
Concept explainers
A smaller disk of radius r and mass m is attached rigidly to the face of a second larger disk of radius R and mass M as shown in Figure P15.48. The center of the small disk is located at the edge of the large disk. The large disk is mounted at its center on a frictionless axle. The assembly is rotated through a small angle θ from its equilibrium position and released. (a) Show that the speed of the center of the small disk as it passes through the equilibrium position is
(b) Show that the period of the motion is
Figure P15.48
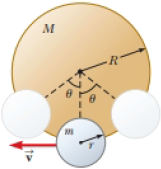
(a)
The speed of the center of the small disk as it passes through the equilibrium position is
Answer to Problem 48CP
The speed of the center of the small disk as it passes through the equilibrium position is
Explanation of Solution
The radius of the smaller disk is
Consider the figure for the given situation.

Figure (1)
The loss in the potential energy at
Write the expression for the height of the smaller disk from the centre point
Here,
Substitute
Here,
Write the expression for the loss in potential energy.
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression for the moment of inertia of the larger disk about the cylinder axis.
Here,
Write the expression for the moment of inertia of the smaller disk about the cylinder axis.
Here,
Write the expression for the moment of inertia of the smaller disk about the diameter.
Here,
Write the expression for the net moment of inertia of the two disk system.
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression for the angular velocity of the disk.
Here,
The gain in kinetic energy of the system is equal to the sum of the center of mass of the small disk, the rotational energy of the larger disk and the rotational energy of the smaller disk about
Write the expression for the gain in kinetic energy of the system.
Here,
Substitute
Apply conservation law of energy.
Substitute
Further solve the above equation.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the speed of the center of the small disk as it passes through the equilibrium position is
(b)
The period of the motion is
Answer to Problem 48CP
The period of the motion is
Explanation of Solution
As the value of angle at which assembly is rotated is very small.
From the figure, write the expression for the equation of motion.
Substitute
Write the expression for the equation of motion.
Compare equations (1) and (2).
Formula to calculate the period of the motion is,
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the period of the motion is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
PHYSICS FOR SCI. & ENGR(LL W/WEBASSIGN)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Biology: Concepts and Investigations
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forwardCar A starts from rest at t = 0 and travels along a straight road with a constant acceleration of 6 ft/s^2 until it reaches a speed of 60ft/s. Afterwards it maintains the speed. Also, when t = 0, car B located 6000 ft down the road is traveling towards A at a constant speed of 80 ft/s. Determine the distance traveled by Car A when they pass each other.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed.arrow_forward
- In the given circuit the charge on the plates of 1 μF capacitor, when 100 V battery is connected to the terminals A and B, will be 2 μF A 1 µF B 3 µFarrow_forwardThe velocity of a particle moves along the x-axis and is given by the equation ds/dt = 40 - 3t^2 m/s. Calculate the acceleration at time t=2 s and t=4 s. Calculate also the total displacement at the given interval. Assume at t=0 s=5m.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed.arrow_forwardThe velocity of a particle moves along the x-axis and is given by the equation ds/dt = 40 - 3t^2 m/s. Calculate the acceleration at time t=2 s and t=4 s. Calculate also the total displacement at the given interval. Assume at t=0 s=5m.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed.arrow_forward
- The velocity of a particle moves along the x-axis and is given by the equation ds/dt = 40 - 3t^2 m/s. Calculate the acceleration at time t=2 s and t=4 s. Calculate also the total displacement at the given interval. Assume at t=0 s=5m.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed. NOT AI PLSarrow_forwardThe velocity of a particle moves along the x-axis and is given by the equation ds/dt = 40 - 3t^2 m/s. Calculate the acceleration at time t=2 s and t=4 s. Calculate also the total displacement at the given interval. Assume at t=0 s=5m.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed.arrow_forwardThe velocity of a particle moves along the x-axis and is given by the equation ds/dt = 40 - 3t^2 m/s. Calculate the acceleration at time t=2 s and t=4 s. Calculate also the total displacement at the given interval. Assume at t=0 s=5m.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed.arrow_forward
- Please don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forwardAn electron and a proton are each accelerated through a potential difference of 21.0 million volts. Find the momentum (in MeV/c) and the kinetic energy (in MeV) of each, and compare with the results of using the classical formulas. Momentum (MeV/c) relativistic classical electron proton Kinetic Energy (MeV)arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning





