
Concept explainers
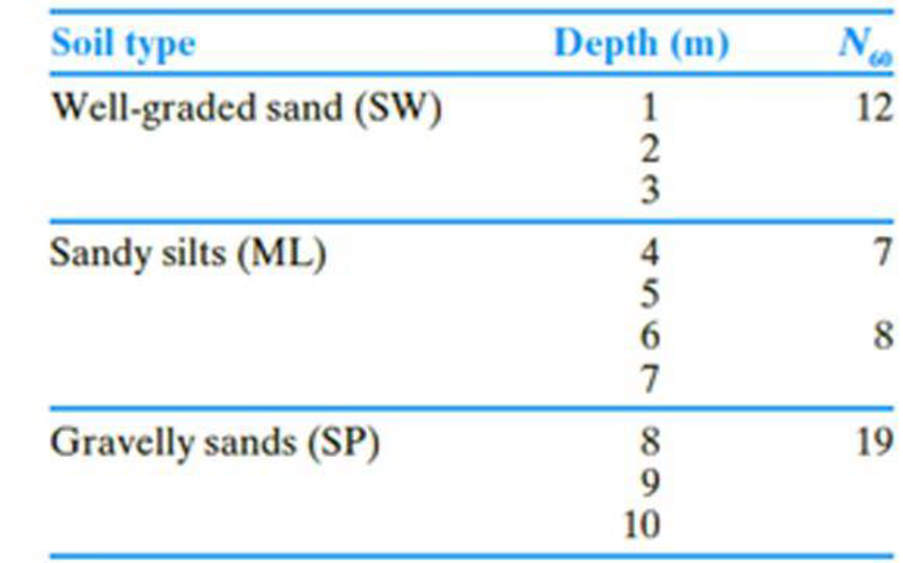
The following table shows the boring log at a site where a multi-story shopping center would be constructed. Soil classification and the standard penetration number, N60, are provided in the boring log. All columns of the building are supported by square footings which must be placed at a depth of 1.5 m. Additionally, the settlement (elastic) of each footing must be restricted to 20 mm. Since the column loads at different location can vary, a design chart is helpful for quick estimation of footing size required to support a given load.
- a. Prepare a chart by plotting the variation of maximum allowable column loads with footing sizes, B = 1 m, 1.5 m, 2 m, and 3 m. Use a factor of safety of 3.
- b. If the gross column load from the structure is 250 kN, how would you use this chart to select a footing size?
- c. What would be the design footing size for the column in Part (b) if you use Terzaghi’s bearing capacity equation? For the well graded sand, assume that ϕ′ = 33°. Use Fs = 3.
- d. Compare and discuss the differences in footing sizes obtained in Parts b and c.
(a)
Plot the variation of maximum allowable column loads with size of footings to prepare a chart.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The location of depth of footing
The given size of the footing B is 1 m, 1.5 m, 2 m, and 3 m.
The settlement of each footing
The given factor of safety
Calculation:
For B value is 1 m:
Determine the depth factor using the relation.
Substitute 1.5 m for
The
The field standard penetration number
Determine the depth of foundation for the field standard penetration number gets averaged.
Substitute 1.5 m for
Determine the averaged
Here,
Substitute 12 for
Determine the net allowable bearing capacity of the soil
Substitute 10 for
Determine the maximum allowable column load
Substitute
For B value is 1.5 m:
Determine the depth factor using the relation.
Substitute 1.5 m for
The field standard penetration number
Determine the depth of foundation for the field standard penetration number gets averaged.
Substitute 1.5 m for
Determine the averaged
Here,
Substitute 7 for
Determine the net allowable bearing capacity of the soil
Substitute 8 for
Determine the maximum allowable column load
Substitute
For B value is 2 m:
Determine the depth factor using the relation.
Substitute 1.5 m for
The field standard penetration number
Determine the depth of foundation for the field standard penetration number gets averaged.
Substitute 1.5 m for
Determine the averaged
Substitute 12 for
Determine the net allowable bearing capacity of the soil
Substitute 9 for
Determine the maximum allowable column load
Substitute
For B value is 3 m:
Determine the depth factor using the relation.
Substitute 1.5 m for
The field standard penetration number
Determine the depth of foundation for the field standard penetration number gets averaged.
Substitute 1.5 m for
Determine the averaged
Here,
Substitute 12 for
Determine the net allowable bearing capacity of the soil
Substitute 12 for
Determine the maximum allowable column load
Substitute
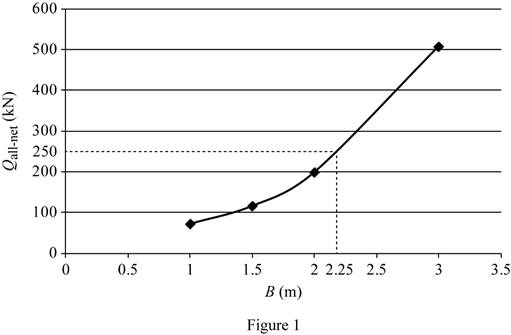
Summarize the calculated values as in Table (1).
| Width B (m) | Column load (kN) |
| 1 | 71 |
| 1.5 | 115 |
| 2 | 198 |
| 3 | 507.5 |
Plot the graph between the size of the footing and the column load as in Figure (1).
(b)
Find the footing size for the given gross column load of 250 kN.
Answer to Problem 16.1CTP
The footing size for the given gross column load of 250 kN is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The location of depth of footing
The given size of the footing B is 1 m, 1.5 m, 2 m, and 3 m.
The settlement of each footing
The given factor of safety
Calculation:
Refer Figure (1).
The size of the footing is 2.25 m for the gross column load of 250 kN.
Therefore, the footing size for the given gross column load of 250 kN is
(c)
Find the design column load for the footing size of 2.25 m using the Terzaghi’s bearing capacity equation.
Answer to Problem 16.1CTP
The design column load for the footing size of 2.25 m using the Terzaghi’s bearing capacity equation is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The value of cohesion
The soil friction angle
The location of depth of footing base
The width of the footing B is 2.25 m.
The given factor of safety
Calculation:
Determine the net ultimate bearing capacity of the soil
Here,
Take the unit weight of the soil
Refer Table 16.1, “Terzaghi’s bearing-capacity factors–
Take the
Substitute
Determine the net allowable bearing capacity
Substitute
Therefore, the design column load for the footing size of 2.25 m using the Terzaghi’s bearing capacity equation is
(d)
Compare and discuss the differences in footing sizes obtained in parts (b) and (c).
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The soil friction angle
The location of depth of footing base
The width of the footing B is 2.25 m.
The given factor of safety
Calculation:
The net allowable column load obtained by using Terzaghi’s bearing capacity equation (2,173 kN) is significantly higher than the method based on the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEER
- ***The answer includes: 1. The correct dimension of variables is: F: MLT^-2, v: LT^-1, μ:ML^-1T^-1, ρ: ML^-3, w: L 2. Choice of repeating variables: (w,v,ρ). Choice does NOT include F. Stick with choice throughout. 3. # pi terms = # variables- # dimensions = 5-3=2. 4. π1= F/w^2v^2ρ 5. π2= μ/wvp These are the correct answers for the problem, I just need the work involved in solving itarrow_forwardThe cross-section shown is used to support the loads on the beam below. The moment of inertia of the section is |= 1384 in4 and distance of the centroid of the section from the bottom is y = 5.8 in. [MA=4800 lb-ft, w=600 lb/ft, P=1400 lb, a=5ft,b=7ft,c= 2 ft,d=5ft] Ma b ཅ་ d 15 in 1.5 in 1.5 in. 2 in. k11 in. Cross section of the beam a) Construct the complete shear-force and bending-moment diagrams for the beam and determine the maximum positive bending moment in the beam. b) determine the maximum negative bending moment in the beam. c) Determine the maximum tension bending stress at any location along the beam. d) Determine the maximum compression bending stress at any location along the beam.arrow_forwardCOMPUTE THE VOLUME OF THE STOCKPILE SHOWN BELOW IN CUBIC YARDS USING THE AVERAGE AREA METHOD. PROVIDE YOUR RESULTS ON THIS PAGE USING THE WINDOWS CLIPBOARD CUT AND PASTE TOOLS. 166 170 168 -172 CONTOUR AREA = 2,663 S.F. CONTOUR AREA = 8,217 S.F CONTOUR AREA = 16,284 S.F CONTOUR AREA = 29,734 S.F. AVERAGE AREA METHOD FOR VOLUME OF EXCAVATION AND STOCKPILE CONTOUR ELEVATION CONTOUR AREA (FT) (FT³) ELEVATION DIFFERENCE (DEPTH) BETWEEN CONSECUTIVE CONTOURS AVERAGE AREA BETWEEM CONSECUTIVE CUMMULATIVE CONTOURS VOLUME (FT³) CUMMULATIVE VOLUME VOLUME (CY) (FT³) (FT) (FT)arrow_forward
