
Concept explainers
The nervous system is composed of two components, which includes the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system includes the brain and the spinal cord, whereas the peripheral nervous system includes the motor and the sensory receptors. The brain is composed of nerve tissues that are protected within the skull. The major functions of the brain include processing sensory information, releasing hormones, and regulating blood pressure and breathing.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
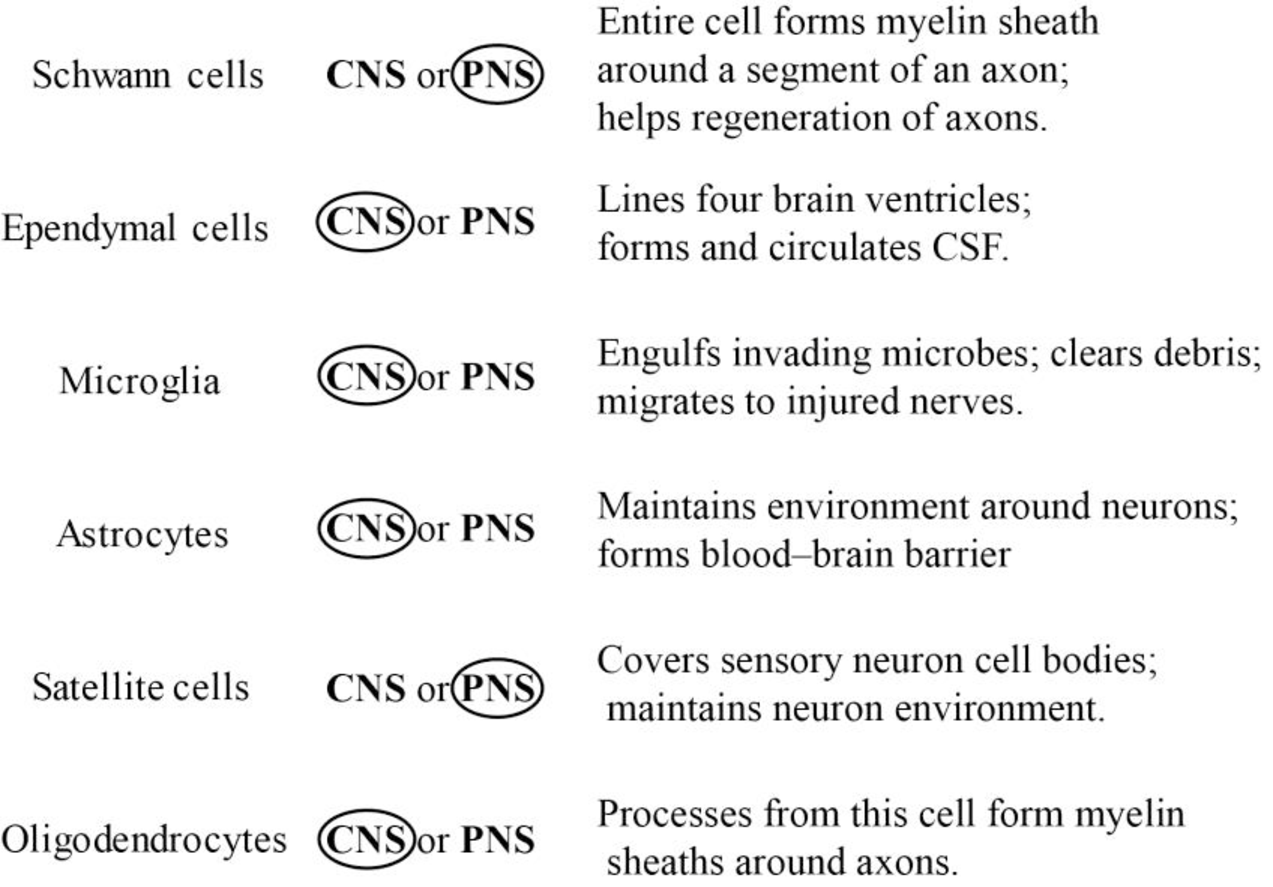
Explanation of Solution
Schwann cell:
The Schwann cell is a glial cell that plays an important role in supporting the PNS. The Schwann cell, also termed as neurilemma cell, is a type of nervous tissue cell in PNS involved in producing the myelin sheath around the neuronal axons and also helps in regenerating the axons.
Ependymal cell:
The ependymal cell is a neuronal support cell, known as neuroglia, which forms the epithelial lining of the ventricles present in the brain and also the central canal of the spinal cord. Moreover, the ependymal cells give rise to the epithelial layer that encircles the choroid plexus. The choroid plexus is a collection of blood vessels that exist in the lateral ventricle walls. Cilia, present in the ventricles of the ependymal cell, help in influencing the cerebrospinal fluid direction and also bring nutrients and other substances to the neuron.
Microglia:
Microglia is a type of neuroglial cell that supports the CNS as it functions as an immune cell. The microglial cell is the smallest cell of all the neuroglia. Its main role is to mediate the immune response in the CNS by acting as macrophage, removing dead neurons, and cellular debris from the nervous tissue through the phagocytosis process.
Astrocytes:
Astrocytes, also termed as astroglia, which is characterized by star-shaped glial cells present in the brain and the spinal cord. It performs numerous functions, like axon guidance, synaptic support, controls blood-brain barrier, and also controls the blood flow. In addition, astrocytes are majorly responsible for homeostasis of the CNS.
Satellite cell:
The satellite cell, also termed as muscle stem cell or myosatellite cell, is a multipotent, flattened cell that usually exists in the ganglia (sympathetic ganglia, parasympathetic ganglia, and sensory ganglia) of the PNS. It encompasses a small amount of cytoplasm present in the mature muscle. The satellite cell plays a major role in regulating and stabilizing the environment around ganglion cell bodies.
Oligodendrocytes:
Oligodendrocyte is a type of neuroglia that supports the CNS by providing support and insulation to axons. The oligodendrocytes create an isolating sheath around the axons for rapid conduction of the signal. This may lead to massive conduction of electrical signals inside the axon.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK LABORATORY MANUAL FOR ANATOMY AND P
- What is behavioral adaptarrow_forward22. Which of the following mutant proteins is expected to have a dominant negative effect when over- expressed in normal cells? a. mutant PI3-kinase that lacks the SH2 domain but retains the kinase function b. mutant Grb2 protein that cannot bind to RTK c. mutant RTK that lacks the extracellular domain d. mutant PDK that has the PH domain but lost the kinase function e. all of the abovearrow_forwardWhat is the label ?arrow_forward
- Can you described the image? Can you explain the question as well their answer and how to get to an answer to an problem like this?arrow_forwardglg 112 mid unit assignment Identifying melting processesarrow_forwardGive only the mode of inheritance consistent with all three pedigrees and only two reasons that support this, nothing more, (it shouldn't take too long)arrow_forward
- Oarrow_forwardDescribe the principle of homeostasis.arrow_forwardExplain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





