
Concept explainers
a.
To calculate: The PV of total outflows of The Bowman Corporation.
Introduction:
The current value of an investment or an asset is termed as its present value. It is evaluated by discounting the
a.
Answer to Problem 17P
The PV of total outflow of The Bowman Corporation is $1,458,528.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of PV of outflows:
Working Notes:
Calculation of payment of call premium:
Calculation of tax saving per year:
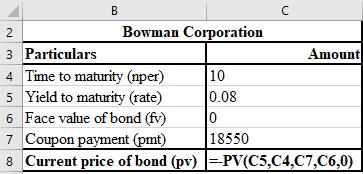
The calculation of current price of bond, that is, PV of future tax savings is shown below.
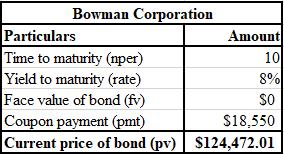
The formula used for the calculation of current price of bond, that is, PV of future tax savings is shown below.
Calculation of underwriting cost of new issue:
b.
To calculate: The PV of the total inflow of The Bowman Corporation.
Introduction:
Present value (PV):
The current value of an investment or an asset is termed as its present value. It is evaluated by discounting the future value of the investment or asset.Â
b.
Answer to Problem 17P
The PV of the total inflow of Bowman Corporation is $1,199,484.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of PV of inflows:
Working Notes:
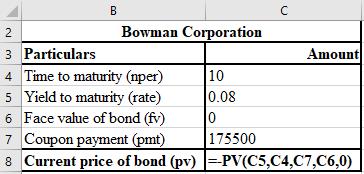
The calculation of PV of future tax savings is shown below.
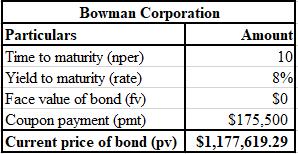
The formula used for the calculation of PV of future tax savings is shown below.
The calculation of PV of deferred future write off is shown below.
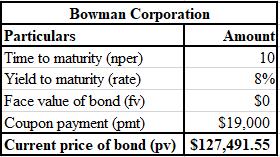
The formula used for the calculation of PV of deferred future write off is shown below.
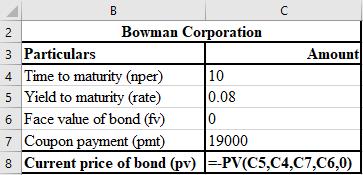
Calculation of gain in old underwriting cost write-off:
Calculation of Underwriting cost write-off:
c.
To calculate: The NPV of The Bowman Corporation.
Introduction:
A project’s NPV profile is the representation done graphically of the project’s NPV corresponding to different values of the rate of discount. It shows the changes that take place in NPV as a result of the changes in the cost of capital.
c.
Answer to Problem 17P
The NPV of The Bowman Corporation is ($259,045).
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of NPV:
d.
To determine: Whether the old issue shall be refunded with The Bowman Corporation’s new debt.
Introduction:
Present value (PV):
The current value of an investment or an asset is termed as its present value. It is evaluated by discounting the future value of the investment or asset.Â
d.
Answer to Problem 17P
No, the old issue of The Bowman Corporation shall not be refunded.
Explanation of Solution
The Bowman’s Corporation’s old issue shall not be refunded, especially if there exists a chance that the rate of interest will further go down, as the NPV calculated in part (c) is negative.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Foundations of Financial Management
- Muskoka Tourism has announced a rights offer to raise $30 million for a new magazine, titled ‘Discover Muskoka’. The magazine will review potential articles after the author pays a nonrefundable reviewing fee of $5,000 per page. The stock currently sells for $52 per share and there are 3.9 million shares outstanding.arrow_forwardSs stores probarrow_forwardHenrietta’s Pine Bakery Corporation would like to raise $75 million to finance its expansion into new markets. The company will sell new shares of equity via a general cash offering to raise the needed funds. If the offer price is $15 per share and the company’s underwriters charge a 6% spread, how many shares need to be sold?arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





