
A cylinder with a circular hole is rolling without slipping on a fixed curved surface as shown. The cylinder would have a weight of 16 lb without the hole, but with the hole it has a weight of 15 lb. Knowing that at the instant shown the disk has an angular velocity of 5 rad/s clockwise, determine (a) the angular acceleration of the disk, (b) the components of the reaction force between the cylinder and the ground at this instant.
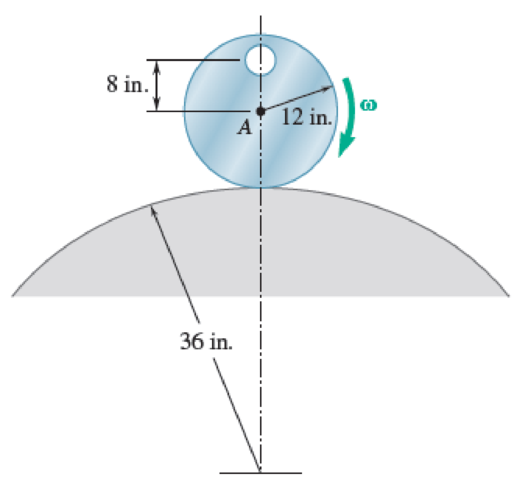
Fig. P16.161
(a)
The angular acceleration of the disk.
Answer to Problem 16.161RP
The angular acceleration of the disk is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of the cylinder without hole is
The weight of the cylinder with hole is
The angular velocity of the disk is
Calculation:
Consider the acceleration due to gravity as
Consider that the mass center of the cylinder is G and it lies at a distance b from center A, and C is the contact point between cylinder and the curved surface is the origin of the coordinate system.
Consider that the radius of cylinder is r and the radius of the curved surface is R.
Sketch the geometry of the cylinder as shown in Figure 1.
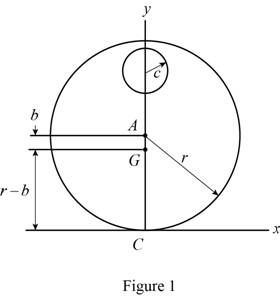
Refer to Figure 1.
Calculate the position vector
The position vector of P with respect to C.
The position vector of G with respect to C.
The position vector of A with respect to C.
The cylinder rolls without slipping on a fixed curved surface hence, the horizontal component of acceleration of point C is
Calculate the acceleration of point C
Substitute 0 for
The acceleration of the disk at A is
Calculate the acceleration of point A
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of point P
Here,
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of point G
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of point A
Substitute
Subtract Equation (2) from Equation (1) as shown below.
Substitute
Calculate the velocity of point A
Calculate the vertical component of acceleration of point A
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of point G
Substitute
Calculate the effective force at the mass center
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of the cylinder as shown in Figure 2.
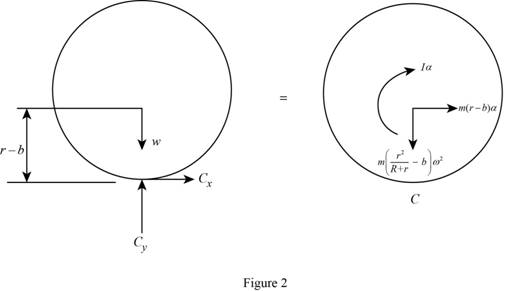
Refer to Figure 2.
Apply the Equilibrium of moment about C as shown below.
Hence, the angular acceleration of the disk is
(b)
The components of the reaction force between the cylinder and the ground.
Answer to Problem 16.161RP
The component of the reaction along x direction is
The component of the reaction along y direction is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of the cylinder without hole is
The weight of the cylinder with hole is
The angular velocity of the disk is
Calculation:
Refer to part (a).
The angular acceleration of the disk is
Refer to Figure 2.
Apply the Equilibrium of force along x direction as shown below.
Substitute 0 for
Hence, the component of the reaction along x direction is
Apply the Equilibrium of force along y direction as shown below.
Sketch the cylinder with hole as shown in Figure 3.
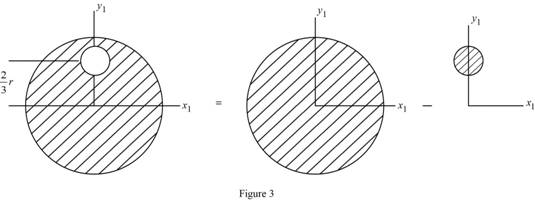
Refer to Figure 3.
Calculate the area of solid cylinder
Calculate the center of gravity of solid cylinder in vertical direction
Calculate the area of hole
Calculate the center of gravity of hole in vertical direction
Calculate the distance
Substitute
Calculate the component of the reaction along y direction as shown below.
Substitute
Therefore, the component of the reaction along y direction is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
<LCPO> VECTOR MECH,STAT+DYNAMICS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
- Sketch and describe hatch coamings. Describe structrual requirements to deck plating to compensate discontinuity for corners of a hatch. Show what is done to the deck plating when the decks are cut away and include the supporting members.arrow_forwardAn Inclining experiment done on a ship thats 6500 t, a mass of 30t was moved 6.0 m transvesly causing a 30 cm deflection in a 6m pendulum, calculate the transverse meta centre height.arrow_forwarda ship 150 m long and 20.5 m beam floats at a draught of8 m and displaces 19 500 tonne. The TPC is 26.5 and midshipsection area coefficient 0.94. Calculate the block, prismatic andwaterplane area coefficients.arrow_forward
- A vessel loads 680 t fuel between forward and aft deep tanks. centre of gravity of forward tank is 24m forward of ships COG. centre to centre between tanks is 42 m. how much in each tank to keep trim the samearrow_forwardBeam of a vessel is 11% its length. Cw =0.72. When floating in SW of relative denisity 1.03, TPC is 0.35t greater than in freshwater. Find the length of the shiparrow_forwardAn inclining experiment was carried out on a ship of 4000tonne displacement, when masses of 6 tonne were moved transverselythrough 13.5 m. The deflections of a 7.5 m pendulurnwere 81, 78, 85, 83, 79, 82, 84 and 80 mm respectively.Caiculate the metacentric height.arrow_forward
- A ship of 10 000 tonne displacement has a waterplanearea of 1300 m2. The ship loads in water of 1.010 t/m3 andmoves into water of 1.026 t/m3. Find the change in meandraughtarrow_forwardA ship of 7000 tonne displacement has a waterplane areaof 1500 m2. In passing from sea water into river water of1005 kg/m3 there is an increase in draught of 10 cm. Find the Idensity of the sea water.arrow_forwardA ship has 300 tonne of cargo in the hold, 24 m forward ofmidships. The displacement of the vessel is 6000 tonne and its centre of gravity is 1.2 m forward of midships.Find the new position of the centre of gravity if this cargo ismoved to an after hold, 40 m from midshipsarrow_forward
- Sketch and describe how ships are supported in dry dock. When and where does the greatest amount of stresses occur?arrow_forwardSketch and desribe a balanced rudder and how it is suspendedarrow_forwardA ship 140 m long and 18 m beam floats at a draught of9 m. The immersed cross-sectionai areas at equai intervais are 5,60, 116, 145, 152, 153, 153, 151, 142, 85 and 0 m2 respectively.Calculate:(a) displacement(b) block coefficient(c) midship section area coefficient(d) prismatic coefficient.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





