
Organic Chemistry; Modified MasteringChemistry with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card; Study Guide and Student Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780134240152
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 15.20, Problem 40P
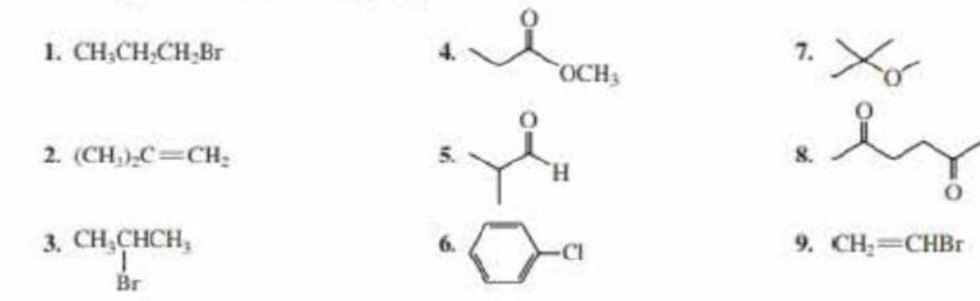
Answer the following questions for each compound:
- a. How many signals are in its 13C NMR spectrum?
- b. Which signal is at the lowest frequency?
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule08:26
Students have asked these similar questions
Using reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition
Consider the following equilibrium:
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) AG⁰ = -34. KJ
Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 8.06 atm of nitrogen (N2) and 2.58 atm of ammonia (NH3) at 106. °C. Answer the following questions about this
system:
?
rise
Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2 tend to rise or fall?
☐ x10
fall
Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂?
In other words, if you said the pressure of N2 will tend to rise, can that be
changed to a tendency to fall by adding H₂? Similarly, if you said the
pressure of N2 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise
by adding H₂?
If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate
the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it.
Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
yes
no
☐
atm
☑
5
00.
18
Ar
i need help with the following
Using reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition
Consider the following equilibrium:
2NO(g) +Cl₂ (g) = 2NOC1 (g) AGº = -41. kJ
Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 8.90 atm of chlorine (C12) and 5.71 atm of nitrosyl chloride (NOC1) at 1075. °C. Answer the following questions
about this system:
rise
Under these conditions, will the pressure of NOCI tend to rise or fall?
x10
fall
Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO?
In other words, if you said the pressure of NOCI will tend to rise, can that
be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO? Similarly, if you said the
pressure of NOCI will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to
rise by adding NO?
yes
no
If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate
the minimum pressure of NO needed to reverse it.
Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
atm
☑
18
Ar
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry; Modified MasteringChemistry with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card; Study Guide and Student Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition (7th Edition)
Ch. 15.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 15.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 15.4 - How many signals would you expect to see in the 1H...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 4PCh. 15.4 - How could you distinguish the 1H NMR spectra of...Ch. 15.4 - Draw an isomer of dichlorocyclopropane that gives...Ch. 15.5 - Prob. 7PCh. 15.5 - Prob. 8PCh. 15.5 - Prob. 9PCh. 15.5 - Where would you expect to find the 1H NMR signal...
Ch. 15.6 - Prob. 11PCh. 15.7 - Prob. 12PCh. 15.7 - Prob. 13PCh. 15.7 - Without referring to Table 14.1, label the proton...Ch. 15.8 - [18]-Annulene shows two signals in its 1H NMR...Ch. 15.9 - How would integration distinguish the 1H NMR...Ch. 15.9 - Which of the following compounds is responsible...Ch. 15.10 - Prob. 19PCh. 15.10 - Explain how the following compounds, each with the...Ch. 15.10 - The 1H NMR spectra of two carboxylic acids with...Ch. 15.11 - Draw a diagram like the one shown in Figure 14.12...Ch. 15.12 - Indicate the number of signals and the...Ch. 15.12 - How can their 1H NMR spectra distinguish the...Ch. 15.12 - Identify each compound from its molecular formula...Ch. 15.12 - Prob. 27PCh. 15.12 - Propose structures that are consistent with the...Ch. 15.12 - Describe the 1H NMR spectrum you would expect for...Ch. 15.13 - Prob. 30PCh. 15.13 - Identify the compound with molecular formula...Ch. 15.14 - Prob. 32PCh. 15.15 - a. For the following compounds, which pairs of...Ch. 15.17 - Explain why the chemical shift of the OH proton of...Ch. 15.17 - Prob. 37PCh. 15.17 - Prob. 38PCh. 15.17 - Prob. 39PCh. 15.20 - Answer the following questions for each compound:...Ch. 15.20 - Prob. 41PCh. 15.20 - How can 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-dinitrobenzene be...Ch. 15.20 - Identify each compound below from its molecular...Ch. 15.22 - Prob. 44PCh. 15.22 - What does cross peak X in Figure 14.34 tell you?Ch. 15 - Prob. 46PCh. 15 - Draw a spitting diagram for the Hb proton and give...Ch. 15 - Label each set of chemically equivalent protons,...Ch. 15 - Match each of the 1H NMR spectra with one of the...Ch. 15 - Determine the ratios of the chemically...Ch. 15 - How can 1H NMR distinguish between the compounds...Ch. 15 - Prob. 52PCh. 15 - The 1H NMR spectra of three isomers with molecular...Ch. 15 - Prob. 54PCh. 15 - Prob. 55PCh. 15 - Prob. 56PCh. 15 - Compound A, with molecular formula C4H9Cl, shows...Ch. 15 - The 1H NMR spectra of three isomers with molecular...Ch. 15 - Would it be better to use 1H NMR or 13C NMR...Ch. 15 - There are four esters with molecular formula...Ch. 15 - An alkyl halide reacts with an alkoxide ion to...Ch. 15 - Identity each of the following compounds from its...Ch. 15 - Identity each of the following compounds from its...Ch. 15 - Prob. 64PCh. 15 - How can the signals in the 6.5 to 8.1 ppm region...Ch. 15 - The 1H NMR spectra of two compounds, each with...Ch. 15 - Draw a splitting diagram for the Hb proton if Jbc...Ch. 15 - Sketch the following spectra that would be...Ch. 15 - How can 1H NMR be used to prove that the addition...Ch. 15 - Identity each of the following compounds from its...Ch. 15 - Dr. N. M. Arr was called in to help analyze the 1H...Ch. 15 - Calculate the amount of energy (in calories)...Ch. 15 - The following 1H NMR spectra are four compounds,...Ch. 15 - When compound A (C5H12O) is treated with HBr, it...Ch. 15 - Identity each of the following compounds from its...Ch. 15 - Identify each of the following compounds from its...Ch. 15 - Identity the compound with molecular formula...Ch. 15 - Identify the compound with molecular formula C6H14...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
One isomer of methamphetamine is the addictive illegal drug known as crank. Another isomer is a medicine for si...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
101. An expandable cube, initially 20 cm on each side, contains 3.0 g of helium at 20°C. 1000 J of heat energy ...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Q1. Which wavelength of light has the highest frequency?
a) 10 nm
b) 10 mm
c) 1 nm
d) 1 mm
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Two culture media were inoculated with four different bacteria. After incubation, the following results were ob...
Microbiology: An Introduction
1. What are the main organs of the skeletal system?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Which type of cartilage is most plentiful in the adult body?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Identifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that HCN is a weak acid. acids: 0.29 mol of NaOH is added to 1.0 L of a 1.2M HCN solution. bases: ☑ other: 0.09 mol of HCl is added to acids: 1.0 L of a solution that is bases: 0.3M in both HCN and KCN. other: 0,0,... ? 00. 18 Ar 日arrow_forwardIdentifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that HF is a weak acid. acids: 0.2 mol of KOH is added to 1.0 L of a 0.5 M HF solution. bases: Х other: ☐ acids: 0.10 mol of HI is added to 1.0 L of a solution that is 1.4M in both HF and NaF. bases: other: ☐ 0,0,... ด ? 18 Ararrow_forwardIdentifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that NH3 is a weak base. acids: ☐ 1.8 mol of HCl is added to 1.0 L of a 1.0M NH3 bases: ☐ solution. other: ☐ 0.18 mol of HNO3 is added to 1.0 L of a solution that is 1.4M in both NH3 and NH₁Br. acids: bases: ☐ other: ☐ 0,0,... ? 000 18 Ar B 1arrow_forward
- Using reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NH3 (g) = N2 (g) +3H₂ —N2 (g) AGº = 34. kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 4.19 atm of ammonia (NH3) and 9.94 atm of nitrogen (N2) at 378. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of NH 3 tend to rise or fall? ☐ x10 fall Х Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂? In other words, if you said the pressure of NH 3 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding H₂? Similarly, if you said the pressure of NH3 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding H₂? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. yes no atm 00. 18 Ar 무ㅎ ?arrow_forwardIdentifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that HF is a weak acid. 2.2 mol of NaOH is added to 1.0 L of a 1.4M HF solution. acids: П bases: Х other: ☐ ப acids: 0.51 mol of KOH is added to 1.0 L of a solution that is bases: 1.3M in both HF and NaF. other: ☐ 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: N2O4 (g) 2NO2 (g) AG⁰ = 5.4 kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 1.68 atm of dinitrogen tetroxide (N204) at 148. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2O4 tend to rise or fall? x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO2? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding NO2? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO 2 needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. yes no 0.42 atm ☑ 5 0/5 ? مله Ararrow_forward
- Homework 13 (Ch17) Question 4 of 4 (1 point) | Question Attempt: 2 of 2 ✓ 1 ✓ 2 = 3 4 Time Remaining: 4:25:54 Using the thermodynamic information in the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy of the following chemical reaction: 2CH3OH (g)+302 (g) → 2CO2 (g) + 4H₂O (g) Round your answer to zero decimal places. ☐ kJ x10 ☐ Subm Check 2020 Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Cearrow_forwardIdentifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria Your answer is incorrect. • Row 2: Your answer is incorrect. • Row 3: Your answer is incorrect. • Row 6: Your answer is incorrect. 0/5 The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that HF is a weak acid. acids: HF 0.1 mol of NaOH is added to 1.0 L of a 0.7M HF solution. bases: 0.13 mol of HCl is added to 1.0 L of a solution that is 1.0M in both HF and KF. Exponent other: F acids: HF bases: F other: K 1 0,0,... ? 000 18 Ararrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NOCI (g) 2NO (g) + Cl2 (g) AGº =41. kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 4.50 atm of nitrosyl chloride (NOCI) and 6.38 atm of chlorine (C12) at 212. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: ? rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of NOCI tend to rise or fall? x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO? In other words, if you said the pressure of NOCI will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO? Similarly, if you said the pressure of NOCI will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding NO? yes no If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 0.035 atm ✓ G 00. 18 Ararrow_forward
- Highlight each glycosidic bond in the molecule below. Then answer the questions in the table under the drawing area. HO- HO- -0 OH OH HO NG HO- HO- OH OH OH OH NG OHarrow_forward€ + Suppose the molecule in the drawing area below were reacted with H₂ over a platinum catalyst. Edit the molecule to show what would happen to it. That is, turn it into the product of the reaction. Also, write the name of the product molecule under the drawing area. Name: ☐ H C=0 X H- OH HO- H HO- -H CH₂OH ×arrow_forwardDraw the Haworth projection of the disaccharide made by joining D-glucose and D-mannose with a ẞ(1-4) glycosidic bond. If the disaccharide has more than one anomer, you can draw any of them. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning
NMR Spectroscopy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SBir5wUS3Bo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY