
Concept explainers
A foreman has determined processing times at a work center for a set of jobs and now wants to sequence them. Given the information shown, do the following:
a. Determine the processing sequence using (1) FCFS, (2) SPT, (3) EDD, and (4) CR. For each sequence, compute the average job tardiness, the average flow time, and the average number of jobs at the work center. The list is in FCFS order.
b. Using the results of your calculations in part a, show that the ratio of average flow time and the average number of jobs measures are equivalent for all four sequencing rules.
c. Determine the processing sequence that would result using the S/O rule.
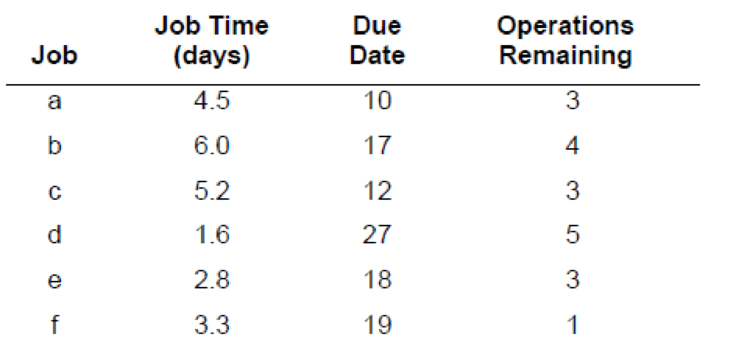
a)
1)
To determine: The processing sequence based on First Come First Served (FCFS).
Introduction: First Come First Served is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, the first come would be served first.
Answer to Problem 15P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Remaining number of operations |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 3 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 4 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 3 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 3 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 |
Determine the sequence using FCFS:
According to FCFS, the first come would be served first. Hence, the jobs should be sequenced in the order as per its arrival.
Hence, the sequence of jobs using FCFS is a-b-c-d-e-f.
Determine average flow time, average tardiness, and average number of jobs for FCFS:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Flow time (days) | Due date (days) | Tardiness |
| a | 4.5 | 4.5 | 10 | 0 |
| b | 6 | 10.5 | 17 | 0 |
| c | 5.2 | 15.7 | 12 | 3.7 |
| d | 1.6 | 17.3 | 27 | 0 |
| e | 2.8 | 20.1 | 18 | 2.1 |
| f | 3.3 | 23.4 | 19 | 4.4 |
| Total | 23.4 | 91.5 | 10.2 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job a:
Flowtime is less than the due date. Hence, there would be tardiness.
Tardiness of Job b:
Flowtime is less than the due date. Hence, there would be tardiness.
Tardiness of Job c:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job c is 3.7.
Note: The procedure continues for all the jobs.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 15.25 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 1.7 days.
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 3.9 jobs.
1)
To determine: The processing sequence based on First Come First Served (FCFS).
Introduction: First Come First Served is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, the first come would be served first.
Answer to Problem 15P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Remaining number of operations |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 3 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 4 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 3 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 3 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 |
Determine the sequence using FCFS:
According to FCFS, the first come would be served first. Hence, the jobs should be sequenced in the order as per its arrival.
Hence, the sequence of jobs using FCFS is a-b-c-d-e-f.
Determine average flow time, average tardiness, and average number of jobs for FCFS:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Flow time (days) | Due date (days) | Tardiness |
| a | 4.5 | 4.5 | 10 | 0 |
| b | 6 | 10.5 | 17 | 0 |
| c | 5.2 | 15.7 | 12 | 3.7 |
| d | 1.6 | 17.3 | 27 | 0 |
| e | 2.8 | 20.1 | 18 | 2.1 |
| f | 3.3 | 23.4 | 19 | 4.4 |
| Total | 23.4 | 91.5 | 10.2 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job a:
Flowtime is less than the due date. Hence, there would be tardiness.
Tardiness of Job b:
Flowtime is less than the due date. Hence, there would be tardiness.
Tardiness of Job c:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job c is 3.7.
Note: The procedure continues for all the jobs.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 15.25 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 1.7 days.
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 3.9 jobs.
2)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule Shortest Processing Time (SPT).
Introduction: Shortest Processing Tine is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, job with the shortest duration would be served first. Then, the process would be going on from shortest to largest duration.
Answer to Problem 15P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Remaining number of operations |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 3 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 4 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 3 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 3 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 |
Determine the sequence using SPT:
According to SPT, the job that has the shortest processing would be served first and it goes on as the processing time increase. Duration should be assembled in the ascending order
Hence, the sequence of jobs using SPT is d-e-f-a-c-b.
Determine average flow time, average tardiness, and average number of jobs for SPT:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Flow time (days) | Due date (days) | Tardiness |
| d | 1.6 | 1.6 | 27 | |
| e | 2.8 | 4.4 | 18 | |
| f | 3.3 | 7.7 | 19 | |
| a | 4.5 | 12.2 | 10 | 2.2 |
| c | 5.2 | 17.4 | 12 | 5.4 |
| b | 6 | 23.4 | 17 | 6.4 |
| Total | 23.4 | 66.7 | 14 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job d, Job e, and Job f:
Flow time of Job d, Job e, and Job f is less than its respective due date. Hence, there would be no tardiness.
Tardiness of Job a:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job a is 2.2.
Tardiness of Job c:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job c is 5.4.
Tardiness of Job b:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job b is 6.4.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 11.12 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 2.33 days.
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 2.85 jobs.
3)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule Earliest Due Date (EDD).
Introduction: Earliest Due Date is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, job with the earliest due date would be served first. Then, the process would be going on from earliest due date to latest due date.
Answer to Problem 15P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Remaining number of operations |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 3 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 4 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 3 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 3 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 |
Determine the sequence using EDD:
According to EDD, the job that has the earliest due date would be served first and it goes on as the due date increases. The job should be arranged based on due date. Due date should be assembled in the ascending order
Hence, the sequence of jobs using EDD is a-c-b-e-f-d.
Determine average flow time, average tardiness, and average number of jobs for EDD:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Flow time (days) | Due date (days) | Tardiness |
| a | 4.5 | 4.5 | 10 | 0 |
| c | 5.2 | 9.7 | 12 | 0 |
| b | 6 | 15.7 | 17 | 0 |
| e | 2.8 | 18.5 | 18 | 0.5 |
| f | 3.3 | 21.8 | 19 | 2.8 |
| d | 1.6 | 23.4 | 27 | 0 |
| Total | 23.4 | 93.6 | 3.3 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job a, Job c, Job b, and Job d:
Flow time of Job a, Job c, Job b, and Job d is less than its respective due date. Hence, there would be no tardiness.
Tardiness of Job e:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job e is 0.5.
Tardiness of Job f:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job f is 2.8.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 15.6 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 0.55 days.
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 4 jobs.
4)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule critical ratio.
Introduction: Critical ratio is kind of scheduling rule that helps to identify that, the task or job is on the correct track. It would help to identify if the task is behind or ahead of the schedule.
Answer to Problem 15P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Remaining number of operations |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 3 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 4 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 3 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 3 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 |
Determine the sequence using critical ratio:
Initial critical ratio should be determined at day 0:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Critical ratio |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 2.22 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 2.83 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 2.31 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 16.88 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 6.43 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 5.76 |
Critical ratio for Job a:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of previous job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Note: Process continues for all the jobs.
Job a has the lowest critical ratio. Thus, it will be completed first. Hence, Job a would be completed first in the sequence of jobs.
Determine the critical ratio after the completion of Job a:
As the processing time of job a is 4.5 days, completion day of completed day would be 4.5.
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Critical ratio |
| a | |||
| b | 6 | 17 | 2.08 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 1.44 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 14.06 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 4.82 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 4.39 |
Critical ratio for Job b:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Note: Process continues for all the jobs.
Job c has the lowest critical ratio. Hence, Job c would be completed next in the sequence of jobs.
Determine the critical ratio after the completion of Job a and Job c:
As the processing time of job a is 4.5 days and Job c is 5.2, completion day of completed day would be 9.7 (4.5+5.2).
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Ratio |
| a | |||
| b | 6 | 17 | 1.22 |
| c | |||
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 10.81 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 2.96 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 2.82 |
Critical ratio for Job b:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Job b has the lowest critical ratio. Hence, Job b would be completed next in the sequence of jobs after Job a and Job c.
Determine the critical ratio after the completion of Job a, Job c and Job b:
As the processing time of job a is 4.5 days, Job b is 6.0, and Job c is 5.2 days. Completion day of completed day would be 15.7 (4.5+5.2+6).
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Ratio |
| a | |||
| b | |||
| c | |||
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 7.06 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 0.82 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 |
Critical ratio for Job d:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Job e has the lowest critical ratio. Hence, Job e would be completed next in the sequence of jobs after Job a, Job c, and Job b.
Determine the critical ratio after the completion of Job a, Job c, Job b, and job e:
As the processing time of job a is 4.5 days, Job b is 6.0, Job c is 5.2 days, and job e is 2.8. Completion day of completed day would be 18.5 (4.5+5.2+6+2.8).
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Ratio |
| a | |||
| b | |||
| c | |||
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5.31 |
| e | |||
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 0.15 |
Critical ratio for Job d:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Job f has the lowest critical ratio. Hence, Job f would be completed next in the sequence of jobs after Job a, Job c, Job b, and Job e.
As Job d is the remaining job, it will be completed next.
Hence, the sequence of jobs using critical ratio is a-c-b-e-f-d.
Determine average flow time, average tardiness, and average number of jobs for critical ratio:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Flow time (days) | Due date (days) | Tardiness |
| a | 4.5 | 4.5 | 10 | 0 |
| c | 5.2 | 9.7 | 12 | 0 |
| b | 6 | 15.7 | 17 | 0 |
| e | 2.8 | 18.5 | 18 | 0.5 |
| f | 3.3 | 21.8 | 19 | 2.8 |
| d | 1.6 | 23.4 | 27 | 0 |
| Total | 23.4 | 93.6 | 3.3 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job a, Job c, Job b, and Job d:
Flow time of Job a, Job c, Job b, and Job d is less than its respective due date. Hence, there would be no tardiness.
Tardiness of Job e:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job e is 0.5.
Tardiness of Job f:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job f is 2.8.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 15.6 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 0.55 days.
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 4 jobs.
b)
To determine: Whether the average flow time and average number of jobs are equivalent for four sequencing rules.
Introduction: Sequencing is the process of arranging the jobs in certain order in which it should be performed.
Answer to Problem 15P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Remaining number of operations |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 3 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 4 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 3 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 3 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 |
Determine whether the average flow time and average number of jobs are equivalent for four sequencing rules:
| Rule | Average flow time | Average number of jobs | Ratio |
| FCFS | 15.25 | 3.91 | 3.9 |
| SPT | 11.12 | 2.85 | 3.9 |
| EDD | 15.6 | 4 | 3.9 |
| CR | 15.6 | 4 | 3.9 |
Calculate ratio for FCFS:
It is calculated by dividing average flow time and average number of jobs.
Calculate ratio for SPT:
It is calculated by dividing average flow time and average number of jobs.
Calculate ratio for EDD:
It is calculated by dividing average flow time and average number of jobs.
Calculate ratio for CR:
It is calculated by dividing average flow time and average number of jobs.
c)
To determine: The processing sequence of the jobs using Slack per Operation (S/O) rule
Introduction: Slack per operation is a scheduling method that helps to determine the sequence of the operation. Slack is the difference between the due date and the required time to process certain job.
Answer to Problem 15P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The following information is given:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date | Remaining number of operations |
| a | 5 | 8 | 2 |
| b | 6 | 5 | 4 |
| c | 9 | 10 | 4 |
| d | 7 | 12 | 3 |
| e | 8 | 10 | 2 |
Determine the processing sequence of the jobs using Slack per Operation:
| Job | Job time (days) | Due date (days) | Operations remaining | Slack | Slack per operation (S/O) | Rank |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 3 | 5.5 | 1.83 | 1 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 4 | 11 | 2.75 | 3 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 3 | 6.8 | 2.27 | 2 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5 | 25.4 | 5.08 | 5 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 3 | 15.2 | 5.07 | 4 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 | 15.7 | 15.7 | 6 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time, due date, and remaining number of operation is given. Rank should be assigned according to the slack per operation.
Calculate slack:
It can be calculated by subtracting the processing time from the due date.
Note: The process continues for all the jobs:
Calculate slack per operation:
It can be calculated by dividing the slack value and the remaining number of operations.
Note: The process continues for all the jobs:
Hence, the sequence of jobs using S/O is a-c-b-e-d-f.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT W/ CNCT+
- I need the answer to requirement C.arrow_forwardImagine you are Susan Kim and are faced with a difficult choice to either follow the orders she was given, or refusing to do so. Using each lens determine what the ethical response would be. Suppot your answer with materials from readings and lectures. For example, using Universalism what would the ethical response be? Do the same for all four lenses.arrow_forwardAnswer all these questions, selecting any company of your choice. Choose a specific type of food company. Select a specific product. Develop all the inputs that are part of the process. Develop the transformation process in a graphic (diagram, etc.). Develop all the outputs or finished products that are part of the process. Describe all the processes involved in one line of production in any manufacturing facility. Also describing how good management is the center of any part of a production company.arrow_forward
- Using exponential smoothing with α =0.2, forecast the demand for The initial forecast for January is 2000 tons. Calculate the capacity utilization for June, July and Discuss the implications of underutilized or over utilized capacity for Green Harvestarrow_forwardIn organizational development when results are improving but relationships are declining, what leadership style is appropriate? directing delegating supporting coachingarrow_forwardWhat is the first thing a leader should do when moving through a cultural change? conduct an assessment comparing the practices to other high-performing organizations learn about the current organizational culture continue to monitor key metrics define expectationsarrow_forward
- The third change leadership strategy, Collaborate on Implementation, is designed to address what type of concerns? impact concerns personal concerns refinement concerns collaboration concernsarrow_forwardIf team members are concerned with specifics such as their tasks, contingency plans, resources, and timeline, what concerns do they have? implementation concerns impact concerns refinement concerns personal concernsarrow_forwardAt the developing stage of organizational development, which leadership style is most appropriate? supporting coaching delegating directingarrow_forward
- During the start-up phase of organizations, which leadership style is appropriate? supporting coaching directing delegatingarrow_forwardRegarding relationships and results, what is typically seen in start-up orgnanizations? low results/high relationships low results/low relationships high results/high relationships high results/ low relationshipsarrow_forwardWhat issues lie within Employee and Labor relations with hours worked and how to solve the issues effectively.arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning


