
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781938168390
Author: Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 16, Problem 11E
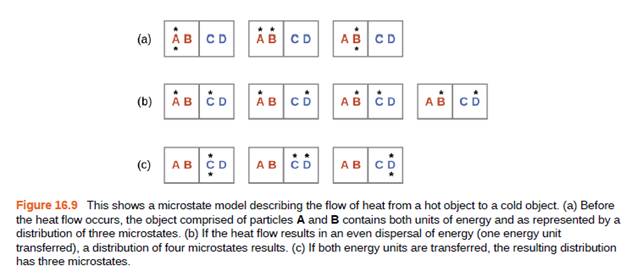
Consider the system shown in Figure 16.9. What is the change in entropy for the process where the energy is initially associated with particles A and B, and the energy is distributed between two particles in different boxes (one in A-B, the other in C-D)?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In the normal hydrogen electrode, the current flows through the electrode when the power difference
of the interface is +5 mV. Calculate the overvoltage n at pH = 2, if the equilibrium potential is -0.118 V.
In the normal hydrogen electrode, the balance potential difference in the interface is 0 and the current flow across the electrode when the interface potential difference is +5 mV. Explain briefly. Is the overvoltage 5 mV?
In the normal hydrogen electrode, the balance potential difference in the interface is 0 mV, the maximum potential is 5 mV. Explain briefly.
Chapter 16 Solutions
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Ch. 16 - What is a spontaneous reaction?Ch. 16 - What is a nonspontaneous reaction?Ch. 16 - Indicate whether the following processes are...Ch. 16 - A helium-filled balloon spontaneously deflates...Ch. 16 - Many plastic materials are organic polymers that...Ch. 16 - In Figure 16.8 all possible distributions and...Ch. 16 - In Figure 16.8 all of the possible distributions...Ch. 16 - How does the process described in the previous...Ch. 16 - Consider a system similar to the one in Figure...Ch. 16 - Consider the system shown in Figure 16.9. What is...
Ch. 16 - Consider the system shown in Figure 16.9. What is...Ch. 16 - Arrange the following sets of systems in order of...Ch. 16 - At room temperature, the entropy of the halogens...Ch. 16 - Consider two processes: sublimation of I2(s) and...Ch. 16 - Indicate which substance in the given pairs has...Ch. 16 - Predict the sign of the entropy change for the...Ch. 16 - Predict the sign of the entropy change for the...Ch. 16 - Write the balanced chemical equation for the...Ch. 16 - Write the balanced chemical equation for the...Ch. 16 - What is the difference between S, S , and S 298...Ch. 16 - Calculate S298 for the following changes. (a)...Ch. 16 - Determine the entropy change for the combustion of...Ch. 16 - Determine the entropy change for the combustion of...Ch. 16 - Thermite reactions have been used for welding...Ch. 16 - Using the relevant S 298 values listed in Appendix...Ch. 16 - From the following information, determine S298 for...Ch. 16 - By calculating Suniv, at each temperature,...Ch. 16 - Use the standard entropy data in Appendix G to...Ch. 16 - Use the standard entropy data in Appendix G to...Ch. 16 - What is the difference between G, G, and G 298 for...Ch. 16 - A reaction has H298=100 kj/mol and S298=250 J/mol ...Ch. 16 - Explain what happens as a reaction starts with G0...Ch. 16 - Use the standard free energy of formation data in...Ch. 16 - Use the standard free energy data in Appendix G to...Ch. 16 - Given: P4(s)+5O2(g)P4O10(s)G298=2697.0kJ/mol...Ch. 16 - Is the formation of ozone (O3(g)) from oxygen...Ch. 16 - Consider the decomposition of red mercury(II)...Ch. 16 - Among other things, an ideal fuel for the control...Ch. 16 - Calculate G for each of the following reactions...Ch. 16 - Calculate G for each of the following reactions...Ch. 16 - Calculate the equilibrium constant at 25 C for...Ch. 16 - Calculate the equilibrium constant at 25 C for...Ch. 16 - Calculate the equilibrium constant temperature...Ch. 16 - Calculate the equilibrium constant temperature...Ch. 16 - Consider the following reaction at 298 K:...Ch. 16 - Determine the normal boiling point (in kelvin) of...Ch. 16 - Under what conditions is N2O3(g)NO(g)+NO2(g)...Ch. 16 - At mom temperature, the equilibrium constant (Kw)...Ch. 16 - Hydrogen sulfide is a pollutant found in natural...Ch. 16 - Consider the decomposition of CaCO3(s) into CaO(s)...Ch. 16 - In the laboratory, hydrogen chloride (HCl(g)) and...Ch. 16 - Benzene can be prepared from acetylene....Ch. 16 - Carbon dioxide decomposes into CO and O2 at...Ch. 16 - Carbon tetrachloride, an important industrial...Ch. 16 - Acetic acid, CH3CO2H, can form a dimer,...Ch. 16 - Nitric acid, HNO3, can be prepared by the...Ch. 16 - Determine G for the following reactions. (a)...Ch. 16 - Given that the Gf for Pb2+(aq) and Cl-(aq) is...Ch. 16 - Determine the standard free energy change, Gf, for...Ch. 16 - Determine the standard enthalpy change, entropy...Ch. 16 - The evaporation of one mole of water at 298 K has...Ch. 16 - In glycolysis, the reaction of glucose (Glu) to...Ch. 16 - One of the important reactions in the biochemical...Ch. 16 - Without doing a numerical calculation, determine...Ch. 16 - When ammonium chloride is added to water and...Ch. 16 - An important source of copper is from the copper...Ch. 16 - What happens to G (becomes more negative or more...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1. ___ Mitosis 2. ___ Meiosis 3. __ Homologous chromosomes 4. __ Crossing over 5. __ Cytokinesis A. Cytoplasmic...
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
81. Write a formula for each acid.
a. phosphoric acid
b. hydrobromic acid
c. sulfurous acid
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
16. Explain some of the reasons why the human species has been able to expand in number and distribution to a g...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Fibrous connective tissue consists of ground substance and fibers that provide strength, support, and flexibili...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY DRAW IT As a consequence of size alone, larger organisms tend to have larger brains than sm...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
The enzyme that catalyzes the C C bond cleavage reaction that converts serine to glycine removes the substitue...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- utron eutro cle TH tro (Na (b) Atoms are said to be electrically neutral. Explain. (c) Distinguish between the following: (i) Atomic number and mass number. (ii) Mass number and relative atomic mass. 2. An isotope Q, has 18 neutrons a mass number of 34. (a) (i) Draw the atomic structure of Q. (ii) Write its electron arrangement (b) To which period and group does Q belong? Explain your answer. (c) How does Q form its ion? Explain. 3. (a) Determine the relative atomic mass of the following elements = compositions occur in the proportions given. (i) Neon 20 21 22. Ne (90.92%), 10Ne (0.26%), and 10Ne (8.82%) (ii) Argon 36 38 40 18 Ar (0.34%), 18 Ar (0.06%) and 18 Ar (99.6%)arrow_forwardIn the normal hydrogen electrode, the balance potential difference in the interface is this, the maximum potential is 5 mV. Explain briefly.arrow_forwardThe electrode balance potential is -0.118 V and the interface potential difference is +5 mV. The overvoltage n will be 0.005 - (-0.118) = 0.123 V. Is it correct?arrow_forward
- In the electrode Pt, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1), if the electrode balance potential is -0.118 V and the interface potential difference is +5 mV. The current voltage will be 0.005 - (-0.118) = 0.123 V ¿Correcto?arrow_forwardIn the electrode Pt, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1) at 298K is 0.79 mA cm-2. If the balance potential of the electrode is -0.118 V and the potential difference of the interface is +5 mV. Determine its potential.arrow_forwardIn one electrode: Pt, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1), the interchange current density at 298K is 0.79 mA·cm-2. If the voltage difference of the interface is +5 mV. What will be the correct intensity at pH = 2?. Maximum transfer voltage and beta = 0.5.arrow_forward
- In a Pt electrode, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1), the interchange current density of an electrode is 0.79 mA cm-2. ¿Qué corriente flow across the electrode of área 5 cm2 when the difference in potential of the interface is +5 mV?.arrow_forwardIf the current voltage is n = 0.14 V, indicate which of the 2 voltage formulas of the ley of Tafel must be applied i a a) == exp (1-B). xp[(1 - ß³): Fn Fn a b) == exp B RT RTarrow_forwardIf the current voltage is n = 0.14 V. Indicate which of the 2 formulas must be applied a) = a T = i exp[(1 - p) F Fn Fn b) i==exp B RTarrow_forward
- Topic: Photochemistry and Photophysics of Supramoleculesarrow_forwardTwo cations that exchange an electron in an interface, the exchange density is worth 1.39 mA/cm2 and the current density is worth 15 mA/cm2 at 25°C. If the overvoltage is 0.14 V, calculate the reaction rate and symmetry factor. Data: R = 8,314 J mol-1 k-1: F = 96500 Carrow_forwardWith the help of the Tafel line, it is estimated that the interchange density of the VO2+/VO2+ system on the carbon paper has a value of 3 mA cm-2. Calculate a) the current density if the voltage has a value of 1.6 mV and the temperature is 25°C. b) the beta value of the anódico process if the Tafel pendulum is 0.6 V at 25°C. Data: R = 8.314 JK-1mol-1, y F = 96485 C mol-1.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning  Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co


Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Laws of Thermodynamics, Entropy, and Gibbs Free Energy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8N1BxHgsoOw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY