
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977305
Author: BEER, Ferdinand P. (ferdinand Pierre), Johnston, E. Russell (elwood Russell), Cornwell, Phillip J., SELF, Brian P.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 15.1, Problem 15.7P
When studying whiplash resulting from rear-end collisions, the rotation of the head is of primary interest. An impact test was performed, and it was found that the angular acceleration of the bead is defined by the relation
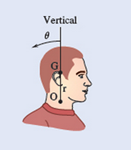
Fig. P16.1
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
can you please help me perform Visual Inspection and Fractography of the attatched image: Preliminary examination to identify the fracture origin, suspected fatigue striation, and corrosion evidences.
can you please help[ me conduct Causal Analysis (FTA) on the scenario attatched: FTA diagram which is a fault tree analysis diagram will be used to gain an overview of the entire path of failure from root cause to the top event (i.e., the swing’s detachment) and to identify interactions between misuse, material decay and inspection errors.
hi can you please help me in finding the stress intensity factor using a k-calcluator for the scenario attathced in the images.
Chapter 15 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Ch. 15.1 - A rectangular plate swings from arms of equal...Ch. 15.1 - Knowing that wheel A rotates with a constant...Ch. 15.1 - The brake drum is attached to a larger flywheel...Ch. 15.1 - The motion of an oscillation flvdee1 is defined by...Ch. 15.1 - The motion of an oscillation flywheel is defined...Ch. 15.1 - Prob. 15.4PCh. 15.1 - A small grinding wheel is attached to the shaft of...Ch. 15.1 - A connecting rod is supported by a knife-edge at...Ch. 15.1 - When studying whiplash resulting from rear-end...Ch. 15.1 - The angular acceleration of an oscillating disk is...
Ch. 15.1 - The angular acceleration of a shaft is defined by...Ch. 15.1 - Prob. 15.10PCh. 15.1 - Prob. 15.11PCh. 15.1 - The rectangular block shown rotates about the...Ch. 15.1 - The rectangular block shown rotates about the...Ch. 15.1 - A circular plate of 120-mm radius is supported by...Ch. 15.1 - In Prob. 15.14, determine the velocity and...Ch. 15.1 - The earth makes one complete revolution around the...Ch. 15.1 - The earth makes one complete revolution on its...Ch. 15.1 - The sprocket wheel and chain shown initially at...Ch. 15.1 - Prob. 15.19PCh. 15.1 - The belt sander shown is initially at rest. If the...Ch. 15.1 - The rated speed of drum B of the belt sander shown...Ch. 15.1 - The two pulleys shown may be operated with the V...Ch. 15.1 - A cyclist uses a statior.ary trainer during the...Ch. 15.1 - gear reduction system consists of three gears A,...Ch. 15.1 - A belt is pulled to the right between cylinders A...Ch. 15.1 - Ring C has an inside radius of 55 mm and an...Ch. 15.1 - At the instant shown, the angular velocity of...Ch. 15.1 - A plastic film moves over two drums. During a 4-s...Ch. 15.1 - Cylinder A is moving downward with a velocity of 3...Ch. 15.1 - The system shown is held at rest by the...Ch. 15.1 - A load is to be raised 20 ft by the hoisting...Ch. 15.1 - A simple friction drive consists of two disks A...Ch. 15.1 - Two friction wheels A and B are both rotating...Ch. 15.1 - Two friction disks A and B are to be brought into...Ch. 15.1 - Two friction disks A and B are brought into...Ch. 15.1 - Steel tape is being wound onto a spool that...Ch. 15.1 - Prob. 15.37PCh. 15.2 - The ball rolls without slipping on the fixed...Ch. 15.2 - Three uniform rods—ABC, DCE, and FGH—are connected...Ch. 15.2 - An automobile travel, to the right at a constant...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 15.39PCh. 15.2 - A painter is halfway up a 10-m ladder when the...Ch. 15.2 - Rod AB can slide freely along the floor and the...Ch. 15.2 - Rod AB can slide freely along the floor and the...Ch. 15.2 - Rod AB moves over a small wheel at C while end A...Ch. 15.2 - The disk shown moves in the xy plane. Knowing that...Ch. 15.2 - The disk shown moves in the xy p1ane. Knowing that...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 15.46PCh. 15.2 - Velocity sensors are placed on a satellite that is...Ch. 15.2 - In the planetary gear system shown, the radius of...Ch. 15.2 - In the planetary gear system shown, the radius of...Ch. 15.2 - The outer gear C rotates with an angular velocity...Ch. 15.2 - In the simplified sketch of a ball bearing shown,...Ch. 15.2 - A simplified gear system for a mechanical watch is...Ch. 15.2 - Arm ACB rotates about point C with an angular...Ch. 15.2 - Arm ACB rotates about point C with an angular...Ch. 15.2 - Knowing that at the instant shown the angular...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 15.56PCh. 15.2 - Knowing that the disk has a constant angular...Ch. 15.2 - The disk has a constant angular velocity of 20...Ch. 15.2 - The test rig is shown was developed to perform...Ch. 15.2 - In the concentric shown, a disk of 2-in. radius...Ch. 15.2 - In the engine system shown, l=160mmandb=60mm ....Ch. 15.2 - In the engine system shown, l=160 mm and b=60 mm....Ch. 15.2 - Knowing that the angular velocity of rod DE is a...Ch. 15.2 - In the position shown bar AB has an anu1ar...Ch. 15.2 - Linkage DBEF is part of a windshield wiper...Ch. 15.2 - Roberts linkage is named after Richard Roberts...Ch. 15.2 - Roberts linkage is named after Richard Roberts...Ch. 15.2 - For the oil pump rig shown, link AB causes the...Ch. 15.2 - For the oil pump rig shown, link AB causes the...Ch. 15.2 - Both 6-in.-radius wheels roll without slipping on...Ch. 15.2 - The 80-mm-radius wheel shown rolls to the left...Ch. 15.2 - For the gearing shown, derive an expression for...Ch. 15.3 - The disk rolls without sliding on the fixed...Ch. 15.3 - Bar BDE is pinned to two links, AB and CD. At the...Ch. 15.3 - A juggling club is thrown vertically into the air....Ch. 15.3 - At the instant shown during deceleration, the...Ch. 15.3 - A helicopter moves horizontally in the x direction...Ch. 15.3 - A 60-mm-radius drum is rigidly attached to a...Ch. 15.3 - Prob. 15.77PCh. 15.3 - In order to uncoil electrical wire from a...Ch. 15.3 - In order to uncoil electrical wire from a spool...Ch. 15.3 - The arm ABC rotates with an angular velocity of 4...Ch. 15.3 - The double gear rolls on the stationary left rack...Ch. 15.3 - An overhead door is guided by wheels at A and B...Ch. 15.3 - Rod ABD is guided by wheels at A and B that roll...Ch. 15.3 - Knowing that at the instant shown the angular...Ch. 15.3 - Prob. 15.85PCh. 15.3 - A motor at O drives the windshield wiper mechanism...Ch. 15.3 - A motor at O drives the windshield wiper mechanism...Ch. 15.3 - Rod AB can slide freely along the floor and the...Ch. 15.3 - Small wheels have been attached to the ends of bar...Ch. 15.3 - Two slots have been cut in plate FG and the plate...Ch. 15.3 - The disk is released from rest and rolls down the...Ch. 15.3 - The pin at B is attached to member ABD and can...Ch. 15.3 - Two identical rods ABF and DBE are Connected by a...Ch. 15.3 - Ann ABD is connected by pins to a collar at B and...Ch. 15.3 - Two rods ABD and DE are Connected to three collars...Ch. 15.3 - Two 500-mm rods are pin-connected at D as shown....Ch. 15.3 - At the instant shown, the velocity of collar A is...Ch. 15.3 - Prob. 15.98PCh. 15.3 - Describe the space centrode and the body centrode...Ch. 15.3 - Describe the space centrode and the body centrode...Ch. 15.3 - Using the method of Sec. 15.3, solve Prob. 15.60.Ch. 15.3 - Using the method of Sec. 15.3, solve Prob. 15.64.Ch. 15.3 - Using the method of Sec. 15.3, solve Prob. 15.65.Ch. 15.3 - Using the method of Sec. 15.3, solve Prob. 15.38.Ch. 15.4 - A rear-wheel-drive car starts from rest and...Ch. 15.4 - A 5-m steel beam is lowered by means of two cables...Ch. 15.4 - For a 5-m steel beam AE, the acceleration of point...Ch. 15.4 - A 900-mm rod rests on a horizontal table A force P...Ch. 15.4 - In Prob. 15.107, determine the point of the rod...Ch. 15.4 - Knowing that point A is moving to the right at a...Ch. 15.4 - Knowing that at the instant shown crank BC has a...Ch. 15.4 - automobile travels to the left at a constant speed...Ch. 15.4 - The 18-in.-radius flywheel is rigidly attached to...Ch. 15.4 - A 3-in.-radius drum is rigidly attached to a...Ch. 15.4 - A 3-in.-radius drum is rigidly attached to a...Ch. 15.4 - A heavy crate is being moved a sbo1 distance using...Ch. 15.4 - A wheel rolls without slipping on a fixed...Ch. 15.4 - The 100-nun-radius drum rolls without slipping on...Ch. 15.4 - In the planetary gear system shown, the radius of...Ch. 15.4 - The 200-mm-radius disk rolls without sliding on...Ch. 15.4 - Knowing that crank AB rotates about point A with a...Ch. 15.4 - Knowing that crank AB rotates about point A with a...Ch. 15.4 - In the two-cylinder air compressor shown, the...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 15.123PCh. 15.4 - Arm AB has a constant angular velocity of 16 rad/s...Ch. 15.4 - Arm AB has a constant angular velocity of 16 rad/s...Ch. 15.4 - A straight rack rests on a gear of radius r=3 in....Ch. 15.4 - The elliptical exercise machine has fixed axes of...Ch. 15.4 - The elliptical exercise machine has fixed axes of...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 15.129PCh. 15.4 - Knowing that at the instant shown bar DE has an...Ch. 15.4 - Knowing that at the instant shown bar AB has a...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 15.132PCh. 15.4 - Prob. 15.133PCh. 15.4 - Prob. 15.134PCh. 15.4 - Roberts linkage is named after Richard Roberts...Ch. 15.4 - For the oil pump rig shown, link AB causes the...Ch. 15.4 - Denoting by rA the position vector of a point A of...Ch. 15.4 - The drive disk of the Scotch crosshead mechanism...Ch. 15.4 - The wheels attached to the ends of rod AB roll...Ch. 15.4 - The wheels attached to the ends of rod AB roll...Ch. 15.4 - A disk of radius r rolls to the right with a...Ch. 15.4 - Ladder AB moves over a smooth corner at C while...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 15.143PCh. 15.4 - Crank4B rotates with a constant c1ockise angular...Ch. 15.4 - Crank 4B rotates with a constant clockwise angular...Ch. 15.4 - Solve the engine system from Sample Prob. 15.15...Ch. 15.4 - The position of rod AB is controlled by a disk of...Ch. 15.4 - A wheel of radius r rolls without slipping along...Ch. 15.4 - In Prob. 15. 148, show that the path of P is a...Ch. 15.5 - A person walks radially inward on a platform that...Ch. 15.5 - Prob. 15.150PCh. 15.5 - Prob. 15.151PCh. 15.5 - Two rotating rods are connected by slider block P....Ch. 15.5 - Two rotating rods are connected by slider block P....Ch. 15.5 - Pin P is attached to the wheel shown and slides in...Ch. 15.5 - Knowing that at the instant shown the angular...Ch. 15.5 - Knowing that at the instant shown the anu1ar...Ch. 15.5 - The motion of pin P is guided by slots cut in...Ch. 15.5 - Four pins slide in four separate slots cut in a...Ch. 15.5 - Solve Prob. 15.158, assuming that the plate...Ch. 15.5 - The cage of a mine elevator moves downward at a...Ch. 15.5 - Prob. 15.161PCh. 15.5 - A rocket sled is tested o a straight track that is...Ch. 15.5 - Prob. 15.163PCh. 15.5 - Prob. 15.164PCh. 15.5 - Prob. 15.165PCh. 15.5 - In the automated welding setup shown, the position...Ch. 15.5 - In the automated welding setup shown, the position...Ch. 15.5 - A chain is looped around two gears of radius 40 mm...Ch. 15.5 - A chain is looped around two gears of radius 40 mm...Ch. 15.5 - Prob. 15.170PCh. 15.5 - The human leg can be crudely approximated as two...Ch. 15.5 - The collar P slides outward at a constant relative...Ch. 15.5 - Pin P slides in a circular slot cut in the plate...Ch. 15.5 - Rod AD is bent in the shape of an are of a circle...Ch. 15.5 - Solve Prob. 15.l74 when =90 .Ch. 15.5 - Prob. 15.176PCh. 15.5 - Prob. 15.177PCh. 15.5 - In Prob. 15.177, determine the angular velocity...Ch. 15.5 - Prob. 15.179PCh. 15.5 - Prob. 15.180PCh. 15.5 - Rod AB passes through a collar that is welded to...Ch. 15.5 - Solve Prob. 15.181 assuming block A moves to the...Ch. 15.5 - In Prob. 15.157, determine the acceleration of pin...Ch. 15.6 - The bowling ball shown rolls without slipping on...Ch. 15.6 - The bowling ball shown rolls without slipping on...Ch. 15.6 - Prob. 15.186PCh. 15.6 - At the instant considered, the radar antenna shown...Ch. 15.6 - Prob. 15.188PCh. 15.6 - The disk of a portable sander rotates at the...Ch. 15.6 - Prob. 15.190PCh. 15.6 - Prob. 15.191PCh. 15.6 - In the system shown, disk A is free to rotate...Ch. 15.6 - Prob. 15.193PCh. 15.6 - A radar system is used to track a new experimental...Ch. 15.6 - Prob. 15.195PCh. 15.6 - A 3-in-radius disk spins at the constant rate 2=4...Ch. 15.6 - The cone shown rolls on the zx plane with its apex...Ch. 15.6 - At the instant shown, the robotic arm ABC is being...Ch. 15.6 - Prob. 15.199PCh. 15.6 - In Prob. 15.199, determine (a) the common angular...Ch. 15.6 - Several rods are brazed together to form the...Ch. 15.6 - In Prob. 15.201, the speed of point B is known to...Ch. 15.6 - Rod AB of length 25 in. is connected by ball...Ch. 15.6 - Rod AB has a length of 13 in. and is connected by...Ch. 15.6 - Rod BC and BD are each 840 mm long and are...Ch. 15.6 - Rod AB is connected by ball-and-socket joints to...Ch. 15.6 - Rod AB of length 29 in. is connected by...Ch. 15.6 - Rod AB of length 300 mm is connected by ball...Ch. 15.6 - Rod AB of length 300 mm is connected by...Ch. 15.6 - Two shafts AC and EG, which lie in the vertical yz...Ch. 15.6 - Solve Prob. 15.210, assuming that the arm of the...Ch. 15.6 - Rod BC has a length of 42 in. and is connected by...Ch. 15.6 - Rod AB has a length of 275 mm and is connected by...Ch. 15.6 - For the mechanism of Prob.15.204, determine the...Ch. 15.6 - In Prob. 15.205, determine the acceleration of...Ch. 15.6 - In Prob. 15.206, determine the acceleration of...Ch. 15.6 - In Prob. 15.207, determine the acceleration of...Ch. 15.6 - In Prob. 15.208, determine the acceleration of...Ch. 15.6 - In Prob. 15.209, determine the acceleration of...Ch. 15.7 - A flight simulator is used to train pilots on how...Ch. 15.7 - A flight simulator is used to train pilots on how...Ch. 15.7 - Prob. 15.222PCh. 15.7 - Prob. 15.223PCh. 15.7 - Rod AB is welded to the 0.3-m-radius plate that...Ch. 15.7 - The bent rod shown rotates at the constant rate of...Ch. 15.7 - The bent pipe shown rotates at the constant rate...Ch. 15.7 - The circular plate shown rotates about its...Ch. 15.7 - Manufactured items are spray-painted as they pass...Ch. 15.7 - Solve Prob. 15.227, assuming that at the instant...Ch. 15.7 - Solve Prob. 15.225, assuming that at the instant...Ch. 15.7 - Using the method of Sec. 15.7A, solve Prob....Ch. 15.7 - Using the method of Sec. 15.7A, solve Prob....Ch. 15.7 - Using the method of Sec. 15.7A, solve Prob....Ch. 15.7 - The 400-mm bar AB is made to rotate at the...Ch. 15.7 - The 400-mm bar AB is made to rotate at the rate...Ch. 15.7 - The arm AB of length 16 ft is used to provide an...Ch. 15.7 - The remote manipulator system (RMS) shown is used...Ch. 15.7 - A disk with a radius of 120 mm rotates at the...Ch. 15.7 - The crane shown rotates at the constant rate...Ch. 15.7 - Prob. 15.240PCh. 15.7 - Prob. 15.241PCh. 15.7 - Prob. 15.242PCh. 15.7 - Prob. 15.243PCh. 15.7 - A square plate of side 2r is welded to a vertical...Ch. 15.7 - Two disks, each of 130-mm radius, are welded to...Ch. 15.7 - In Prob. 15.245, determine the velocity and...Ch. 15.7 - The position of the stylus tip A is controlled by...Ch. 15 - A wheel moves in the xy plane in such a way that...Ch. 15 - Two blocks and a pulley e connected by...Ch. 15 - A baseball pitching machine is designed to deliver...Ch. 15 - The flywheel OD on the elliptical machine analyzed...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.252RPCh. 15 - Knowing that at the instant shown rod AB has zero...Ch. 15 - Rod AB is attached to a collar at A and is fitted...Ch. 15 - flows through a curved pipe .AB that rotates with...Ch. 15 - A disk of 0.15-m radius rotates at the constant...Ch. 15 - Two rods AE and BD pass through holes drilled into...Ch. 15 - Rod BC of length 24 in. is connected by ball...Ch. 15 - In the positions shown, the thin rod moves at a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Hi, can you please help me .Identify and justify suitable analytical techniques of the scenario below, bearing in mind the kinds of information being handled to reach a conclusion (methodology). A child swing set was discovered to have failed at the fixing at the top of the chains connecting the seat to the top of the swing set. A 12 mm threaded steel bolt, connecting the shackle to the top beam, failed at the start of the threaded region on the linkage closest to the outside side of the swing set . The linkage and bolts were made of electro galvanised mild steel . The rigid bar chain alternatives and fixings were of the same material and appeared to be fitted in accordance with guidelines. The yield strength of the steel used is 260 MPa and the UTS is 380 MPa. The bolt that failed was threaded using a standard thread with a pitch (distance between threads) of 1.75 mm and a depth of approximately 1.1 mm. The swing set in question had been assigned to ‘toddlers’ with the application of…arrow_forwardHi, can you please define and calculate the failure mode of the linkage that failed on the swing (images added) : A child swing set was discovered to have failed at the fixing at the top of the chains connecting the seat to the top of the swing set. A 12 mm threaded steel bolt, connecting the shackle to the top beam, failed at the start of the threaded region on the linkage closest to the outside side of the swing set . The linkage and bolts were made of electro galvanised mild steel . The rigid bar chain alternatives and fixings were of the same material and appeared to be fitted in accordance with guidelines. The yield strength of the steel used is 260 MPa and the UTS is 380 MPa. The bolt that failed was threaded using a standard thread with a pitch (distance between threads) of 1.75 mm and a depth of approximately 1.1 mm. The swing set in question had been assigned to ‘toddlers’ with the application of a caged-type seat. However, the location was within the play area not…arrow_forwardPage 11-68. The rectangular plate shown is subjected to a uniaxial stress of 2000 psi. Compute the shear stress and the tensile developed on a plane forming an angle of 30° with the longitud axis of the member. (Hint: Assume a cross-sectional area of unity) 2000 psi 2000 psi hparrow_forward
- 11-70. A shear stress (pure shear) of 5000 psi exists on an element. (a) Determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses caused in the element due to this shear. (b) Sketch the element showing the planes on which the maximum tensile and compressive stresses act.arrow_forward11-20. An aluminum specimen of circular cross section, 0.50 in. in diameter, ruptured under a tensile load of 12,000 lb. The plane of failure was found to be at 48° with a plane perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the specimen. (a) Compute the shear stress on the failure plane. (b) Compute the maximum tensile stress. (c) Compute the tensile stress on the failure plane. hparrow_forwardA long flat steel bar 13 mm thick and 120 mm wide has semicircular grooves as shown and carries a tensile load of 50 kN Determine the maximum stress if plate r= 8mm r=21mm r=38mmarrow_forward
- Problem 13: F₁ = A =250 N 30% Determine the moment of each of the three forces about point B. F₂ = 300 N 60° 2 m -3 m B 4 m F3=500 Narrow_forward3 kN 3 kN 1.8 kN/m 80 mm B 300 mm D an 1.5 m-1.5 m--1.5 m- PROBLEM 5.47 Using the method of Sec. 5.2, solve Prob. 5.16 PROBLEM 5.16 For the beam and loading shown, determine the maximum normal stress due to bending on a transverse section at C.arrow_forward300 mm 3 kN 3 kN 450 N-m D E 200 mm 300 mm PROBLEM 5.12 Draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the beam and loading shown, and determine the maximum absolute value (a) of the shear, (b) of the bending moment.arrow_forward
- CORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I REALLY NEED FBD. The cantilevered spandrel beam shown whose depth tapers from d1 to d2, has a constant width of 120mm. It carries a triangularly distributed end reaction.Given: d1 = 600 mm, d2 = 120 mm, L = 1 m, w = 100 kN/m1. Calculate the maximum flexural stress at the support, in kN-m.2. Determine the distance (m), from the free end, of the section with maximum flexural stress.3. Determine the maximum flexural stress in the beam, in MPa.ANSWERS: (1) 4.630 MPa; (2) 905.8688 m; (3) 4.65 MPaarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I REALLY NEED FBD A concrete wall retains water as shown. Assume that the wall is fixed at the base. Given: H = 3 m, t = 0.5m, Concrete unit weight = 23 kN/m3Unit weight of water = 9.81 kN/m3(Hint: The pressure of water is linearly increasing from the surface to the bottom with intensity 9.81d.)1. Find the maximum compressive stress (MPa) at the base of the wall if the water reaches the top.2. If the maximum compressive stress at the base of the wall is not to exceed 0.40 MPa, what is the maximum allowable depth(m) of the water?3. If the tensile stress at the base is zero, what is the maximum allowable depth (m) of the water?ANSWERS: (1) 1.13 MPa, (2) 2.0 m, (3) 1.20 marrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I NEED FBD A short plate is attached to the center of the shaft as shown. The bottom of the shaft is fixed to the ground.Given: a = 75 mm, h = 125 mm, D = 38 mmP1 = 24 kN, P2 = 28 kN1. Calculate the maximum torsional stress in the shaft, in MPa.2. Calculate the maximum flexural stress in the shaft, in MPa.3. Calculate the maximum horizontal shear stress in the shaft, in MPa.ANSWERS: (1) 167.07 MPa; (2) 679.77 MPa; (3) 28.22 MPaarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY