
Concept explainers
The elliptical exercise machine has fixed axes of rotation at points A and E. Knowing that at the instant shown the flywheel AB has a constant angular velocity of 6 rad/s clockwise, determine (a) the angular acceleration of bar DEF, (b) the acceleration of point F.
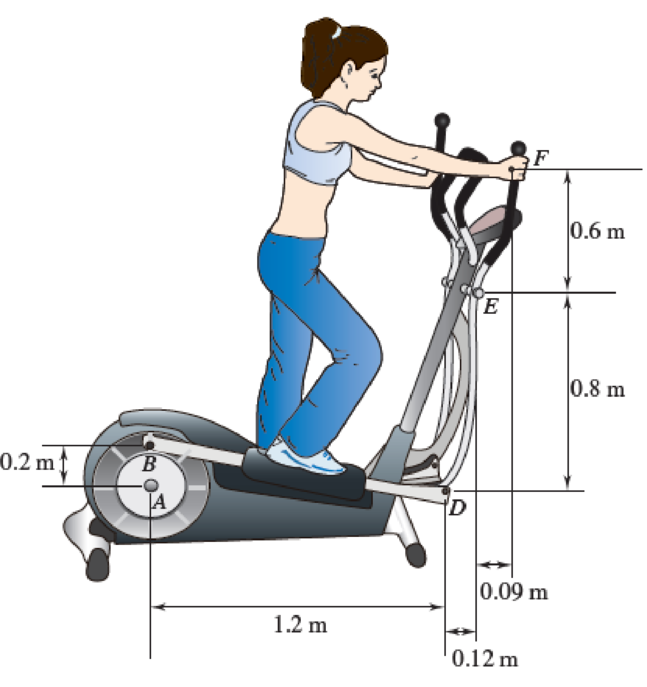
Fig. P15.127 and P15.128
(a)
Find the angular acceleration of the bar DEF.
Answer to Problem 15.128P
The angular acceleration of the bar DEF is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Consider the angular acceleration of the bar DEF is denoted by
The constant angular acceleration of the flywheel AB is
The angular acceleration of the flywheel AB is
Consider the position of the point B with respect to point A is denoted by
Consider the position of the point D with respect to point B is denoted by
Consider the position of the point D with respect to point E is denoted by
The axis of rotation points A and E are fixed. Then,
The velocity at the point A and E are
Show the relation between the velocity of the point B and A as follows:
Show the relation between the velocity of the point B and D as follows:
Modify Equation (2) using Equation (1).
Show the relation between the velocity of the point E and D as follows:
Equate Equation (3) and (4).
Substitute
Equate j component of the Equation (5).
Equate i component of the Equation (5).
Substitute
Substitute
The axis of rotation points A and E are fixed. Then,
The acceleration at the point A and E are
Show the relation between the acceleration of the point B and A as follows:
Show the relation between the acceleration of the point B and D as follows:
Modify Equation (2) using Equation (1).
Show the relation between the acceleration of the point E and D as follows:
Equate Equation (9) and (10).
Substitute
Equate j component of the Equation (5).
Equate i component of the Equation (5).
Substitute
Thus, the angular acceleration of the rod DEF is
(b)
Find the acceleration at point F.
Answer to Problem 15.128P
The acceleration at F is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation:
Consider the position of the point F with respect to the point E is
Calculate the acceleration at F using the relation:
Substitute
Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration at D as follows:
Calculate the direction of the acceleration at D as follows:
Thus, the acceleration at F is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYNA.(LL)-W/ACCESS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
- CORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE 1. The truss shown is supported by hinge at A and cable at E.Given: H = 4m, S = 1.5 m, α = 75⁰, θ = 33⁰.Allowable tensile stress in cable = 64 MPa.Allowable compressive stress in all members = 120 MPaAllowable tensile stress in all members = 180 MPa1.Calculate the maximum permissible P, in kN, if the diameter of the cable is 20 mm.2.If P = 40 kN, calculate the required area (mm2) of member BC.3. If members have solid square section, with dimension 15 mm, calculate the maximum permissible P (kN) based on the allowable strength of member HI.ANSWERS: (1) 45.6 kN; (2) 83.71 mm2; (3) 171.76 kNarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE 2: A wire 4 meters long is stretched horizontally between points 4 meters apart. The wire is 25 mm2 in cross-section with a modulus of elasticity of 200 GPa. A load W placed at the center of the wire produces a sag Δ.1.Calculate the tension (N) in the wire if sag Δ = 30 mm.2.Calculate the magnitude of W, in N, if sag Δ = 54.3 mm.3. If W is 60 N, what is the sag (in mm)?ANSWERS: (1) 562 N, (2) 100 N, (3) 45.8 Narrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE 4 : A cable and pulley system at D is used to bring a 230-kg pole (ACB) to a vertical position as shown. The cable has tensile force T and is attached at C. The length of the pole is 6.0 m, the outer diameter is d = 140 mm, and the wall thickness t = 12 mm. The pole pivots about a pin at A. The allowable shear stress in the pin is 60 MPa and the allowable bearing stress is 90 MPa. The diameter of the cable is 8 mm.1.Find the minimum diameter (mm) of the pin at A to support the weight of the pole in the position shown.2.Calculate the elongation (mm) of the cable CD.3.Calculate the vertical displacement of point C, in mm.ANSWERS: (1) 6 mm, (2) 1.186 mm, (3) 1.337 mm--arrow_forward
- 1. Derive an expression for H(w) filter or bandpass/reject filter. = for the circuit below. Qualitatively determine if it's a high/lowpass L ell R ww Voarrow_forward2. Obtain the transfer function, H(w) = 0 for the circuit below for R₁ = 1 kQ2, R2 = 10 kQ, and Vi C = 1 μF. What role, if any, does the capacitor play? Explain. R₁ R2 + C + Voarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE 3 (15 points): A 12-meter-long precast pile segment is to be lifted from a trailer down to the ground and then set in place prior to driving by a crane.1. If two slings are to be used in lifting the pile to the ground, at what distance from the ends must the slings be placed for minimum bending due to its own weight?2. At what distance from the ends must the slings be placed for minimum shear due to its own weight?3. Using one sling to set the pile in a vertical position before driving at what distance from one end must the sling be placed for minimum bending due to its own weight?ANSWERS: (1) 2.48 m, (2) 3.00 m, (3) 3.51 marrow_forward
- Consider blood flowing down an inclined plane. Derive an expression for the velocity profile assuming that blood follows the constitutive equation for a Casson fluid. You can either use a shell balance or the equation of motion in terms of shear stress as your starting point. What is the velocity at x = 0 and at x = xc?arrow_forwardBlood (HD = 0.45 in large diameter tubes) is forced through hollow fiber tubes that are 20 µm in diameter.Equating the volumetric flowrate expressions from (1) assuming marginal zone theory and (2) using an apparentviscosity for the blood, estimate the marginal zone thickness at this diameter. The viscosity of plasma is 1.2 cP.arrow_forwardhand-written solutions only please!arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





