
Concept explainers
Included in the December 31, 2018, Jacobi Company
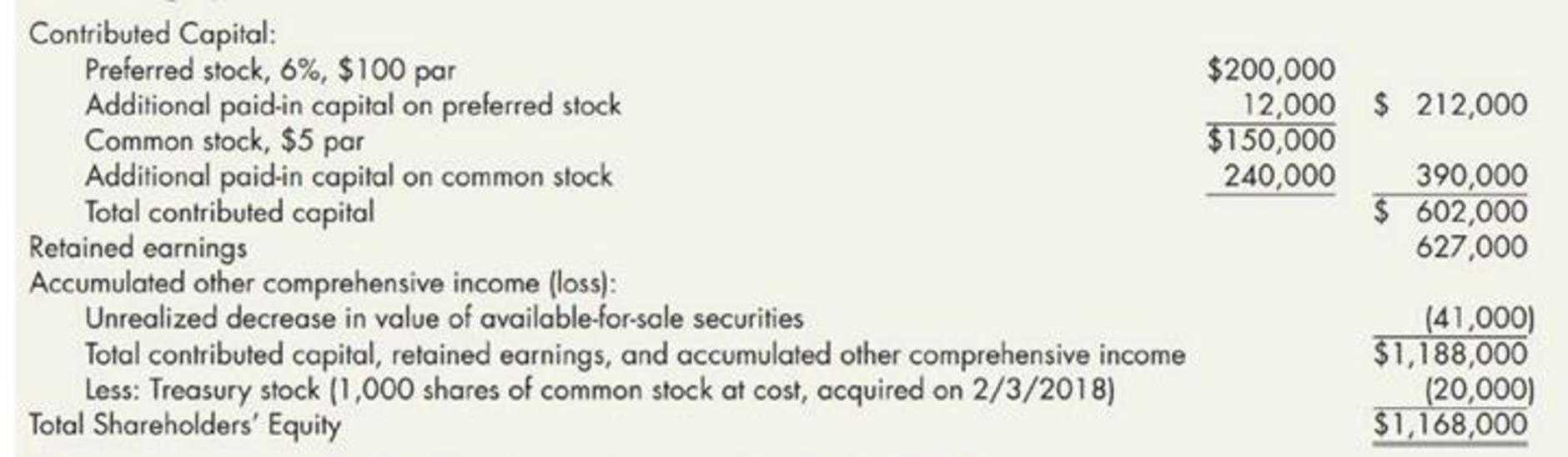
The company engaged in the following stock transactions during 2019:
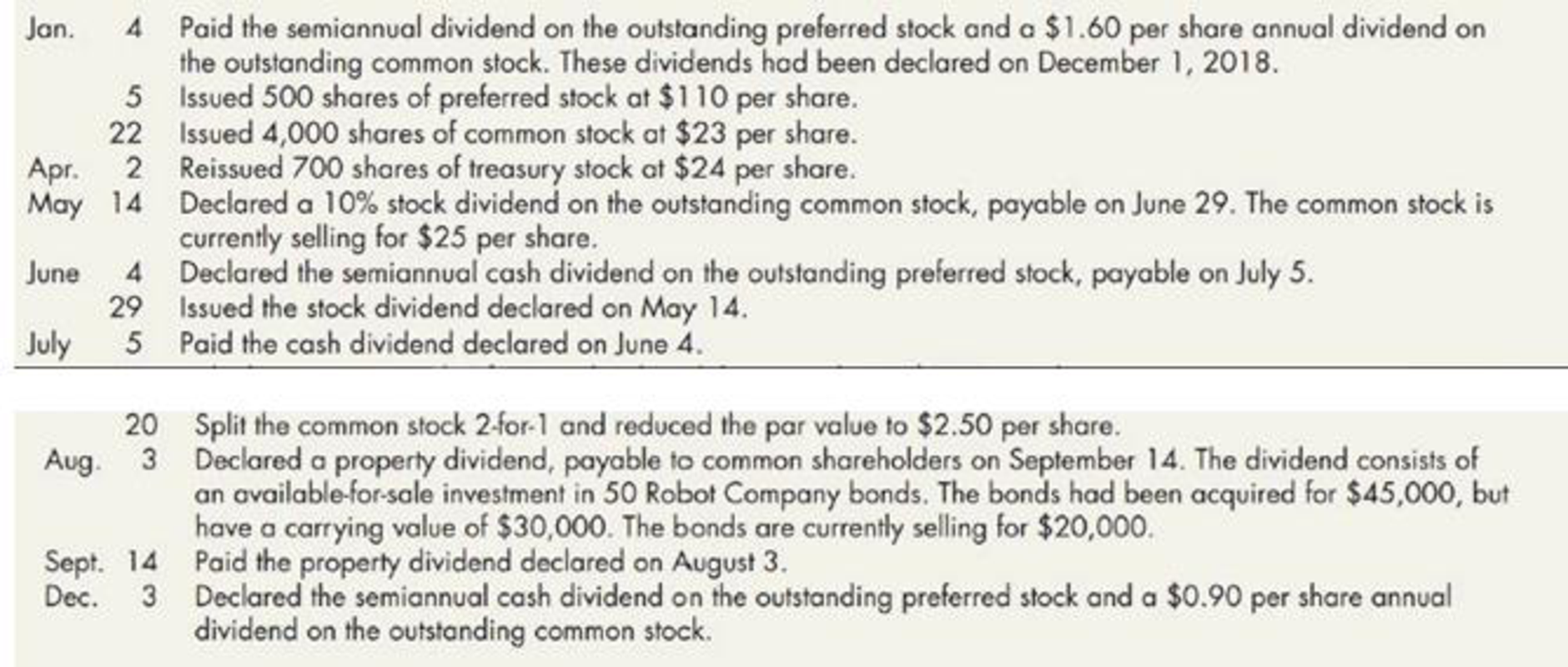
Required:
- 1. Prepare
journal entries to record the preceding transactions. - 2. Prepare the December 31, 2019, shareholders’ equity section (assume that 2019 net income was $270,000).
1.
Prepare journal entry to record the given transactions.
Explanation of Solution
Stockholders’ Equity Section: It is refers to the section of the balance sheet that shows the available balance stockholders’ equity as on reported date at the end of the financial year.
Prepare journal entry to record the given transactions.
| Date | Account Titles and explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January 4, 2019 | Dividend payable: Preferred | 6,000 | |
| Dividend payable: Common (1) | 46,400 | ||
| Cash | 52,400 | ||
| (To record declaration of preferred and common stock) | |||
| January 5, 2019 | Cash | 55,000 | |
| Preferred stock, $100 par | 50,000 | ||
| Additional paid-in capital on preferred stock | 5,000 | ||
| ( To record issuance of preferred stock) | |||
| January 22, 2019 | Cash | 92,000 | |
| Common stock, $5 par | 20,000 | ||
|
Additional paid-in capital on common stock | 72,000 | ||
| ( To record issuance of common stock) | |||
| April 2, 2019 | Cash | 16,800 | |
| Treasury stock | 14,000 | ||
|
Additional paid-in capital on treasury stock | 2,800 | ||
| (To record the reissuance of treasury stock) | |||
|
May 14, 2019 | Retained earnings (2) | 84,250 | |
|
Common stock to be distributed | 16,850 | ||
| Additional paid-in capital from stock dividend | 67,400 | ||
| (To record declaration of stock dividend) | |||
| June 4, 2019 | Retained earnings | 7,500 | |
| Dividends payable: Preferred (3) | 7,500 | ||
| (To record the declaration of annual per share dividend to the preferred) | |||
| August 29, 2019 | Common stock to be distributed | 16,850 | |
| Common stock, $5 par | 16,850 | ||
| (To record the issuance of stock dividend) | |||
| July 5, 2019 | Dividends payable: Preferred stock | 7,500 | |
| Cash | 7,500 | ||
| (To record the amount of dividend paid on preferred stock) | |||
| July 20, 2019 | No entry is required | ||
| August 3 ,2019 | Loss on disposal of investment | 25,000 | |
|
Unrealized decrease in the value of available-for-sale of securities | 15,000 | ||
|
Allowance for change in value investment | 10,000 | ||
| (To record the declaration of property dividend) | |||
| Retained earnings | 20,000 | ||
| Property dividend payable | 20,000 | ||
| (To record the current value of the bond) | |||
| September 1,2019 | Property dividend payable | 20,000 | |
| Allowance for change in value of investment | 25,000 | ||
| Investment in Company A stock | 45,000 | ||
| (To record the issuance of property dividend) | |||
| December 3, 2019 | Retained earnings | 74,226 | |
| Dividends payable: Preferred (3) | 7,500 | ||
| Dividends payable: Common (4) | 66,726 | ||
| (To record the declaration of annual per share dividend to the preferred and common stock) |
Table (1)
Note:
Note 1: On July 20 memorandum entry is made as the common stock split two for one and the par value is reduced from $5 to $2.50.
Note 2: On July 20 memorandum entry is made when number of shares issued on common stock increases from 37,370
Working note (1): Calculate the amount of dividend payable to the common stock:
Working note (2): Calculate the amount of retained earnings:
| Particulars | Amount in $ |
| Shares issued | 34,000 |
| Less: Treasury shares | 300 |
| Shares outstanding | 33,700 |
| Multiply: Stock dividend | 10% |
| Shares in stock dividend | 3,370 |
| Multiply: Current market price | $25 |
| Reduction in retained earnings | 84,250 |
Table (2)
Working note (3): Calculate the amount of dividend payable to the preferred stock:
Working note (4): Calculate the amount of dividend payable to the common stock:
2.
Prepare Company J’s statement of stockholder’s equity section for 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare Company J’s statement of stockholder’s equity section for 2019.
| Company J | |
| Shareholder's equity | |
| For the year ended December 31, 2019 | |
| Particulars | Amount in $ |
| Contributed Capital: | |
|
Preferred stock (6%, $100 par, 2,500 shares issued and outstanding) | 250,000 |
| Additional paid-in capital on preferred stock | 17,000 |
|
Common stock ($2.50 par, 74,740 shares issued of which 600 are in the corporate treasury) | 186,850 |
| Additional paid-in capital on common stock | 312,000 |
| Additional paid-in capital from treasury stock | 2,800 |
| Additional paid-in capital from stock dividend | 67,400 |
| Total contributed capital | 836,050 |
|
Retained earnings (restricted in the amount of $6,000, the cost of the treasury shares) (5) | 711,024 |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss): | |
| Unrealized decrease in value of available-for-sale securities | (26,000) |
| Total contributed capital, retained earnings, and accumulated other comprehensive income | 1,521,074 |
| Less: Treasury stock (600 shares of common at $10 per share) | (6,000) |
| Total Shareholders’ Equity | 1,515,074 |
(Table 3)
(5) Calculate the amount of retained earnings:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting and Analysis (Looseleaf)
- Home Insert Draw Page Layout Formulas Data Review View Automate Developer Calibri (Body) 12 ✓ Α Αν Conditional Formatting ✓ ☑Insert v Σ Custom Paste B I U ✓ ✓ $ ✓ %9 0 .00 →0 Format as Table ✓ Cell Styles ▾ Delete ✓ Format ✓ C26 fx A B D E F G 1 Instruction: 2 1. Please complete the following budget plan using appropriate cell references format (the cells highlighted in grey) 3 2. Please use fill handler to complete the table. E.g. in cell C16, build one formula and generate other formulas to D16 and E16 with fill handler. 4 3. For "Cost of Goods Sold" section (before "COGS Subtotal"), build one formula in cell C19, and generate formulas until E21. Overhead (B21) is 20% (B10) of the labor cost (B20). 5 4. For "COGS Subtotal", build one formula in C22, and generate the formulas to E22. 6 5. Similar requirements for "Selling Expenses" and "Projected Earnings" section. 7 6. Please be noted, for all items under "Cost of Goods Sold", and "Selling Expenses" the cost is per ONE shoe, not per…arrow_forwardProvide correct solution and accountingarrow_forwardSolve this question accountingarrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
