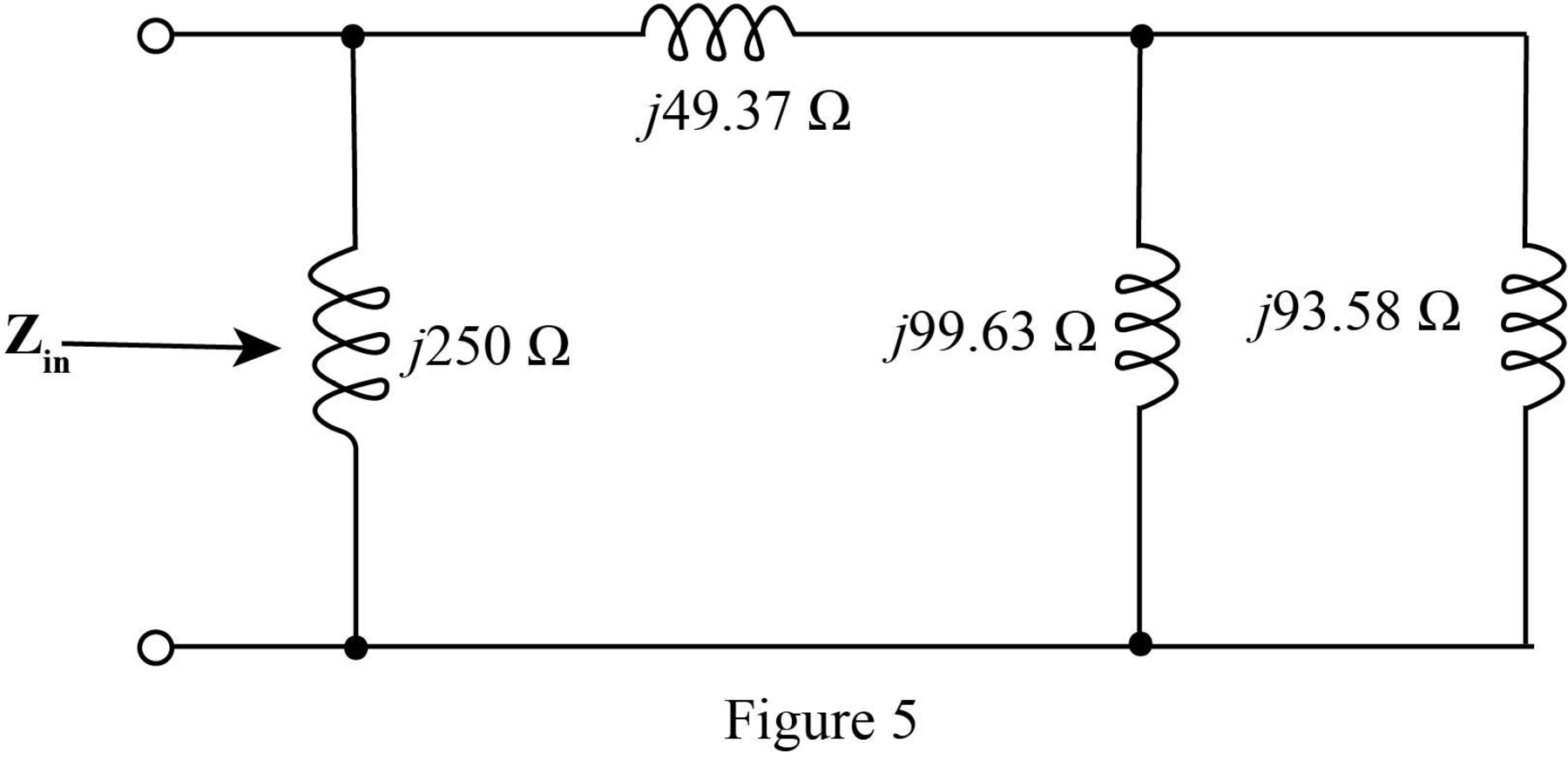
In the above circuit
Thus, the parallel combination
Mark the equivalent impedance and redraw the circuit.
The required figure is shown in Figure 6.
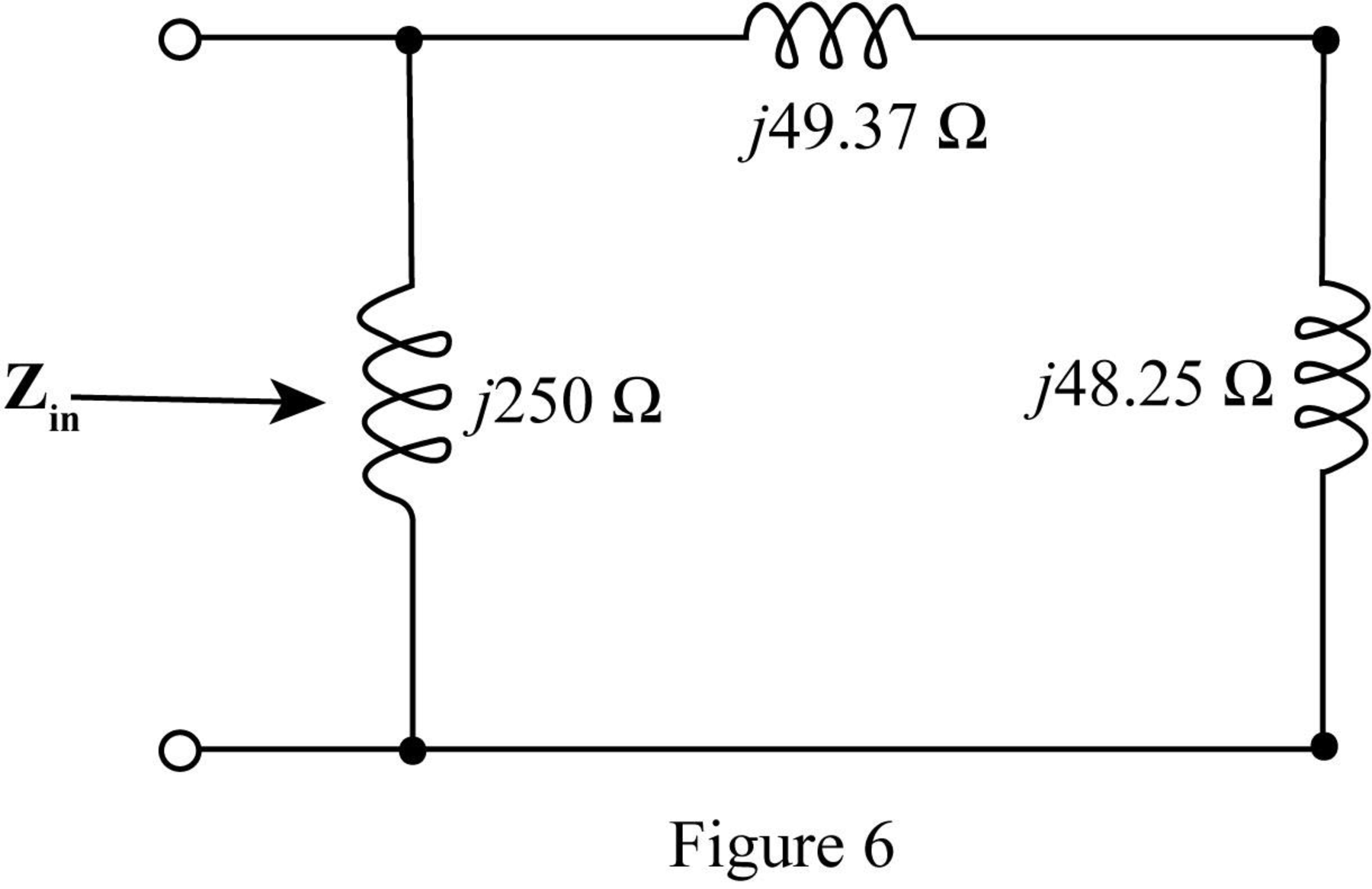
The value of the input impedance
Solve it further as,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of the input impedance for
(b)
The input impedance of the circuit is determined for
Answer to Problem 23E
The value of the input impedance for
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The value of
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Mark the impedances and redraw the circuit.
The required diagram is shown in Figure 7
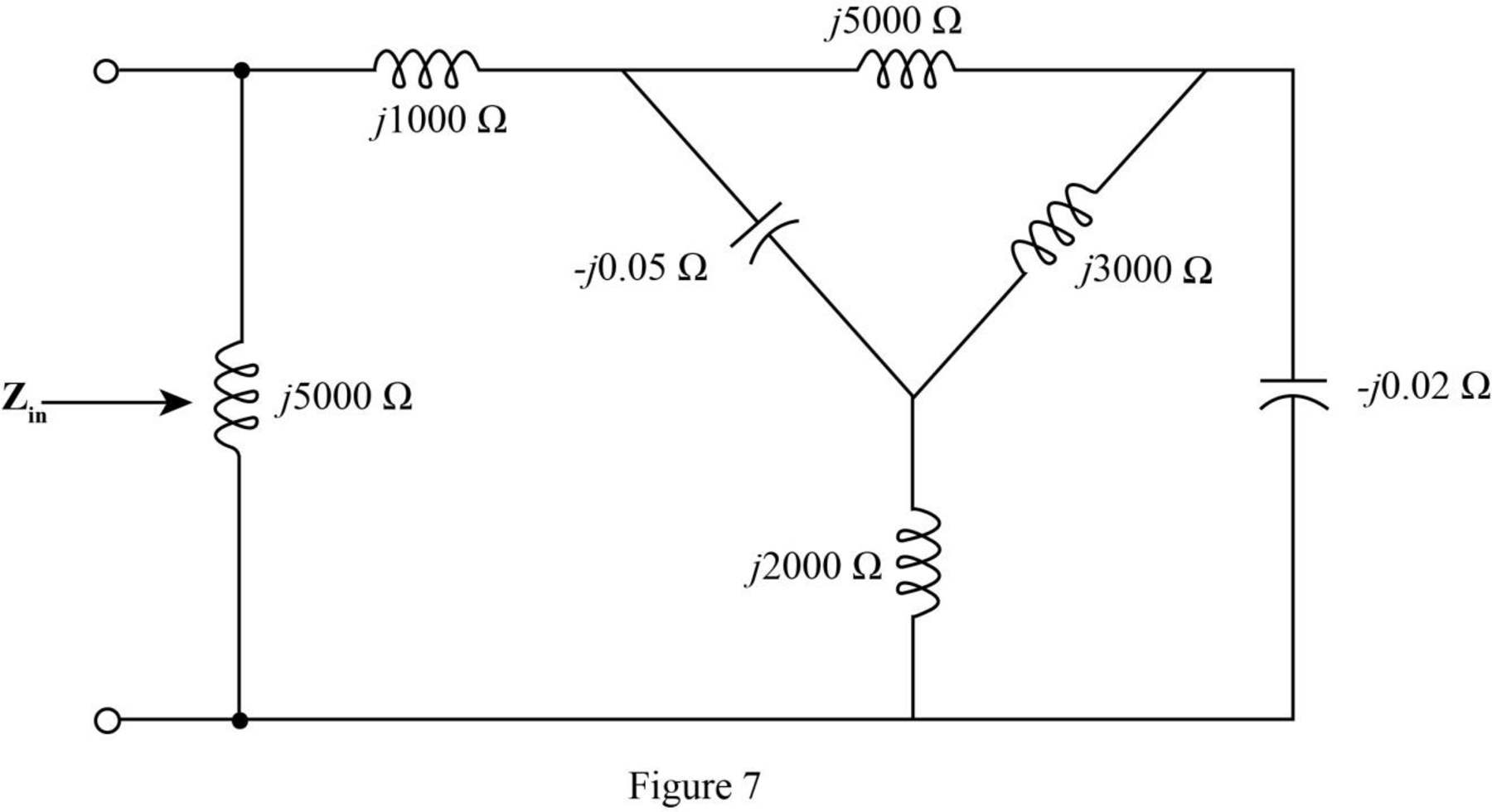
The
The required diagram is shown in the Figure 8
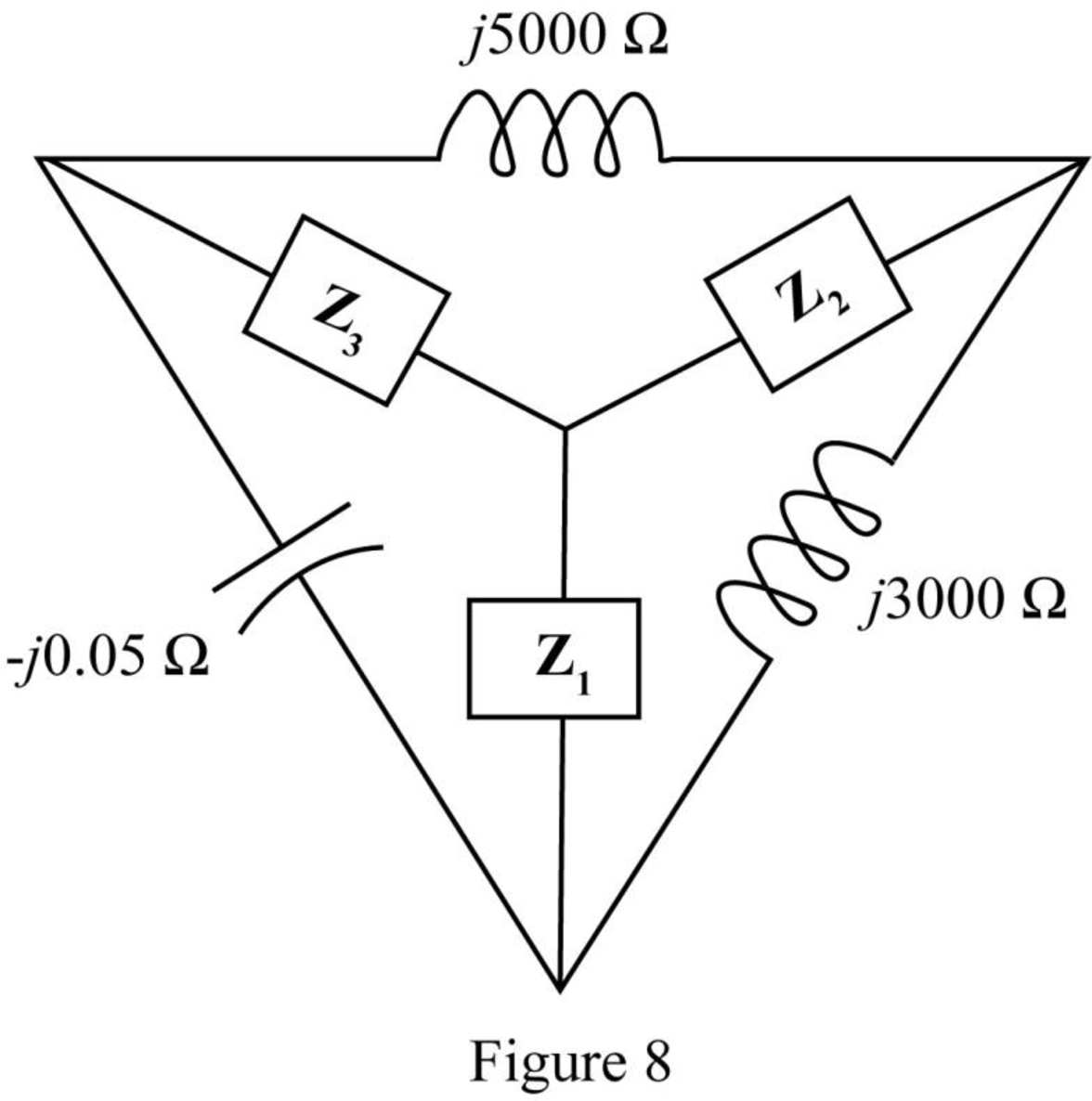
Here,
The impedance
The impedance
The impedance
The modified diagram is shown in Figure 9.
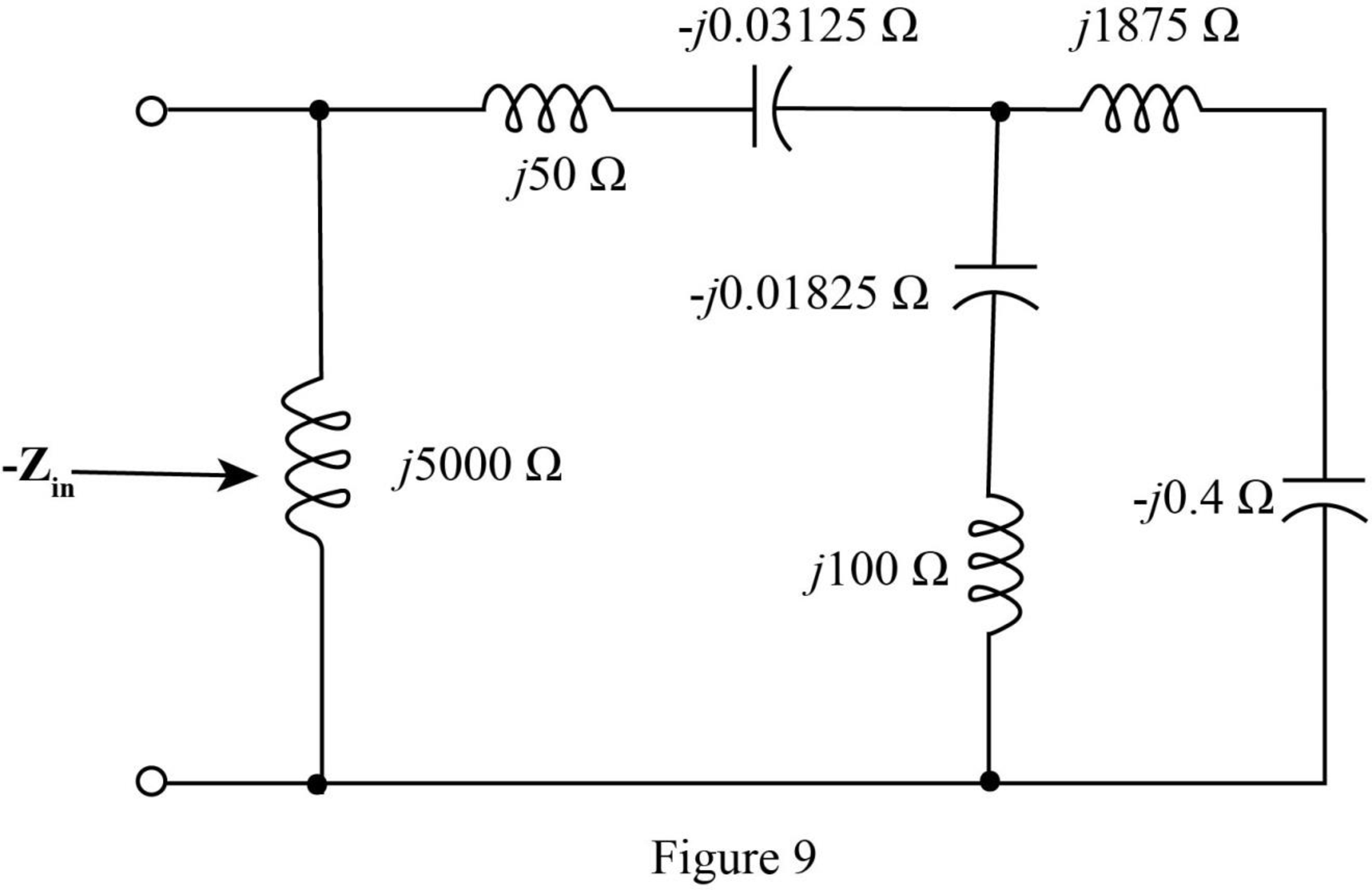
Add the impedances in series in the above network and redraw the network.
The required diagram is shown in Figure 10.
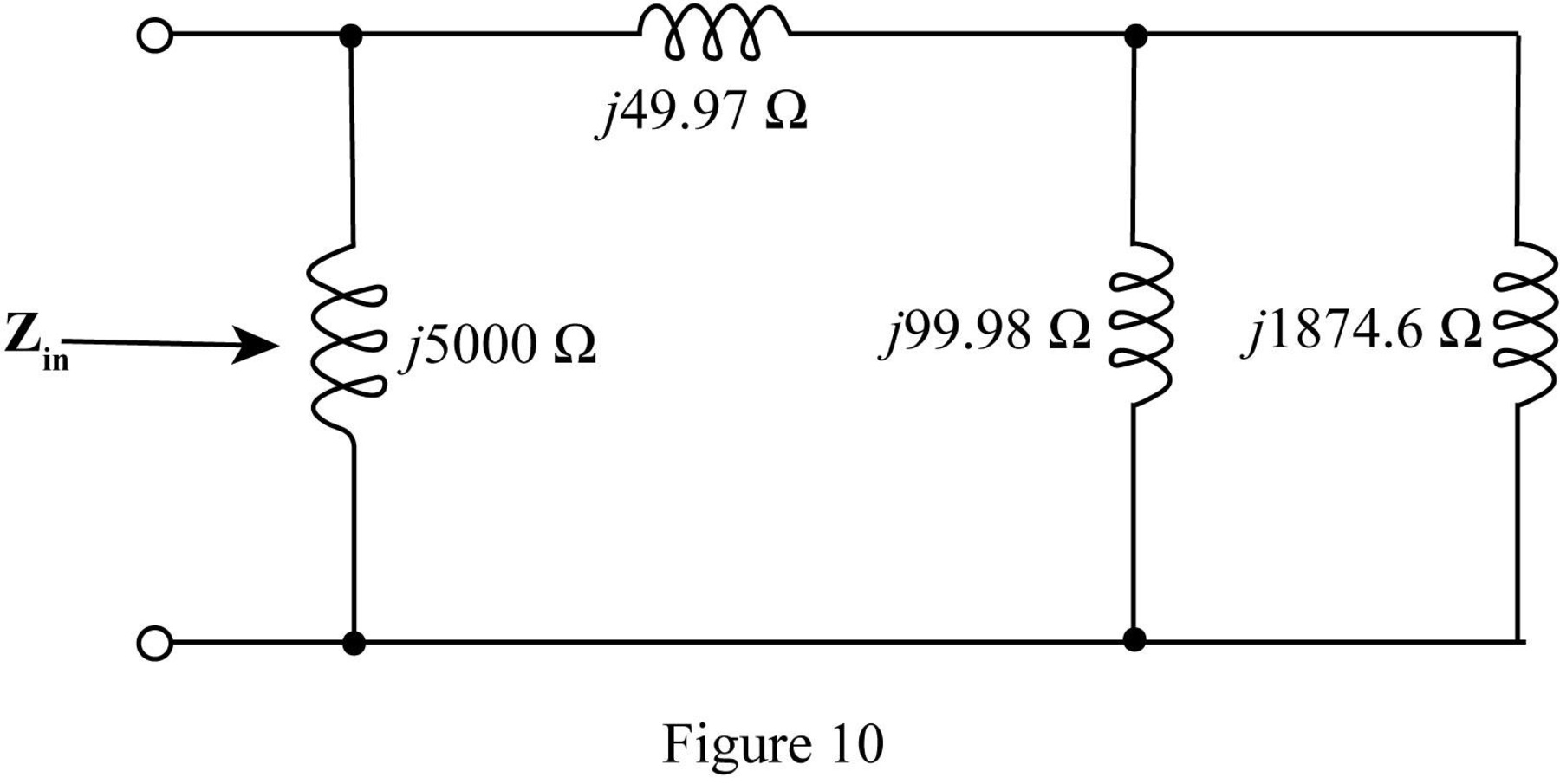
In the above circuit
Thus, the parallel combination
Mark the equivalent impedance and redraw the circuit.
The required figure is shown in Figure 11.
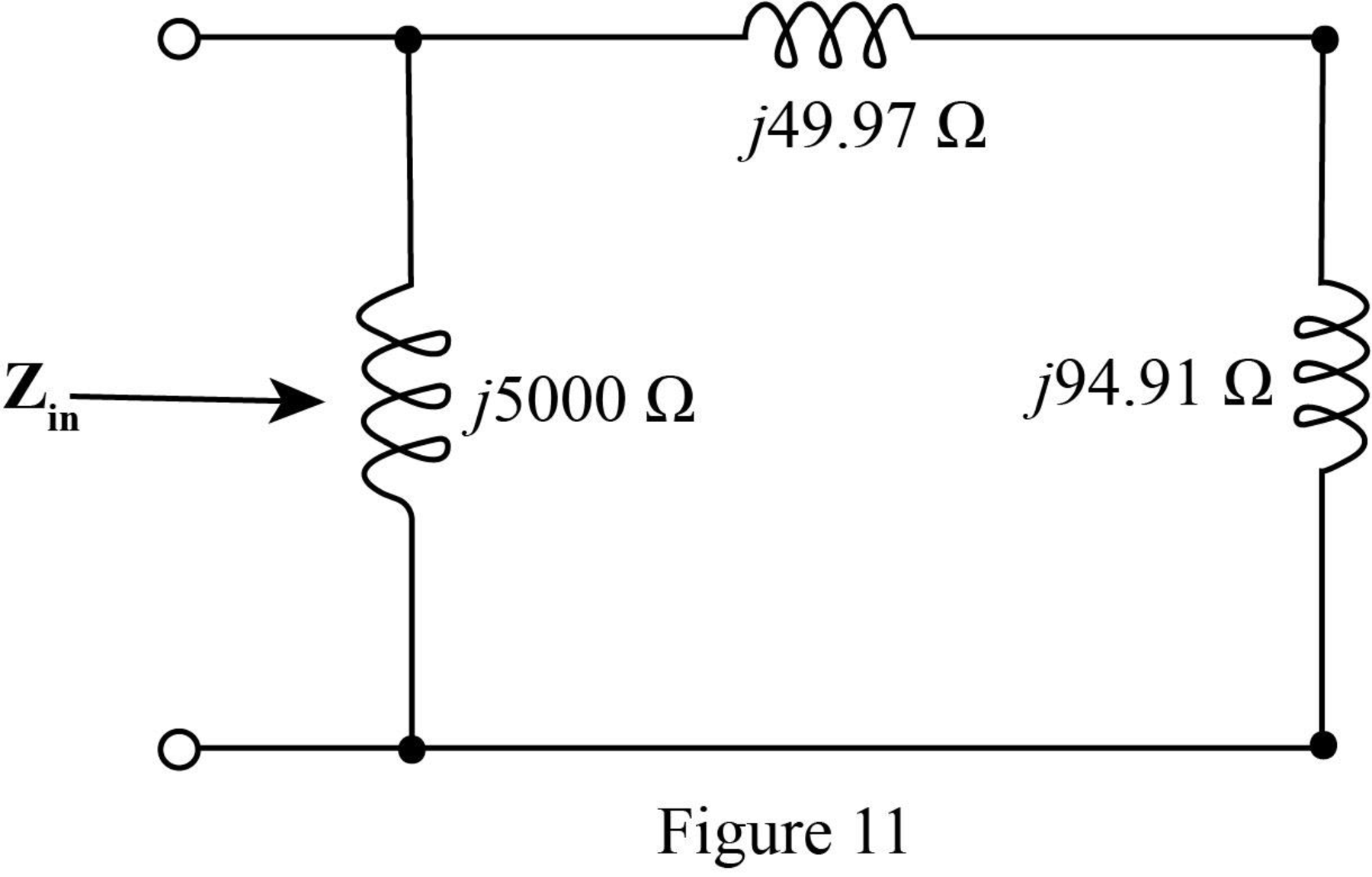
The value of the input impedance
Solve it further as,
Conclusion:
Therefore the value of the input impedance for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
ENGINEERING CIRCUIT...(LL)>CUSTOM PKG.<
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Starting Out with C++: Early Objects (9th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- 15arrow_forwardGiven the following, assume 0.7 V votlage drop across LEDs when they are positively biased.(a) When VB=0V, which LED is on?(b) When VB=5V, which LED is on?(c) If you want to limit the current through the LEDs to 10mA for both cases of 3(a) and 3 (b), find out the resistor values of RG and RR.arrow_forwardGiven the following, the intial condtion of output Q is high (H). (a) When /ALM is pushed on, creating a short to ground, what are the inputvoltages of S and R, and the output voltage Q?(b) After (a) happens, /ALM is released. What is the output voltage Q?(c) After (a) and (b) happen, /RESET is pushed on, creating a short to ground,what are the input voltages of S and R, and the output voltage Q?(d) After (a), (b) and (c) happen, /RESET is released. What is the output voltageQ?arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