- Using the graphic below, computer the bearings for courses AF, AB, and BC and azimuths for courses AF and BC. 128°28'58" 0.00 TRV-A 65°5'34" F 86°34'27" B 0.00 TRY-B • Azimuth AF: Bearing AF: Bearing AB: Azimuth BC: Bearing BC:arrow_forward4G 46:58 Problem 1 You are in the process of designing a water supply system for the whole Iligan City, and the design life of your system is to end in the year 2070. The population in the town has been measured every 10 years since 1980 by the Philippine Statistics Authority, and the reported populations are tabulated below. Estimate the population in the town using (a) arithmetic growth projection, (b) geometric growth projection (exponential formula), (c) declining growth projection (assuming a saturation concentration of 480,000 people), and (d) logistic curve projection. Population Year 1980 167,358 1990 226,568 2000 285,061 2010 322,821 2020 342,618 1.a) Arithmetic growth projection estimate Your answer * 5 points 1.b) Geometric growth * 5 points projection estimate Your answer 1.c) Declining growth projection estimate Your answer * 10 points כ 95arrow_forward2. Design a W section for a beam of A 36 steel Fy = 248 MPa to carry a uniform load of 293 kN/m on a simply supported span of 1.5 m. Assume lateral bracing is adequate for stability. Wt. of beam Area Depth (d) Properties of W sections available W 12 x 27 394.9 N/m Flange width (bf) Flange thickness (tf) Web thickness (tw) Moment of inertia (IX) Section modulus (SX) 5129 303.78 165.02 10.16 6.02 84.9 x 106 mm² 560.4 x 103 mm³ 3 W 12 x 31 453.4 N/m 5890 W 14 x 26 380.27 N/m 4948 307.09 352.81 165.74 127.64 11.81 10.62 6.73 6.48 99.5 x 106 mm² 101.56 x 106 mm4 674.3 x 103 mm³ 575.2 x 103 mm³arrow_forward
- ⚫ For the semi-circular arch shown in Fig.2, draw shear and bending moment diagram. 10 kN 5 m SkNarrow_forwardQ2: A 2 m X 3 m foundation is expected to carry a column load with eccentricities eB = 0.15 m and eL = 0.2 m. It is placed in a soil where e' = 10.0 kN/m2, 0'= 22°, and y = 18.0 kN/m², at 1.0 m depth. Determine the maximum load the foundation can carry with factor of safety of 3.arrow_forwardDetermine the forces in each member for the truss shown in using joint method and state if the member is in tension or compression. Wake table to show your final results. 24 kN 4 m 4 m 4 m SkN 3m shear Narrow_forward
- I need help calculating my VPC 0f 14+50, VPI 17+00 and VPT 19+50 elevations if I am given Sta 11+00 with elevation 5946.31. Problem 32 in the image below gives g1 and g2, k=64.arrow_forwardused to support the loads on the beam below. The moment of inertia of the section is |= 1384 in and distance of the centroid of the section from the bottom is y = 5.8 in. [MA 4000 lb-ft, w=900 lb/ft, P=1500 lb, a = 5 ft, b = 8 ft, c = 3 ft, d = 6 ft] Ma W a b B d P 1.5 in.k 1.5 in. 15 in. z- 2 in. 11 in. Cross section of the beam Construct the complete shear- force and bending-moment diagrams for the beam and determine the maximum positive bending moment in the beam.arrow_forwardThe cross-section shown is used to support the loads on the beam below. The moment of inertia of the section is |= 1384 in and distance of the centroid of the section from the bottom is y = 5.8 in. [MA-4000 lb-ft, w=900 lb/ft, P=1500 lb, a = 5 ft, b = 8 ft, c = 3 ft, d = 6 ft] Ma 15 in 1.5 in 13 in. 2 in 11 in. Cross section of the beam Determine the maximum tension bending stress at any location along the beam.arrow_forward
 Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning

