Concept explainers
To review:
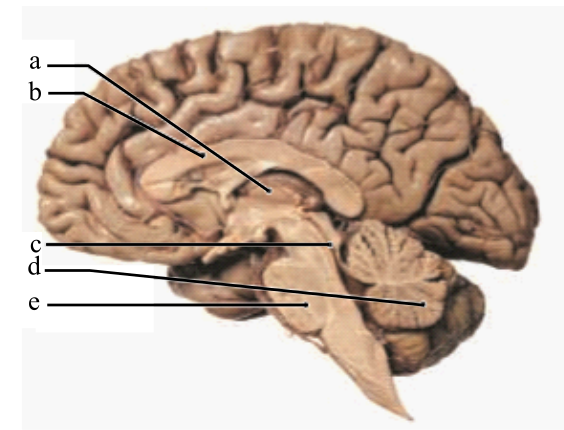
Label the following terms in the given diagram of the midsagittal section of the brain: pons, corpus callosum, cerebellum, thalamus, and cerebral aqueduct.
Introduction:
The brain is the prime organ of the CNS (central nervous system). It is divided into six major regions on the basis of structure and function, which are cerebrum, cerebellum, medulla oblongata, pons, diencephalon, and mesencephalon.
Explanation of Solution
The structures of the midsagittal section of the brain are labeled as below:
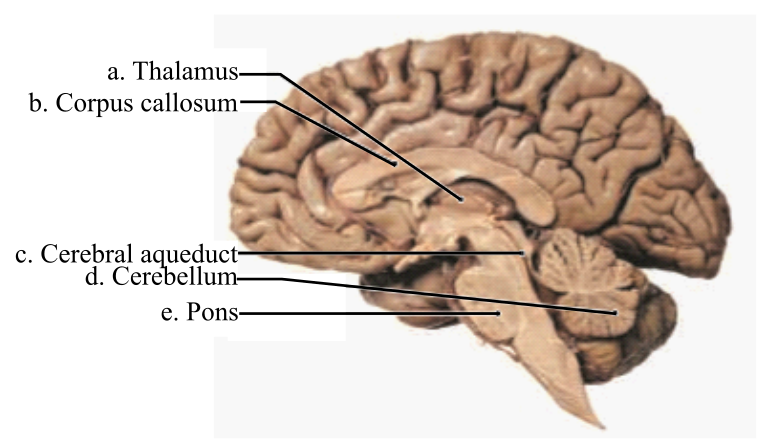
Thalamus: It is a part of the diencephalon that is further divided into right and left thalamus. This region is assigned the duty to relay and process sensory information across the brain.
Corpus callosum: It is a bundle of commissural fibers that connects the two cerebral hemispheres. It functions to transfer information from one hemisphere to another. It contains the largest portion of the white matter in the brain.
Cerebral aqueduct: It is a part of the mesencephalon or midbrain. It connects the third and fourth ventricles within the diencephalon and mesencephalon respectively. It is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which flows into the ventricles.
Cerebellum: It is a part of the hindbrain and called as the small brain. It functions to relay motor sensations and is involved in intellectual development. It also maintains the posture of the body.
Pons: It is a part of the brainstem and is located below the midbrain, above the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum. It functions to relay sensory information between the thalamus and the cerebellum. It is responsible for the maintenance of body posture, hearing, taste, touch, pain, facial expression, chewing, salivation, and secretion of tears.
Therefore, the structures of a midsagittal section of the brain are:
| a | Thalamus |
| b | Corpus callosum |
| c | Cerebral aqueduct |
| d | Cerebellum |
| e | Pons |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY COMM COLL PHILADELPHIA
- Amino Acid Coclow TABle 3' Gly Phe Leu (G) (F) (L) 3- Val (V) Arg (R) Ser (S) Ala (A) Lys (K) CAG G Glu Asp (E) (D) Ser (S) CCCAGUCAGUCAGUCAG 0204 C U A G C Asn (N) G 4 A AGU C GU (5) AC C UGA A G5 C CUGACUGACUGACUGAC Thr (T) Met (M) lle £€ (1) U 4 G Tyr Σε (Y) U Cys (C) C A G Trp (W) 3' U C A Leu בוט His Pro (P) ££ (H) Gin (Q) Arg 흐름 (R) (L) Start Stop 8. Transcription and Translation Practice: (Video 10-1 and 10-2) A. Below is the sense strand of a DNA gene. Using the sense strand, create the antisense DNA strand and label the 5' and 3' ends. B. Use the antisense strand that you create in part A as a template to create the mRNA transcript of the gene and label the 5' and 3' ends. C. Translate the mRNA you produced in part B into the polypeptide sequence making sure to follow all the rules of translation. 5'-AGCATGACTAATAGTTGTTGAGCTGTC-3' (sense strand) 4arrow_forwardWhat is the structure and function of Eukaryotic cells, including their organelles? How are Eukaryotic cells different than Prokaryotic cells, in terms of evolution which form of the cell might have came first? How do Eukaryotic cells become malignant (cancerous)?arrow_forwardWhat are the roles of DNA and proteins inside of the cell? What are the building blocks or molecular components of the DNA and proteins? How are proteins produced within the cell? What connection is there between DNA, proteins, and the cell cycle? What is the relationship between DNA, proteins, and Cancer?arrow_forward
- please fill in the empty sports, thank you!arrow_forwardIn one paragraph show how atoms and they're structure are related to the structure of dna and proteins. Talk about what atoms are. what they're made of, why chemical bonding is important to DNA?arrow_forwardWhat are the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins).arrow_forward
- The Sentinel Cell: Nature’s Answer to Cancer?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question You are working to characterize a novel protein in mice. Analysis shows that high levels of the primary transcript that codes for this protein are found in tissue from the brain, muscle, liver, and pancreas. However, an antibody that recognizes the C-terminal portion of the protein indicates that the protein is present in brain, muscle, and liver, but not in the pancreas. What is the most likely explanation for this result?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forward
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Sectional Anatomy: An Imaging App...BiologyISBN:9781133960867Author:Denise L. LazoPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Sectional Anatomy: An Imaging App...BiologyISBN:9781133960867Author:Denise L. LazoPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





