
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the given oxides are acidic, basic, amphoteric or neutral has to be classified.
Concept Information:
Oxides of metals and non-metals may be,
Acidic - exhibits acidic character
Basic - exhibits basic character
Amphoteric - exhibits both acidic and basic character
Neutral - does not exhibit any of the acidic or basic character
Except Beryllium oxide (
None of the oxides of non-metals show basic property.
Oxides of non-metals with higher oxidation number of the main group elements are highly acidic whereas those with lesser oxidation number does not exhibit measurable acidic properties.
Beryllium oxide (
To Classify: The given oxide
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given oxide
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the given oxides are acidic, basic, amphoteric or neutral has to be classified.
Concept Information:
Oxides of metals and non-metals may be,
Acidic - exhibits acidic character
Basic - exhibits basic character
Amphoteric - exhibits both acidic and basic character
Neutral - does not exhibit any of the acidic or basic character
Except Beryllium oxide (
None of the oxides of non-metals show basic property.
Oxides of non-metals with higher oxidation number of the main group elements are highly acidic whereas those with lesser oxidation number does not exhibit measurable acidic properties.
Beryllium oxide (
To Classify: The given oxide
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given oxide
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the given oxides are acidic, basic, amphoteric or neutral has to be classified.
Concept Information:
Oxides of metals and non-metals may be,
Acidic - exhibits acidic character
Basic - exhibits basic character
Amphoteric - exhibits both acidic and basic character
Neutral - does not exhibit any of the acidic or basic character
Except Beryllium oxide (
None of the oxides of non-metals show basic property.
Oxides of non-metals with higher oxidation number of the main group elements are highly acidic whereas those with lesser oxidation number does not exhibit measurable acidic properties.
Beryllium oxide (
To Classify: The given oxide 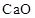 as acidic, basic, amphoteric or neutral
as acidic, basic, amphoteric or neutral
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given oxide
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether the given oxides are acidic, basic, amphoteric or neutral has to be classified.
Concept Information:
Oxides of metals and non-metals may be,
Acidic - exhibits acidic character
Basic - exhibits basic character
Amphoteric - exhibits both acidic and basic character
Neutral - does not exhibit any of the acidic or basic character
Except Beryllium oxide (
None of the oxides of non-metals show basic property.
Oxides of non-metals with higher oxidation number of the main group elements are highly acidic whereas those with lesser oxidation number does not exhibit measurable acidic properties.
Beryllium oxide (
To Classify: The given oxide
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The given oxide
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether the given oxides are acidic, basic, amphoteric or neutral has to be classified.
Concept Information:
Oxides of metals and non-metals may be,
Acidic - exhibits acidic character
Basic - exhibits basic character
Amphoteric - exhibits both acidic and basic character
Neutral - does not exhibit any of the acidic or basic character
Except Beryllium oxide (
None of the oxides of non-metals show basic property.
Oxides of non-metals with higher oxidation number of the main group elements are highly acidic whereas those with lesser oxidation number does not exhibit measurable acidic properties.
Beryllium oxide (
Interpretation:
Whether the given oxides are acidic, basic, amphoteric or neutral has to be classified.
Concept Information:
Oxides of metals and non-metals may be,
Acidic - exhibits acidic character
Basic - exhibits basic character
Amphoteric - exhibits both acidic and basic character
Neutral - does not exhibit any of the acidic or basic character
Except Beryllium oxide (
None of the oxides of non-metals show basic property.
Oxides of non-metals with higher oxidation number of the main group elements are highly acidic whereas those with lesser oxidation number does not exhibit measurable acidic properties.
Beryllium oxide (
To Classify: The given oxide
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The given oxide
(f)
Interpretation:
Whether the given oxides are acidic, basic, amphoteric or neutral has to be classified.
Concept Information:
Oxides of metals and non-metals may be,
Acidic - exhibits acidic character
Basic - exhibits basic character
Amphoteric - exhibits both acidic and basic character
Neutral - does not exhibit any of the acidic or basic character
Except Beryllium oxide (
None of the oxides of non-metals show basic property.
Oxides of non-metals with higher oxidation number of the main group elements are highly acidic whereas those with lesser oxidation number does not exhibit measurable acidic properties.
Beryllium oxide (
To Classify: The given oxide
(f)
Explanation of Solution
The given oxide
(g)
Interpretation:
Whether the given oxides are acidic, basic, amphoteric or neutral has to be classified.
Concept Information:
Oxides of metals and non-metals may be,
Acidic - exhibits acidic character
Basic - exhibits basic character
Amphoteric - exhibits both acidic and basic character
Neutral - does not exhibit any of the acidic or basic character
Except Beryllium oxide (
None of the oxides of non-metals show basic property.
Oxides of non-metals with higher oxidation number of the main group elements are highly acidic whereas those with lesser oxidation number does not exhibit measurable acidic properties.
Beryllium oxide (
To Classify: The given oxide
(g)
Explanation of Solution
The given oxide
(h)
Interpretation:
Whether the given oxides are acidic, basic, amphoteric or neutral has to be classified.
Concept Information:
Oxides of metals and non-metals may be,
Acidic - exhibits acidic character
Basic - exhibits basic character
Amphoteric - exhibits both acidic and basic character
Neutral - does not exhibit any of the acidic or basic character
Except Beryllium oxide (
None of the oxides of non-metals show basic property.
Oxides of non-metals with higher oxidation number of the main group elements are highly acidic whereas those with lesser oxidation number does not exhibit measurable acidic properties.
Beryllium oxide (
To Classify: The given oxide
(h)
Explanation of Solution
The given oxide
(i)
Interpretation:
Whether the given oxides are acidic, basic, amphoteric or neutral has to be classified.
Concept Information:
Oxides of metals and non-metals may be,
Acidic - exhibits acidic character
Basic - exhibits basic character
Amphoteric - exhibits both acidic and basic character
Neutral - does not exhibit any of the acidic or basic character
Except Beryllium oxide (
None of the oxides of non-metals show basic property.
Oxides of non-metals with higher oxidation number of the main group elements are highly acidic whereas those with lesser oxidation number does not exhibit measurable acidic properties.
Beryllium oxide (
To Classify: The given oxide
(i)
Explanation of Solution
The given oxide
(j)
Interpretation:
Whether the given oxides are acidic, basic, amphoteric or neutral has to be classified.
Concept Information:
Oxides of metals and non-metals may be,
Acidic - exhibits acidic character
Basic - exhibits basic character
Amphoteric - exhibits both acidic and basic character
Neutral - does not exhibit any of the acidic or basic character
Except Beryllium oxide (
None of the oxides of non-metals show basic property.
Oxides of non-metals with higher oxidation number of the main group elements are highly acidic whereas those with lesser oxidation number does not exhibit measurable acidic properties.
Beryllium oxide (
To Classify: The given oxide
(j)
Explanation of Solution
The given oxide
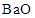 is an oxide of alkaline earth metal. Therefore,
is an oxide of alkaline earth metal. Therefore,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK GENERAL CHEMISTRY: THE ESSENTIAL CO
- Identify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forwardWhy isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forward
- What is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forward
- Q Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardb. ὋΗ CH3CH2OH H2SO4arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





