
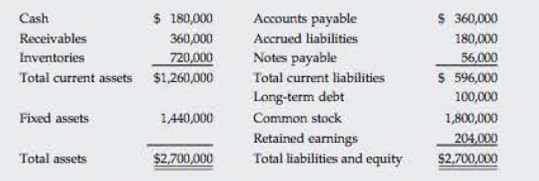
ADDITIONAL FUNDS NEEDED Morrissey Technologies Inc.’s 2016 financial statements are shown here.
Morrissey Technologies Inc.:
Morrissey Technologies Inc.: Income Statement for December 31, 2016
| Sales | $3,600,000 |
| Operating costs including depredation | 3,279,720 |
| EBIT | $ 320,280 |
| Interest | 20,280 |
| EBT | $ 300,000 |
| Taxes (40%) | 120,000 |
| Net Income | $ 180,000 |
| Per Share Data: | |
| Common stock price | $45.00 |
| Earnings per share (EPS) | $ 1.80 |
| Dividends per share (DPS) | $ 1.08 |
Suppose that in 2017, sales increase by 10% over 2016 sales. The firm currently has 100,000 shares outstanding. It expects to maintain its 2016 dividend payout ratio and believes that its assets should grow at the same rate as sales. The firm has no excess capacity. However, the firm would like to reduce its operating costs/sales ratio to 87.5% and increase its total liabilities-to-assets ratio to 30%. (It believes its liabilities-to-assets ratio currently is too low relative to the industry average.) The firm will raise 30% of the 2017 forecasted interest- bearing debt as notes payable, and it will issue long-term bonds for the remainder. The firm
- a. Construct the forecasted financial statements assuming that these changes are made. What are the firm’s forecasted notes payable and long-term debt balances? What is the forecasted addition to
retained earnings ? - b. If the profit margin remains at 5% and the dividend payout ratio remains at 60%, at what growth rate in sales will the additional financing requirements be exactly zero? In other words, what is the firm’s sustainable growth rate? (Hint: Set AFN equal to zero and solve for g.)
a.
To construct: The forecasted financial statements for the year 2017 and to calculate the firm’s forecasted notes payable and long-term debts balance and forecasted addition to retained earnings
Introduction:
Financial Statements:
Financial statements are the statements, which tell about the financial activities of the company. A financial statement of a company includes its income statement, balance sheet, and cash flows statement.
Income Statement:
Income statement is a business’s financial statement, which tells the financial performance of a company in an accounting period. It shows the income generated by a company and expenses incurred by a company through its operations.
Balance Sheet:
Balance sheet is the summarize statement of total assets and total liabilities of a company in an accounting period. It is one of the financial statements.
Additional Fund Needed:
Additional fund needed is also known as external financing needed. It is the state in which a company needed finance to increase its operation. Additional fund needed is a method in which a company raises the funds through external resources to increase its assets, which would increase the sales revenue of the firm.
But according to additional fund needed method, a company do not change its financial ratio. Liabilities and retained earnings spontaneously increase with the increase in sales and assets.
Explanation of Solution
| Company M | |
| Income Statement | |
| For the year ended December 31,2017 | |
| Particulars |
Amount ($) |
| Sales | 3,960,000 |
| Less:-Operating costs including depreciation | 3,465,000 |
| EBIT | 495,000 |
| Less:-Interest | 111,375 |
| EBT | 383,625 |
| Less:-Taxes | 153,450 |
| Net income | 230,175 |
| Per Share Data: | |
| Common stock price | 45 |
| Earnings per share (EPS) | 2.30 |
| Dividends per share (DPS) | 1.38 |
Table (1)
| Company M | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2017 | ||
| Assets |
Amount ($) |
Amount ($) |
| Current assets: | ||
| Cash | 198,000 | |
| Accounts receivable | 396,000 | |
| Inventories | 792,000 | |
| Total current assets | 1,386,000 | |
| Fixed assets | 1,584,000 | |
| Total Assets | 2,970,000 | |
| Liabilities and Owners' Equity | ||
| Current Liabilities: | ||
| Notes payable | 728,000 | |
| Total current Liabilities | 728,000 | |
| Long-term debt | 163,000 | |
| Total Liabilities | 891,000 | |
| Owners' Equity: | ||
| Common stock | 1,782,930 | |
| Retained Earnings | 296,070 | |
| Total Stockholders' Equity | 2,079,000 | |
| Total Liabilities and Owners' Equity | 2,970,000 | |
Calculation of forecasted notes payable for 2017,
Given,
Notes payable for 2016 are $56,000.
Company will raise notes payable by 30%.
Formula to calculate the forecasted notes payable for 2017,
Substitute $560,000 for notes payable for 2016 and 30% for increment in notes payable.
Calculation of forecasted long term debts for 2017,
Given,
Liabilities (excluding retained earnings and common stock) for 2017 are $891,000 (working notes).
Notes payable for 2017 are $728,000.
Formula to calculate long term debts for 2017,
Substitute $891,000 for liabilities (excluding retained earnings and common stock) and $728,000 for notes payable.
Calculation of addition to retained earnings for the year 2017
Given,
Dividend paid for the year ended 2017 is $138,105.
Net income for the year ended is $230,175.
Formula to calculate addition to retained earnings,
Substitute $230,175 for net income and $138,105 for dividend paid.
Working notes:
Calculation of estimated sales for the year 2017
Given,
Sales for the year 2016 are $3,600,000.
Increment in sales is 10%.
Calculation of estimated sales for 2017,
Calculation of estimated operating costs including depreciation for the year 2017
Given,
The firm would like to reduce its operating cost/sales ratio to 87.5%.
Sales of the year 2017 are $3,960,000.
Calculation of operating costs including depreciation,
Calculation of estimated total assets for 2017,
Given,
Value of total assets for 2016 is $2,700,000.
The assets should grow at the same rate as sales, which is 10%.
Calculation of the total assets,
Calculation of estimated cash for 2017,
Given,
Value of cash for 2016 is $180,000.
The assets should grow at the same rate as sales, which is 10%.
Calculation of estimated cash for 2017,
Calculation of estimated receivable for 2017,
Given,
Value of receivable for 2016 is $360,000.
The assets should grow at the same rate as sales, which is 10%.
Calculation of estimated receivable for 2017,
Calculation of estimated inventories for 2017,
Given,
Value of inventories for 2016 is $720,000.
The assets should grow at the same rate as sales, which is 10%.
Calculation of estimated inventories for 2017,
Calculation of estimated fixed assets for 2017,
Given,
Fixed assets for 2016 are $1,440,000.
The assets should grow at the same rate as sales, which is 10%.
Calculation of estimated fixed assets for 2017,
Calculation of estimated total liabilities (excluding retained earnings and common stock) for 2017,
Given,
The liabilities-to-assets ratio for 2017 is 30%.
Estimated assets for 2017 are 2,970,000.
Calculation of estimated liabilities (excluding retained earnings and common stock) for 2017,
Calculation of estimated interest for 2017,
Given,
Forecasted notes payable for 2017 are $728,000.
Forecasted long terms debts are $891,000.
Interest rate is 12.5%.
Calculation of estimated interest,
Calculation of taxes
Given,
Tax rate is 40%
EBT for the year 2017 is $383,625.
Calculation of taxes,
Calculation of Earnings per share,
Given,
Estimated net income for 2017 is $230,175.
Shares outstanding are 100,000.
Calculation of EPS,
Calculation of dividend paid in 2016,
Given,
Dividend per share for 2016 is $1.08.
Shares outstanding for 2016 is 100,000
Formula to calculate Dividend paid in 2016,
Calculation of dividend payout ratio,
Given,
Dividend paid for the year 2016 is $108,000.
Net income for the year 2016 is $180,000.
Calculation of the dividend payout ratio,
Calculation of dividend paid during 2017
Given
Dividend payout ratio remains constant, which is 60%.
Net income for the year 2017 is $230,175.
Calculation of dividend paid during 2017,
Calculation of estimated dividend per share for 2017,
Given,
Dividend paid during 2017 is $138,105.
Shares outstanding are 100,000.
Calculation of dividend per share,
Calculation of estimated value of common stock for 2017,
Given,
Estimated total assets for 2017 are $2,970,000.
Estimated liabilities (excluding retained earnings and common stock) are $891,000
Estimated retained earnings for 2017 are $92,070.
Calculation of common stock for 2017,
The forecasted notes payable for 2017 are $728,000, the forecasted long term debts are $163,000 and the addition in retained earnings are 92,070.
b.
To find: Firm’s sustainable growth rate in sales.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of sustainable growth rate,
Given,
The profit margin is 5%.
The dividend payout ratio is 60%.
Current sales for 2017 are $3,960,000.
Total assets for 2017 are $2,970,000.
Spontaneous current liability for 2017 is $891,000.
Formula to calculate sustainable growth rate in sales,
Substitute 5% (or 0.05) for profit margin, 6% (or 0.6) for payout ratio, $3,960,000 for current sales, $2,970,000 for total assets and $891,000 for spontaneous current liability.
The sustainable growth rate is 3.96%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Bundle: Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edition, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Aplia, 1 term Printed Access Card
- Alfa international paid $2.00 annual dividend on common stock and promises that the dividend will grow by 4% per year, if the stock’s market price for today is $20, what is required rate of return?arrow_forwardgive answer general accounting.arrow_forwardGive me answers in general financearrow_forward
- General Finance Question Solution Please with calculationarrow_forwardGeneral Financearrow_forwardAs CFO for Everything.Com, you are shopping for 6,000 square feet of usable office space for 25 of your employees in Center City, USA. A leasing broker shows you space in Apex Atrium, a 10-story multitenanted office building. This building contains 360,000 square feet of gross building area. A total of 54,000 square feet is interior space and is nonrentable. The nonrentable space consists of areas contained in the basement, elevator core, and other mechanical and structural components. An additional 36,000 square feet of common area is the lobby area usable by all tenants. The 6,000 square feet of usable area that you are looking for is on the seventh floor, which contains 33,600 square feet of rentable area, and is leased by other tenants who occupy a combined total of 24,000 square feet of usable space. The leasing broker indicated that base rents will be $30 per square foot of rentable area Required: a. Calculate total rentable area in the building as though it would be rented to…arrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardGeneral Finance Questionarrow_forwardConsider the following simplified financial statements for the Yoo Corporation (assuming no income taxes): Income Statement Balance Sheet Sales Costs $ 40,000 Assets 34,160 $26,000 Debt Equity $ 7,000 19,000 Net income $ 5,840 Total $26,000 Total $26,000 The company has predicted a sales increase of 20 percent. Assume Yoo pays out half of net income in the form of a cash dividend. Costs and assets vary with sales, but debt and equity do not. Prepare the pro forma statements. (Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Pro forma income statement Sales Costs $ 48000 40992 Assets $ 31200 Pro forma balance sheet Debt 7000 Equity 19000 Net income $ 7008 Total $ 31200 Total 30304 What is the external financing needed? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Negative amount should be indicated by a minus sign.) External financing needed $ 896arrow_forward
- An insurance company has liabilities of £7 million due in 10 years' time and £9 million due in 17 years' time. The assets of the company consist of two zero-coupon bonds, one paying £X million in 7 years' time and the other paying £Y million in 20 years' time. The current interest rate is 6% per annum effective. Find the nominal value of X (i.e. the amount, IN MILLIONS, that bond X pays in 7 year's time) such that the first two conditions for Redington's theory of immunisation are satisfied. Express your answer to THREE DECIMAL PLACES.arrow_forwardAn individual is investing in a market where spot rates and forward rates apply. In this market, if at time t=0 he agrees to invest £5.3 for two years, he will receive £7.4 at time t=2 years. Alternatively, if at time t=0 he agrees to invest £5.3 at time t=1 for either one year or two years, he will receive £7.5 or £7.3 at times t=2 and t=3, respectively. Calculate the price per £5,000 nominal that the individual should pay for a fixed-interest bond bearing annual interest of 6.6% and is redeemable after 3 years at 110%. State your answer at 2 decimal places.arrow_forwardThe one-year forward rates of interest, f+, are given by: . fo = 5.06%, f₁ = 6.38%, and f2 = 5.73%. Calculate, to 4 decimal places (in percentages), the three-year par yield.arrow_forward
 Fundamentals Of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781337902571Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals Of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781337902571Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781305635937Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781305635937Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning



